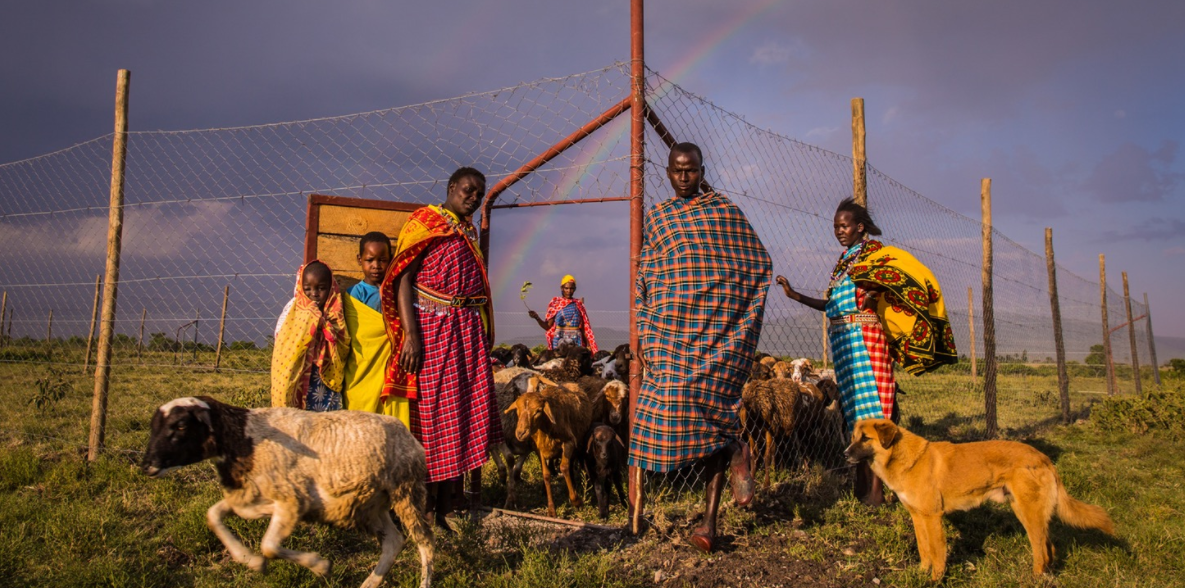
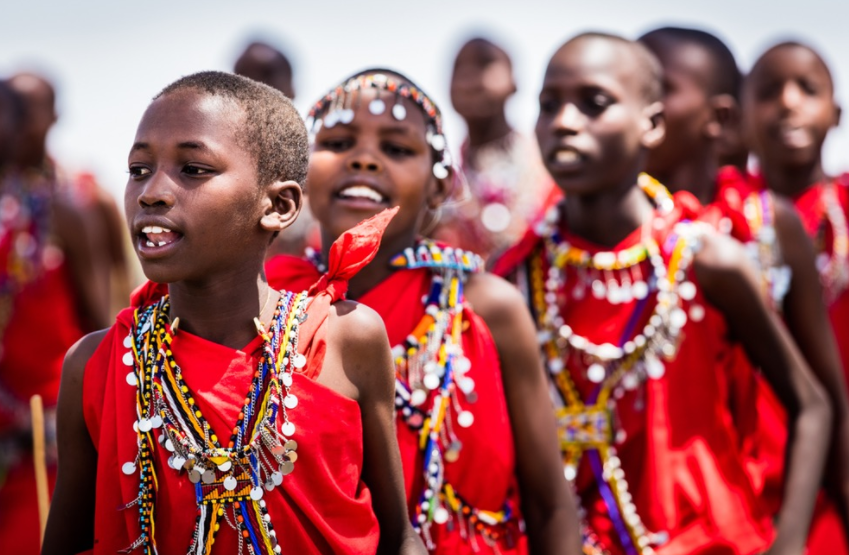
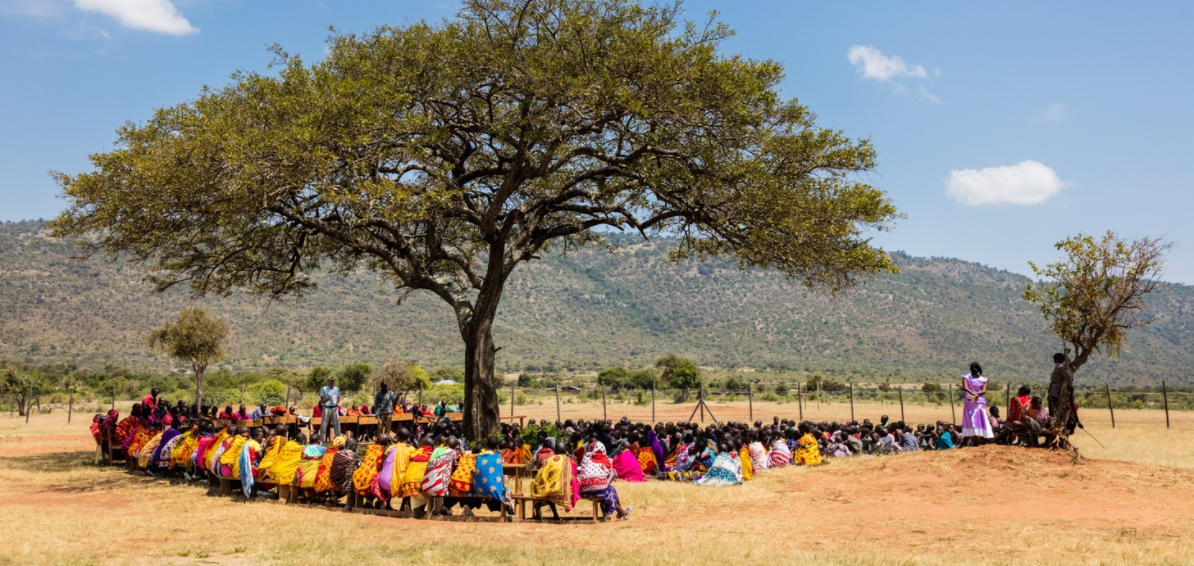
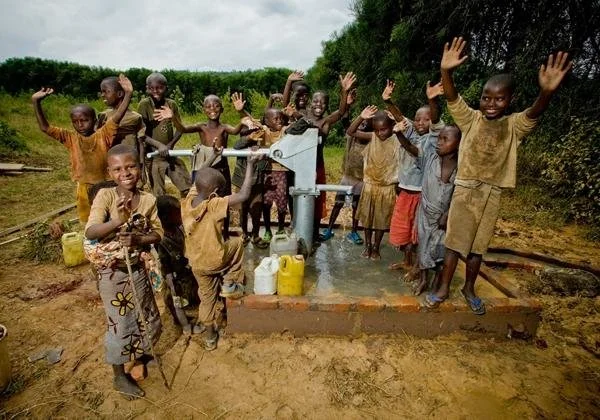
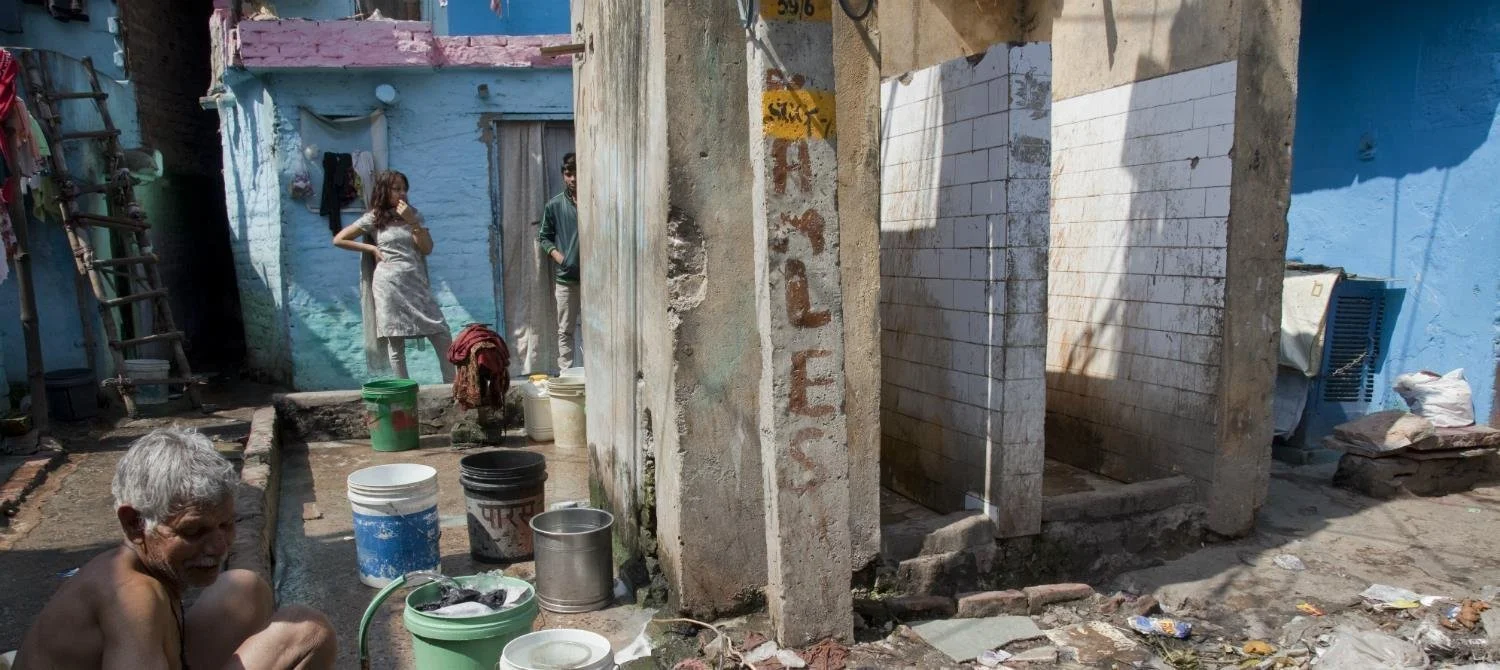