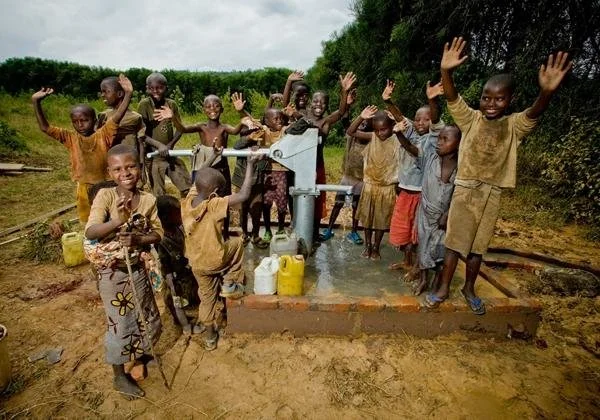
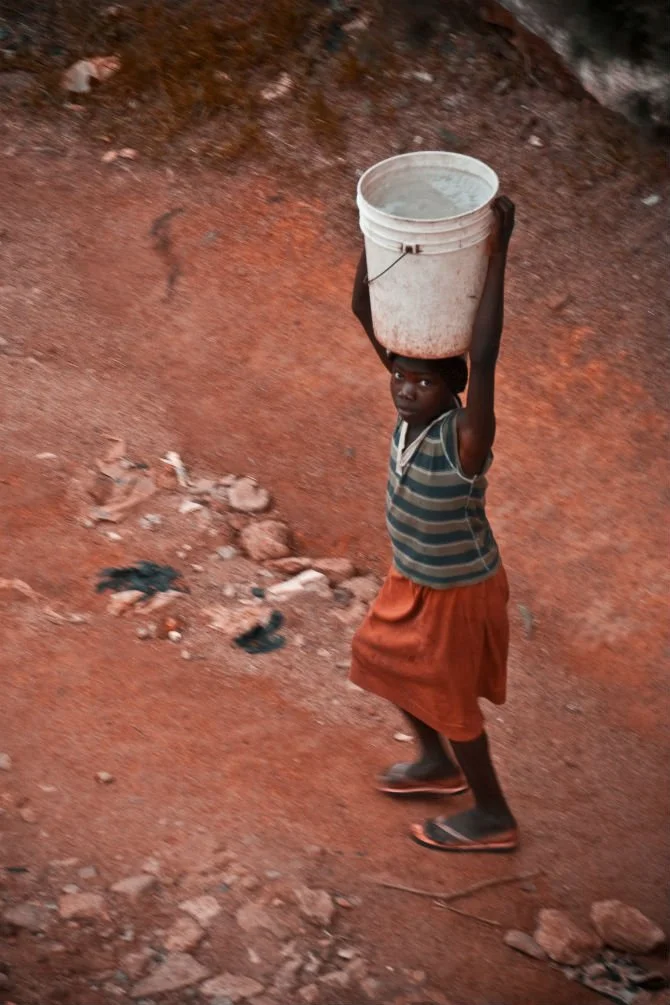Hydro Wind Energy’s Quench Sea device offers a portable solution to the global water crisis, providing communities with access to clean drinking water through innovative desalination technology.
Read MoreDry Spell: Drought Endangers Lives Across South America
With rainfall still scarce, Colombia has begun taking drastic measures to conserve what little water they have left.
The parched earth characteristic of a drought. Pmau. CC BY-SA 4.0
2024 has been one of the driest years in Colombia’s history. The summer months are usually the rainiest in the country, but this year has seen an alarming lack of precipitation and a drastic reduction in rivers and reservoirs. As the country slowly dries up, officials have started implementing policies to ration water, which will only become more severe as the drought continues.
In the last three months, the Chuza Reservoir (one of the largest in Bogota, Colombia) has lost a huge portion of its water supply. During the 2023 dry season, the reservoir was reduced to 58% capacity; as of mid-September 2024, it dropped to just 36%. This led to the second implementation of water rationing this year (the first was enacted in April 2024) but as rainfall remains scarce, these regulations have grown even more stringent. Currently, citizens are prohibited from washing their cars, irrigating gardens, and using fountains or other water decorations. However, as water supplies continue to dwindle, the city has also enacted a system by which residents will have to spend 24 hours without water once every nine days.