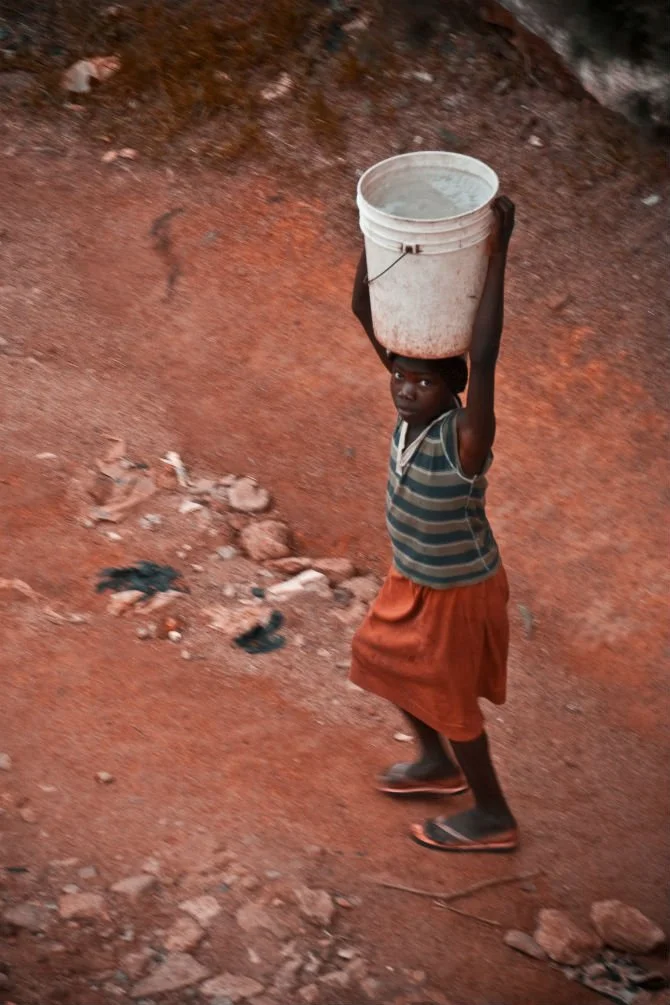Women's NGOs play crucial roles in development projects, often mobilizing, organizing and building projects that otherwise would never have been launched.
Read MoreKenyans Face Up to 4 Years In Prison For Using Plastic Bags
Beginning today, plastic bags will no longer be found in Kenya. If someone is found using one, then they will face a $38,000 fine or potential four-year jail sentence.
It’s officially the world’s harshest plastic bag deterrent.
A full ban on producing, selling, or using plastic bags went into law Monday after a court rejected challenges brought by two large plastic bag importers. The new law was successfully implemented on the third time around, after the first bag-ban in Kenya was proposed over 10 years ago.
Plastic bag pollution is a persistent problem in Kenya. It is not uncommon to see large piles of the single use bags littering the streets of urban centers, where vendors and customers frequently use them to sell and transport items.
Though the bags are convenient, the ultimate cost to the environment is astounding.
"Plastic bags now constitute the biggest challenge to solid waste management in Kenya,” said Kenya's Environment Minister Judy Wakhungu in an interview with the BBC. “This has become our environmental nightmare that we must defeat by all means.”
According to Wakhungu, plastic bags can last anywhere from 20 to 1,000 years in a landfill before they biodegrade. In the meantime, they pose environmental hazards to the communities they end up in.
Serious concerns were raised about the safety of bag disposal when rements of plastic bags were found in the stomach of cows who were to be slaughtered for human consumption. Leaching of plastics into beef destined for supermarkets pose a worrying health risk, according to local veterinarian Mbuthi Kinyanjui.
“This is something we didn’t get 10 years ago but now it’s almost on a daily basis,” he told the Guardian.
Scientists are concerned that the pile up of plastic bags is having a similar negative effect on the marine food chain, where plastic particles can easily make their way into the fish humans eat. The bags also threaten sea life not consumed by humans, such as dolphins, whales, and turtles.
In a country that uses an estimated 24 million plastic bags per month, many see the move as a victory for the environment.
However, some people in the business community worry that the ban will ultimately harm economic prosperity, and generally make life more difficult for the average Kenyan.
Kenya is a major exporter of plastic bags in Africa.
In an interview with the Guardian, spokesman for the Kenyan Association of Manufacturers Samuel Matonda said the ban would eliminate 60,000 jobs and cause 176 manufacturers to close.
“The knock-on effects will be very severe,” Matonda said. “It will even affect the women who sell vegetables in the market – how will their customers carry their shopping home?”
Right now, Kenyans discovered using bags will only have them confiscated with a warning. Soon, they could face the penalties of what is being called the “world’s toughest law against plastic bags.”
Several other African nations have already enacted similar bans or fines on plastic bag use, as have more than 40 countries around the world including China, France, and Italy.
THIS ARTICLE WAS ORIGINALLY PUBLISHED ON GLOBAL CITIZEN.
ANDREW MCMASTER
Andrew McMaster is an editorial intern at Global Citizen. He believes that every voice is significant, and through thoughtful listening we can hear how every person is interrelated. Outside of the office he enjoys cooking, writing, and backpacking.
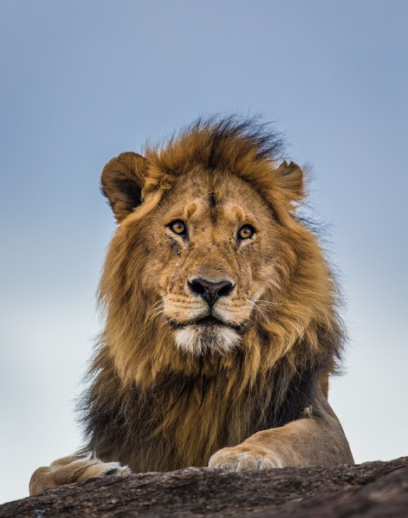
The Lion Guardians
With human-wildlife conflict on the rise in East Africa, the hunt for a long-term, viable conservation solution is on. From conservancies that benefit the Maasai landowners, to the transformation of their young warriors into lion protectors, to “predator-proofing” livestock, a massive cultural shift is underway.
DAWN IS JUST BREAKING WHEN KAMUNU SAITOTI SETS OUT ACROSS THE AMBOSELI BUSH IN SEARCH OF LIONS.