Colombian officials have stated that the nation’s only real hope is the return of regular rainfall. Reservoirs cannot fully recover without precipitation, and without reliable water stores, cities will be forced to reduce their water consumption even further. The severity of this drought has also inspired fears of reaching “Day Zero,” the point at which a city’s water supply falls below the necessary amount to support daily life. As of Oct. 10, 2024, Bogota’s Chuza Reservoir is just 7% above this cutoff point.
Columbia is not the only South American country experiencing drought. The majority of the continent is drying up, generating a variety of other crises, including a drastic increase in wildfires. Additionally, the Amazon River is experiencing an alarming dry spell, jeopardizing the lives of the communities that depend on it for food and water. Endangered species such as river dolphins are also threatened by the mass evaporation, which has reduced the river to about 10% of its previous size.
Although officials have stated that there is little that can be done for Bogota (and Colombia at large), several nonprofits around the world have taken action to provide aid for affected civilians. These include WaterAid, a company that focuses on providing clean water for underprivileged communities. During this drought, their efforts are more needed than ever. Interested parties can donate to their various projects here. Another such organization is Water Fund Bogota, which focuses specifically on restoring and maintaining natural sources of clean water like rivers and lakes.
Ryan Livingston
Ryan is a senior at The College of New Jersey, majoring in English and minoring in marketing. Since a young age, Ryan has been passionate about human rights and environmental action and uses his writing to educate wherever he can. He hopes to pursue a career in professional writing and spread his message even further.
Dirty Water: The Frantic Rush to Clean the Seine Before the 2024 Olympics
Officials of the French government are trying to clean the Seine, which has been deemed unswimmable for a century, in time for the 2024 Summer Olympics swim competition.
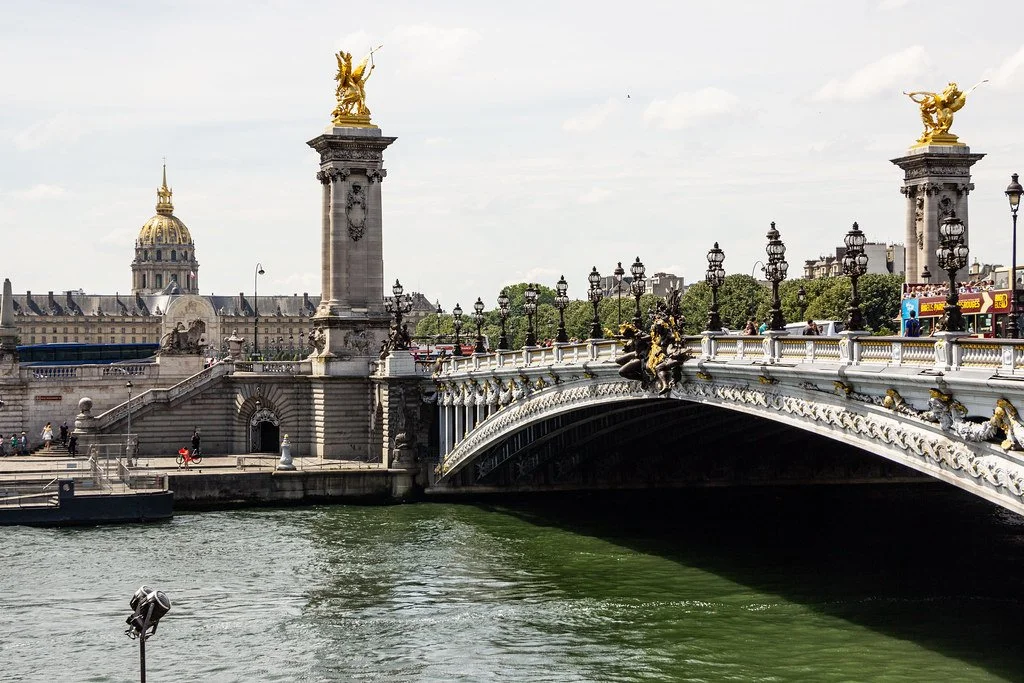
Pont Alexandre III on the River Seine, Billy Wilson, CC BY-NC 2.0
With the 2024 Olympics set for Paris, the French government has faced backlash for its efforts to quickly clean the Seine, the main river that runs through Paris. The Seine is approximately 13 kilometers long and, in Paris, accompanied by 37 bridges. The staple has promoted water travel and inspired classic French songs such as, “Sous le Pont Mirabeau” and “Sous les Ponts de Paris.” The Seine also has a long history of supplying water to Parisians. In Medieval Paris, citizens and street vendors would collect water from the Seine before they had access to running water. In 1802, Napoleon constructed the Canal St Martin connecting the Seine to the Bassin de La Villette with the goal of supplying water via public fountains throughout the city. The River Seine was in wide use, with people engaging in walks along its banks and recreational swimming, until a decree was passed in 1923 that banned such activities due to pollution and waste runoff. News Writer Olivia Craighead explains that, “The city is old as hell, and as such, sometimes sewage ends up in the Seine.” While people are still allowed to visit its banks, the River Seine has been closed to swimmers since the decree. Until the announcement of the 2024 Olympics.