On first glance, he appears much like any other Maasai warrior. Lean and tall, his dark red shuka is wrapped around his torso and waist concealing his only weapon, a long knife with a simple wooden handle. Brightly colored beads adorn Saitoti’s neck, ears, forearms, and ankles, and his feet, far more weathered than the rest of his body, are only partially covered by dusty sandals fashioned from discarded car tires.
“I killed my first lion when I was 21,” Saitoti says as he scans the horizon. In all, he has killed five lions. This, he says, was an integral part of his family history, part of being raised as a moran, a Maasai warrior. “My brother and father have also killed lions.”
A male lion surveys his territory on the outskirts of Masai Mara National Reserve.
Traditional Maasai beads adorn Saitoti’s ankles.
The Maasai are traditionally a nomadic people subsisting almost exclusively on the milk, blood, and meat of cattle grazed on East Africa’s vast rangeland, once home to endless numbers of wild animals.
In the past, lion killing for the Maasai was as much about cultural tradition as it was about protecting their livestock from predators. To hunt and kill a lion was a critical right of passage known as olamayio — the way in which all young Maasai males became men. The tradition also created a powerful connection between warriors and lions, with each young moran receiving a lion name after his first successful hunt. Saitoti’s lion name, Meiterienanka, means “one who is faster than all the others.”
But traditions are beginning to change. On this day, in place of a spear, Saitoti carries a radio telemetry kit. He unfolds the antenna in a manner suggesting he has done this countless times before, and looks around in search of a hill — not an easy task in a landscape as flat as this. He settles for the remnants of an abandoned termite mound and begins to scan for a signal. Once he has a sense of the direction the signal is coming from, he packs away the kit and begins walking, dust trailing his brisk march along the well-used track.
Standing on the remains of an old termite mound, Lion Guardian Kamunu Saitoti scans for a signal. A number of the lions in the area have been fitted with radio collars.
For the next three hours, Saitoti stops only to look for signs of lions, or to talk to herders. Most tracks he sees are too old to bother with, but as the sun nears its zenith, he finds a set that elicits visible excitement — a departure from his otherwise solemn demeanor. These are the tracks of lion cubs, young ones, and very fresh. Patience, however, will be required here. The narrow trail leads into a maze of dense shrubs, and that is no place to follow a lioness with cubs — even for someone as experienced as Saitoti is.
At 36, Saitoti is a seven-year veteran, and one of Kenya’s three regional coordinators, of an organization called Lion Guardians. Established in 2007, the program is dedicated to finding ways for Maasai and lions to coexist. At its core is a shift in the relationship between the moran and the lion:
Hunters have become protectors. This profound change in perspective is a critical component of East Africa’s lion conservation efforts.
But the Guardians have a lot of ground to cover — just 45 Maasai warriors patrol a million acres of Kenyan rangelands — and human-wildlife conflict is a bigger problem than one organization, or one approach, can solve.
Lion Guardian Kamunu Saitoti takes meticulous notes about his observations, including GPS readings of animal tracks.
Lion Guardians is just one of a number of small- and medium-sized efforts by government officials, NGOs, and locals to reduce human-wildlife conflicts in Kenya and elsewhere in Sub-Saharan Africa. As human populations in the region have exploded, consuming increasing amounts of wildlife habitat in the process, the numbers of some of the region’s most iconic and important species have been in steep decline. Populations of many of Kenya’s large herbivores have fallen by 70 to 90 percent since the late 1970s. And as their prey have become more scarce, so too have lions.
Scientists estimate that lion populations have fallen by more than 40 percent in the past 20 years, and the 20,000 or so wild lions that remain in Africa occupy just 8 percent of the species’ historical range.
In many ways, the need for such intervention has never been greater. Yet, in a region where droughts are common and famine is never completely out of sight, finding a path toward peaceful coexistence between herders and the predators that hunt their livestock will require a great deal of persistence, creativity, and a shift in how the region’s wildlife is valued.
For most Maasai, the response to finding a leopard in your goat pen, surrounded by several slain goats, would be simple and quick: Kill the leopard. There would be no repercussions, as Kenya’s wildlife laws allow citizens to dispatch so-called problem animals. One particular young male leopard, who like his mother before him, had been terrorizing the small village of Ngerende, was certainly a good fit for that description.
Known to a number of neighboring communities for years, he had already killed hundreds of goats — losses that are keenly felt in what is one of Kenya’s poorest regions, and a hotbed of human-wildlife conflict. With the leopard’s paw now caught in the fencing of a traditional pen, or boma, as livestock enclosures are called, it seems there can be only one possible outcome. But the owner of this particular boma, Mark Ole Njapit, is no ordinary Maasai.
Mark Ole Njapit, who also known as “Pilot,” is a respected elder in the Masaai community of Ngerende.
“I understand the value of wildlife for the future of our people,” says Njapit (48), a Ngerende community elder known by most as “Pilot.”
“Everyone here was very upset and wanted to spear the leopard, but I calmed them down and called KWS (the Kenya Wildlife Service).” Fortunately for the leopard, KWS officers were treating some elephants nearby and responded quickly. After tranquilizing the cat, they were able to cut him free and move him to a new area where he would be less likely to get into trouble.
That was six months ago. Today, Pilot is supervising as members of his village work in partnership with the Anne K. Taylor Fund (AKTF) — an organization working to reduce human-wildlife conflicts — to construct his new boma.
Workers stretch out the chain-link fencing for Pilot’s new ‘boma.’ The process typically takes two days, one for setting the posts in cement, and another for attaching the fencing.
The enclosure that the AKTF team is building is formidable, with welded corner posts interspersed with termite-proof eucalyptus timber poles, all set in concrete. The chain-link fence is stretched tight, seven feet above ground and another foot buried in the soil; the fence is designed to be virtually impossible for a predator to push over, climb, or dig beneath. (While a leopard could easily scale a similar-sized fence constructed entirely of wood, they tend to avoid chain-link fencing.) Today, after more than two years and nearly a hundred of the latest iteration of AKTF bomas constructed, the program’s record remains intact: Not a single livestock animal protected by one of these enclosures has been killed by a wild predator.
Members of Pilot’s family stand at the gate of his newly constructed predator-proof ‘boma,’ just a few miles from the edge of the Masai Mara National Reserve.
The effectiveness of the new bomas means that they are in high demand among the locals. And while AKTF doesn’t normally work in villages as far north as Ngerende, when Pilot reached out, the program’s construction director, Felix Masaku, decided to make an exception. “Here is a man whose small village loses maybe ten goats a week choosing not to kill the leopard that is doing much of that damage. That is very unusual, and it is important to support this man so others might follow his example.”
In general, AKTF prioritizes cases in which livestock losses have been greatest. “This is about conservation and co-existence,” Masaku continues. “We want to minimize conflict and retaliatory killings. If someone is losing five goats and two cows every week, that person is more likely to try to kill predators than someone who loses maybe one goat a month.”
A traditional ‘boma’ that has been constructed of wood and thorny branches.
By reducing the vulnerability of livestock to predation, this program and others like it aim to reduce, if not eliminate, retaliatory killings, known as olkiyioi. This practice poses a grave threat to lions in particular, especially when angry cattle owners turn to poison rather than spears with the intention of wiping out entire prides of lions. In recent years, there have been a number of high-profile killings. For example, several members of the Marsh pride (of BBC Big Cat Diary fame) were deliberately poisoned in the Masai Mara National Reserve (MMNR) in 2015, and six lions, including two cubs, were speared to death outside Nairobi National Park in early 2016.
One troubling detail about the slaughter of the Marsh pride members is that it was carried out by Maasai seeking revenge for cattle killed while being grazed illegally inside the reserve. This practice is not uncommon. In fact, a paper published in the Journal of Zoology in 2011 estimated that by the early 2000s, livestock made up 23 percent of the MMNR’s mammal biomass — up from a mere 2 percent a few decades earlier. Today, this figure greatly exceeds that of any resident wildlife species in the protected area with the exception of buffalo. This is as much a sign of declining wildlife populations as it is of human incursions into the reserve, and it underscores significant challenges both in terms of protecting livestock and preventing human-wildlife conflicts.
As Anne Taylor, the founder of AKTF, put it:
“Inside the bomas is one thing, but keeping cattle or livestock safe if they are literally brought into the lions’ den is virtually impossible.”
Wildebeest pause before crossing the Sand River. While the Masai Mara’s resident wildebeest are all but gone, their numbers decimated primarily by agricultural expansion, each year, more than a million cross the border from Tanzania’s Serengeti National Park.
For many Maasai today, lions and other predators have become an expensive nuisance at best, and a source of deep-seated resentment at worst. In general, this resentment is not directed toward the predators themselves, but toward a government — and the world at large — which often appears to place more value on the big cats (and the tourism dollars they generate) than on Maasai lives and livelihoods.
National parks and reserves cover a mere 8 percent of Kenya’s land area and support only a third of its wildlife. The remaining two-thirds of the country’s wild animals inhabit private and communal rangelands. This is land that they share with the Maasai, Samburu, and other pastoral people who have been here for thousands of years. Many think it is here, outside of the parks and reserves, that the future of Kenya’s wildlife will be decided.
According to a recent report co-authored by Panthera, WildAid, and the Wildlife Conservation Research Unit, loss of habitat due to agricultural expansion, which invariably pushes wildlife into closer contact with farmers and pastoralists, is the underlying factor of all major threats that lions face.
To many, the conversion of unprotected rangelands to agriculture might seem inevitable as the region’s population grows, but Calvin Cottar, a fourth-generation Kenyan whose great-grandfather emigrated from Iowa in 1915 and today runs a safari service in partnership with the Maasai community, disagrees. According to Cottar, it all comes down to economic security.
“We are talking about some of the world’s poorest people,” Cottar says. “For them it is about survival.
“Why should we expect them to care about lions or elephants when they are struggling to put food on the table ... Wildlife is costing them money, not earning them money, and that is what has to change.”
Calvin Cottar is presented with a goat as a token of appreciation for building Olpalagilagi Primary School, as well as funding salaries and meals. In the long run, the hope is that land lease fees will enable locals to fund their own projects, bringing greater autonomy.
Toward this end, while working with the Kenya Wildlife Service (KWS), the Cottars Wildlife Conservation Trust has initiated the formation of several district wildlife associations in an attempt to help local landowners acquire ownership rights to the wildlife residing on their lands. Because all wild animals in Kenya have historically been considered property of the state, benefits to the local communities that have to co-exist with these creatures have generally been few and far between.
Now in his 50s, Cottar says there is much more to be done. He is more convinced than ever that the future of Kenya’s wildlife lies with the people sharing the land with them — and with a shift in government policy.
“It’s really quite simple,” Cottar explains. “We all have to pay for ecosystem services. Pay the Maasai landowners a monthly lease for their land in return for leaving it intact. The problem is that wildlife has no value to them, whereas cattle and commercial agriculture do.”
While removing snares, building livestock enclosures, and monitoring lion populations are all important management practices, Cottar says, they don’t solve the root cause of human-wildlife conflict. Wild animals are basically a nuisance and a liability to the Maasai, he explains.