Since the 2008 Olympics, there have been two open water swimming events: the triathlon and the 10k marathon swim. Pierre Rabadan, the deputy mayor in charge of sports, Olympics, and Paralympics, has said that, “Our objective is an Olympic legacy.” In 2015, Paris introduced the "Plan Baignade" (“Swimming Plan” in English), a plan to make the river swimmable for the Olympics and regular citizens by 2024. As a result, the government has invested upwards of $1.5 billion to make their plan a reality. Despite their efforts, test results from the week of June 10 reveal that E. coli levels in the river are over twice the maximum allowed in water for Olympic events. Marc Guillame, a top government official for Paris, says that these recent readings “are not in line with the standards we will have in the summer.” With the Seine, most bacteria is killed with sunlight and warm temperatures, both of which Paris has seen very little of at this point in the summer. Instead, it has endured heavy rain and cloudy conditions. Phillippe Leclercq, an 18 year old living on a houseboat on the River Seine, notes that, “When it’s good, it’s a nice green color, lately it’s just been brown.”
To ease concerns citizens and athletes have about the River Seines’ cleanliness, President Emmanuel Macron and Mayor of Paris Anne Hidalgo have pledged to be the first swimmers. Originally scheduled to take a dip on June 23, the two have moved their swim back to July 14. Hidalgo stresses that this was not due to the condition of the water, but the current weather and political atmosphere: “Yes, I will swim in the River Seine, not now because the weather is not so well in Paris, but also because we have an election. It is not possible to organize the jump to the river during the election.”
Aanya Panyadahundi
Aanya is a student at the University of Michigan studying sociology and journalism on a pre-law path. She loves to travel the world whenever she can, always eager to learn more about the different cultures and societies around her. In her free time, she likes to play the violin, ski, and listen to podcasts
VIDEO: The 12-Year-Old Scientist Taking On Flint's Water Crisis
When Gitanjali Rao first heard about the water crisis in Flint, Michigan, she wanted to help in any way she could. Now, at only 12 years old, Gitanjali is the proud inventor of “Tethys,” a portable device that detects lead in water. Named “America’s Top Young Scienist,” Gitanjali hopes to inspire other kids to get moving and make a difference in their own communities.
The Cape Town Water Crisis: Delaying Day Zero
In the Broadway musical Urinetown, people line up to use the toilet because a 20 year old drought has made private toilets a thing of the past. And when the protagonist rises up finally and allows unrestricted toilet use, the water supply completely evaporates. The final scenes ominously hint at more worrisome issues for the citizens, who, once concerned only with toilet use, most grapple with dying of thirst among other problems.
Although Urinetown is a satire, residents of Cape Town might see it as a scary prediction of their future if Day Zero arrives. As apocalyptical as it sounds, it does accurately embody the looming doomsday scenario: Day Zero is when the taps run dry. How? An unexpected three year drought, starting in 2014, drastically depleted the six dams that serve Cape Town. Whereas 20 years ago water management in Cape Town could rely on seasonal rainfall patterns and small conservation measures, it is now relying on unreliable rain and big changes.