“We have to make maintaining wildlife the most productive land use, and do this in a way that respects the Maasai lifestyle and culture.”
Local schoolchildren perform a traditional Maasai dance to open proceedings at a meeting hosted by Olpalagilagi Primary School.
That is why Cottar now finds himself sitting in a circle with perhaps 50 Maasai — young and old, men and women. The topic for discussion, just as it has been for the last three years, is the formation of the Olderkesi Conservancy, on the land where Cottar’s safari camp currently stands.
In general, the conservancy model consists of land being leased directly from its owners for conservation purposes. Olderkesi is slightly different in that the 100,000-hectare ranch is yet to be subdivided, making it the last communally owned ranch left in Kenya. As a result, the land will be leased from a trust representing all 6,000 land owners, and because the agreement involves the Maasai, complete consensus is required before anything can be signed. In Maasailand, patience is not so much a virtue as an absolute necessity.
Members of the Maasai community meet at Olpalagilagi Primary School to discuss the formation of the Olderikesi Wildlife Conservancy.
Joining Cottar in the circle is one of the community’s most respected elders, Kelian Ole Mbirikani (58), a member of the Olderkesi Land Committee and Chairman of the Olentoroto land owners group, which holds the deeds to the land immediately surrounding Cottar’s safari camp. Mbirikani is also one of the key driving forces behind the conservancy initiative.
“The Maasai depend almost completely on their cattle,” Mbirikani explains, “so convincing them that it is possible to have both wildlife and livestock at the same time is our biggest challenge. In their experience, when land is set aside for wildlife, all of the cattle disappear. That’s what national parks do.”
Kelian Ole Mbirikani, a member of the Olderkesi Land Committee and Chairman of the Olentoroto land owners group, with his cattle.
Mbirikani is convinced the conservancy concept can work, though. He and a group of other Maasai traveled with Cottar recently to conservancies as far north as Samburu. There, they saw wildlife and met landowners who are still able to graze their cattle. “The people are really benefitting,” Mbirikani says. “Their children are being educated all through university level with the money from the conservancies. That is what we want for our people, too.”
The AKTF team spend much of their time searching for and removing snares from inside the Masai Mara National Reserve. Although the snares are set primarily to catch herbivores they are indiscriminate killers, also trapping lions, leopards, and other predators.
There are nine other conservancies around the MMNR, and a handful more in other parts of the country, which all make regular, direct payments to local landowners. Similar approaches have been employed by Wilderness Safaris in Namibia and the Nature Conservancy in the United States, among others, and while none can be said to offer financial benefits on the same scale as Olderkesi, Cottar is clearly not alone in seeing this as a promising solution.
The snares displayed here by the members of the AKTF anti-poaching team were found during a single morning’s patrol in the Masai Mara National Reserve.
Indeed, two studies published last year demonstrate the effectiveness of Kenya’s conservancy approach. According to one of these assessments, despite lack-luster political support conservancies managed to achieve “direct economic benefits to poor landowner households, poverty alleviation, rising land values, and increasing wildlife numbers.” The other study saw a direct positive effect on lion populations within Kenya’s conservancies, with a nearly three-fold increase in just ten years.
However, while these results seem promising, there will always be areas outside conservancy boundaries — borderlands and buffer zones — where human-wildlife conflict are bound to continue. There is simply not enough funding to expand conservancies enough to eliminate these conflict zones.
The question, then, is whether people can learn to co-exist with lions and other wildlife even when there is no monthly payment to be collected.
Lion Guardian and accomplished tracker Kamunu Saitoti keeps a lookout.
BACK IN THE BUSH, KAMUNU SAITOTI WAITS PATIENTLY, HOPING TO GLIMPSE THE NEW LION CUBS WHEN THEY FINALLY EMERGE FROM THE THICKET.
He has been joined by a younger Lion Guardian, Kikanai Ole Masarie, and not long after, a battered Land Cruiser arrives with one of the organization’s founders, Director of Science Stephanie Dolrenry. The two warriors pile into the vehicle and they all set off in search of the cubs. “These lions are not like those in the parks,” Dolrenry explains. “There’s no tourism here, so they are not habituated to people or cars. We’ll be lucky if we find them at all. They can be extremely shy, especially with young cubs.”
But this is a lucky day, it seems. With thorny acacia bushes screeching against the glass and metal of the bouncing vehicle, the team suddenly finds itself in a veritable crowd of cats. Dolrenry, like the Guardians, is able to identify them all. Mere meters from the car, Meoshi, her three cubs, and her mother, Selenkay, lounge in the shade. A few dozen paces away, but on their way to join them, Meoshi’s sister Nenki with her own four cubs. Much smaller than Meoshi’s, these were the young lions whose tracks Saitoti was following. This is the first time anyone has laid eyes on this new generation.
The team’s first sighting of lioness Nenki’s four young cubs.
“Selenkay is a bit of a celebrity around here,” Dolrenry says. “She causes problems like no other lion, but she’s a tough one, and it’s hard not to admire her.” Saitoti nods. Selenkay is his favorite lion — her guile and tenacity are something to be respected. She and her family frequently target cattle and are well known for giving the Guardians plenty of headaches. She has been hunted more times than anyone cares to remember. One of her sisters has fallen victim to poison, and so too has one of her mates, while another sister was killed by spear. She has endured three male takeovers, and has even attacked a Maasai moran to protect her young cubs. Like the owners of the livestock she frequently kills, Selenkay is a true warrior.