Since Day Zero has been first predicted in early 2018, it has been continuously delayed. Projections now suggest Day Zero will occur in 2019. And in recent weeks, many are rejoicing in water returning to the dry dams. In the words of Anton Bedell, minister of Local Government, Environmental Affairs, and Development Planning: “It’s…good to see Clanwilliam dam at 20.4%. A few weeks ago the dam was below 6%.” The other dams have reflected similar increases, but the relief is only temporary as the dams await more rain—if it will come.
Theewaterskloof dam in February 2018 (source: 2oceanvibes)
Waters return in early June (source: Storm Report)
The biggest assistance in delaying Day Zero is restrictions implemented on February 1st. The main restriction was the allowance of 50 liters, a little more than 13 gallons, of water per person. Comparatively, the average individual in the United States uses 80-100 gallons of water a day and the average family over 300 gallons a day. The question of how Americans end up using so much illustrates just how little 13 gallons is for a Capetonian. For example, imagine the average bathroom break. A toilet flush requires at least 1.6 gallons with water efficient models, but if it is an older model it will need up to 4 gallons. Then you will wash your hands with about 3 gallons of water. Considering most people take at least four bathrooms breaks a day, that’s already 18.4 gallons used in one day (on a water efficient toilet): more than what one Capetonian is allowed in a single day.
So it is no wonder people are following the “if it’s yellow, let it mellow” rule and putting reminders in bathroom stalls around Cape Town. Even restaurant and bar washroom taps are shut off. But it is not just in the bathroom that changes are being made. Any use of municipal drinking water for irrigation, watering, hosing down paved surfaces, washing vehicles, or filling a private pool is not allowed. Agricultural users have to decrease water usage by 60% and commercial places by 45% compared to their pre-drought usage in 2015. And for residential units that use too much, you’ll face a fine or have to install water management devices.
And globally, Cape Town is a sign of the future. As population increases, especially in urban centers, water resources are straining to accommodate. This is against a backdrop of climate changes that favor extreme weather events like frequent droughts. What might have worked in the past, is not necessarily the solution for the future. California, Beijing, Sao Paulo, Jakarta, Mexico City are just some cities that may be the next unwilling host of Day Zero. And water shortages lead to other problems such as famine and violence. The International Panel on Climate Change predicts the Middle East and North Africa will face the most severe water shortage problems. And already, many Somalis have become climate change refugees—leaving their rural farms for the capital, Mogadishu, in hope of different sources of income with farming no longer possible. Millions more are projected in the years to come as climate change makes itself even more apparent.
It is a bleak picture, but subtle changes are happening as global leaders are becoming more aware of the looming water crisis. But we can also start at home with our own water usage. Maybe you don’t need to take a long bath after a hard day and use 36 gallons of water simply to unwind. Instead, take a quick shower and find something else to help you relax. The small changes might sound silly but it is the little things that matter as Capetonians will tell you.
TERESA NOWALK is a student at the University of Virginia studying anthropology and history. In her free time she loves traveling, volunteering in the Charlottesville community, and listening to other people’s stories. She does not know where her studies will take her, but is certain writing will be a part of whatever the future has in store.
The Zambia Project
Janssen Powers had the pleasure of shooting this piece for World Vision. He said "to say it was an eye opening trip would be an understatement. As crazy as it is to imagine drinking contaminated water everyday, it's even crazier when you realize that so many people spend the majority of their time just looking for it."
World Vision is an amazing organization doing great things in Zambia and all over the world. To learn more about their effort to bring Zambia clean water, visit worldvisionwater.org.
What You Need to Know About Water and Sanitation
Water, Sanitation and Hygiene, or WASH, are issues that affect the health and wellbeing of every person in the world. Everyone needs clean water to drink. Everyone needs a safe place to pee and poop. And everyone needs to be able to clean themselves. For many people, WASH concerns are taken for granted and their combined impact on life isn’t always appreciated.
But for hundreds of millions of others, water, sanitation and hygiene are constant sources of stress and illness. The quality of water, sanitation and hygiene in a person’s life is directly correlated to poverty, as it is usually joined by lack of education, lack of opportunity and gender inequality.