Yet Selenkay’s legacy is far greater than her own reputation. Her longevity, itself the result of the unyielding commitment of Saitoti, Masarie, and the other Guardians, combined with the growing tolerance of the Maasai inhabiting these rangelands, has helped to connect populations in vital conservation areas, and has added much-needed genetic diversity to established prides in the region. One of her sons has made it as far north as Nairobi National Park where he is now breeding successfully.
A pair of male lions seeks respite from the heat in the shade of a tree.
Saitoti did not become a Guardian because he loved lions. Instead, he was in trouble and needed a job. Arrested for being part of an illegal hunt, his father had to sell three cows to have him released on bail. That made him reconsider his path. Killing lions, despite bringing prestige and honor, also brought hardship. “For the first two years my feelings about lions were the same,” Saitoti says. “This was just a job. But slowly, things began to change. They give food for my family, they help educate my children, I even buy veterinary medicine for my cattle with my salary from the lions.”
Lion Guardian Kikanai Ole Masarie celebrates the sighting of lioness Nenki’s cubs with a fresh cup of tea. Note the Lion Guardians symbol hung around his neck, alongside his traditional handmade Maasai beads.
“And we still get the girls!” Masarie chips in with a broad smile, referring to the social status that killing lions — and, more recently, protecting lions — can bring to an eligible young Maasai man. At 24, he is part of a younger generation of Guardians, and his words are significant, as they hint at an ability for long-held Maasai beliefs and traditions to change. “The other warriors mostly stay at home, but here we are, close to the lions every day, tracking them and finding lost cattle. The girls know we must be very brave!”
Saitoti smiles and continues, “For me, now, I feel there is no difference between the lions and my cows at home. I care about them equally.”
LEARN HOW YOU CAN HELP TODAY
The success of conservancies like Olderkesi, supported by Cottars Wildlife Conservation Trust, indicates their importance as long-term viable solutions for conservation in partnership with the landowners themselves, the Maasai people. Explore more about other Masai Mara Conservancies here.
The Lion Guardians organisation have been conserving lions and preserving cultures since 2007. Learn more about their work and donate to support them at lionguardians.org. The 750 predator-proof bomas constructed by the Anne K. Taylor Fund have saved many lives and you can learn more and support their work at annektaylorfund.org. I hope you will join me in supporting the work of these dedicated organisations!
THIS ARTICLE WAS ORIGINALLY PUBLISHED ON MAPTIA.
MARCUS WESTBERG
Marcus Westberg is a a Swedish photographer, writer, conservationist, and guide working primarily in Sub-Saharan Africa.
How Poaching Is Changing the Face of African Elephants
Elephants and their ancestors have roamed the African continent for millions of years. They are the largest land animals on earth and can live up to 70 years. Elephants are profoundly intelligent and social creatures. They have trunks that serves as their nose, arm, and fingers. But elephant populations have taken a massive hit to their populations. Despite an international ban on the ivory trade and other laws to protect elephants, their overall populations continue to fall due to habitat loss and rampant poaching for their tusks. Because of that, a once rare trait is being passed onto more African elephants. The trait is tusklessness, The loss of tusks is only the beginning. The real devastation occurs with the loss of a groups matriarch. The oldest and most experienced grandmothers are the family’s living memory of migration routes, friendly elephants, food and water sources, etc. Matriarchs are also, the first in line to protect their families and without them an entire group of elephants can fall apart. But with China banning ivory in 2017, providing stronger incentives to protect elephants, and sustained conservation efforts from organizations like ElephantVoices, African Parks, and others, elephants may stand a chance to roam the continent as their ancestors once did.
What the Earth would look like if all the ice melted
We learned last year that many of the effects of climate change are irreversible. Sea levels have been rising at a greater rate year after year, and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change estimates they could rise by another meter or more by the end of this century.
The Refugee Crisis Is a Sign of a Planet in Trouble
We must shift the structures of society to ensure the Earth remains healthy and everyone has access to a decent livelihood.
The plight of immigrant families in the United States facing threat of deportation has provoked a massive compassionate response, with cities, churches, and colleges offering sanctuary and legal assistance to those under threat. It is an inspiring expression of our human response to others in need that evokes hope for the human future. At the same time, we need to take a deeper look at the source of the growing refugee crisis.
There is nothing new or exceptional about human migration. The earliest humans ventured out from Africa to populate the Earth. Jews migrated out of Egypt to escape oppression. The Irish migrated to the United States to escape the potato famine. Migrants in our time range from university graduates looking for career advancement in wealthy global corporations to those fleeing for their lives from armed conflicts in the Middle East or drug wars in Mexico and Central America. It is a complex and confusing picture.
There is one piece that stands out: A growing number of desperate people are fleeing violence and starvation.
I recall an apocryphal story of a man standing beside a river. Suddenly he notices a baby struggling in the downstream current. He immediately jumps into the river to rescue it. No sooner has he deposited the baby on the shore, than he sees another. The babies come faster and faster. He is so busy rescuing them that he fails to look upstream to see who is throwing them in.
According to a 2015 UN Refugee Agency (UNHCR) report, 65.3 million people were forcibly displaced by conflict or persecution in 2015, the most since the aftermath of World War II. It is the highest percentage of the total world population since UNHCR began collecting data on displaced persons in 1951.
Of those currently displaced outside their countries of origin, Syrians make up the largest number, at 4.9 million. According to observers, this results from a combination of war funded by foreign governments and drought brought on by human-induced climate change. The relative importance of conflict and drought is unknown, because there is no official international category for environmental refugees.
The world community will be facing an ever-increasing stream of refugees.