What's the scope of the problem?
780 million people do not have regular access to clean water.
2.4 billion people, or 35% of the global population, do not have access to adequate sanitation.
Photo credit: Flickr - Gates Foundation
Inadequate sanitation generally means open defecation. When people defecate in the open without a proper waste management system, then the feces generally seeps into and contaminates water systems. Just standing in an open defecation zone can lead to disease, if, for instance, the person is barefoot and parasites are there.
The problem is concentrated in Sub-Saharan Africa, Southern Asia and Eastern Asia. The country with the most people lacking adequate WASH is India.
Girls are the hardest hit by lack of clean water and sanitation for a few reasons. When schools lack functional toilets or latrines, girls often drop out because of the stigma associated with periods. Also, when families don’t have enough water, girls are generally forced to travel hours to gather some, leaving little time for school. This lack of education then contributes to higher poverty rates for women.
What are the health risks?
There are a lot of health risks associated with inadequate WASH. Just imagine what it would be like if you were drinking contaminated water and everyone in your community defecated in the open.
801,000 kids under the age of 5 die each year because of diarrhea. 88% of these cases are traced to contaminated water and lack of sanitation.
More than a billion people are infected by parasites from contaminated water or open defecation. One of these parasites is called the Guinea Worm Disease, which consists of worms up to 1 meter in size that emerge from the body through blisters.
Photo credit: Flickr - Andrew Moore
The bacterial infection Trachoma generally comes from contaminated water and is a leading cause of blindness in the world.
Other common WASH-related diseases include Cholera, Typhoid and Dysentery.
And, again, step back to consider what life without clean water and adequate sanitation would be like. A lot of your time would be spent trying to get clean water and avoid sanitation problems in the first place. And the hours not revolving around these concerns would probably be reduced quality of life because of the many minor health problems associated with poor water quality. Ultimately, inadequate WASH leads to reduced quality of life all the time.
What's being done?
For every $1 USD invested in WASH programs, economies gain $5 to $46 USD. In the US, for instance, water infrastructure investments had a 23 to 1 return rate in the 20th century. When people aren’t always getting sick, they’re more productive and everyone benefits.
While the numbers are daunting, a lot is being done. And the economic benefits of WASH investments make the likelihood of future investments and future progress much higher.
Some investments are small-scale, others are large-scale. On the smaller side of the spectrum, investments can go toward water purification methods, community wells or sources of water and the construction of community latrines.
Photo credit: Michael Sheldrick
For instance, in a slum in Nairobi, Kenya, the government recently installed ATM-style water dispensers that provide clean water to the whole community.
Larger scale investments include piped household water connections and household toilets with adequate sewage systems or septic tanks.
An often overlooked aspect of WASH involves behavioral hygiene, and, more specifically, hand washing. Simply washing your hands with soap can reduce the risk of various diseases, including the number 1 killer of the world’s poorest children: pneumonia.
What progress has been made?
In 1990, 76% of the global population had access to safe drinking water and 54% had access to adequate sanitation facilities.
In 2015, even though the population had climbed by more than 2 billion people, 91% of people had access to safe drinking water and 68% had access to improved sanitation.
That means in 25 years, 2.6 billion people gained access to safe drinking water and 2.1 billion gained access to improved sanitation.
India is currently in the process of an unprecedented WASH investment program. At the 2014 Global Citizen Festival, Prime Minister Narendra Modi committed to end open defecation in the country and has since mobilized substantial resources with the help of The World Bank.
What role does Global Citizen play in all this?
Global Citizen puts pressure on world leaders to focus on and direct money to poverty solutions around the world. When it comes to WASH, global citizens have helped raise awareness of the various associated problems and motivate politicians to invest in specific programs.
ORIGINALLY PUBLISHED ON GLOBAL CITIZEN
JOE MCCARTHY
Joe McCarthy is a Content Creator at Global Citizen. He believes apathy is the biggest threat to creating a more just world and tries his hardest to stay open-minded and curious. Living in New York keeps him aware of how interconnected our world is, how every action has ripples.