Without a category for environmental refugees, we have no official estimate of their numbers, but leading scientists tell us the numbers are large and expected to grow rapidly in coming years. Senior military officers warn that food and water scarcity and extreme weather are accelerating instability in the Middle East and Africa and “could lead to a humanitarian crisis of epic proportions.” Major General Munir Muniruzzaman, former military advisor to the president of Bangladesh and now chair of the Global Military Advisory Council on Climate Change, notes that a one-meter sea level rise would flood 20 percent of his country and displace more than 30 million people.
Already, the warming of coastal waters due to accelerating climate change is driving a massive die-off of the world’s coral reefs, a major source of the world’s food supply. The World Wildlife Federation estimates the die-off threatens the livelihoods of a billion people who depend on fish for food and income. These same reefs protect coastal areas from storms and flooding. Their loss will add to the devastation of sea level rise.
All of these trends point to the tragic reality that the world community will be facing an ever-increasing stream of refugees that we must look upstream to resolve.
This all relates back to another ominous statistic. As a species, humans consume at a rate of 1.6 Earths. Yet we have only one Earth. As we poison our water supplies and render our lands infertile, ever larger areas of Earth’s surface become uninhabitable. And as people compete for the remaining resources, the social fabric disintegrates, and people turn against one another in violence.
The basic rules of nature present us with an epic species choice. We can learn to heal our Earth and shift the structures of society to assure that Earth remains healthy and everyone has access to a decent livelihood. Or we can watch the intensifying competition for Earth’s shrinking habitable spaces play out in a paroxysm of violence and suffering.
THIS ARTICLE WAS ORIGINALLY PUBLISHED IN YES MAGAZINE.
DAVID KORTEN
David Korten wrote this opinion piece for YES! Magazine as part of his series of biweekly columns on “A Living Earth Economy.” David is co-founder and board chair of YES! Magazine, president of the Living Economies Forum, a member of the Club of Rome, and the author of influential books, including When Corporations Rule the World and Change the Story, Change the Future: A Living Economy for a Living Earth. His work builds on lessons from the 21 years he and his wife, Fran, lived and worked in Africa, Asia, and Latin America on a quest to end global poverty. Follow him on Twitter @dkorten and on Facebook.
5 Lessons I Learned from Living with an Extreme Eco-Witch
In a rural town in the coast of Ecuador I had the pleasure of living with a woman. An eccentric woman. Some even said a witch. Witch or not she challenged me to challenge myself and my ecological standing. Here is what I learnt.
The walls of the Secret Garden were embedded with glass shards. Above the wall sat strategically placed barbed wire. The wall stood 10 ft. high communicating something along the lines of “I dare you to even try”. I pictured every shard of glass as a remnant of the woman behind it. Hidden for 8 years by high fences and rumors that she was a witch. From inside she watched the uninterrupted life outside of her icy fortress. A bird that once caged itself and has been trapped ever since.
The Secret Garden was not so aptly named. It was the largest house on the block by at least one whole story. The Secret Garden. I repeated it to myself. The irony tingled on my tongue. My partner Alex held my hand as we entered what was to be home for the next month.
Bucket Showers
We’ve been here a few days shy of a month and for the most part have caused this eccentric woman a drought. We’ve been showering with a one liter measuring jug. While the locals nearby go to a well, she collects rain water. The roof has pipes fringing the roof which collect in a tank. From there it is pumped upwards into a second tank and then she uses gravity for the last step. Water flows from the highest tank into the taps. She relays to me she’s only had running water for 6 months though she has been collecting rain water for much longer. It’s going to be the second time she calls the truck. She holds my glance as she says this, looking me up and down and reinforcing the message. “The second time!”.
All water is conserved here. There are two buckets in the sink. One for washing and one for rinsing. It works in a cycle. The washing water is thrown out over the garden and replaced by the rinse water. Furthermore any water that goes down the sink or in the shower is collected in another tank.
The water truck comes. She looks defeated. Her statements are witty and passive aggressive as though she knows I was using 2 liters of water for my bucket showers instead of one. In my defense it is the dry season.
Lesson 1: Be conscious of water usage. Water doesn’t just fall from the sky ya know.
Fishy Road Kill and Voodoo Dolls
There was something missing about the house and for the first few days we couldn’t figure it out… and then we went grocery shopping. This woman didn’t own a fridge. Overall, it was a good thing as it meant that all left overs were eaten rather than thrown to the back of the fridge. She tossed us a Styrofoam box filled with brown goo; “just buy ice… oh and give it a wash”. Our seafood, was always bought fresh. Every morning there are fisherman detangling their catch from nets with the patience and precision that only years of practice could bestow. We would wait until lunch to cook our spoils and because of this it always had a thick pasty consistency and fishy road kill flavor. Our broccoli, too, was always expired. I cursed firstly the heat and then the cooler which only offered half a day of solace from the tormenting sun.
But we were not the only ones. She keeps her homemade cat food in a neighbor’s fridge. Two out of three of her cats’ bellies sag so low they sweep the floor. From what I saw this was her favorite neighbor. The man in the blue house down the road. The family behind her think that she is a witch. A label she perpetuates by leaving voodoo dolls over their side of the fence. The family adjacent to her vacated when she told them that she came from a land of devils. A clever play on words for the Tasmanian Devil in Australia. “The locals here are a little superstitious”, she cackles.
Lesson 2: Buy fresh and eat fresh. More walks to the market isn’t necessarily a bad thing.
You Threw THAT away?
Need I say this woman recycled? She owned a series of garbage containers distinguishing intricacies in the material. She was working towards a plastic free home, a feat much more difficult than it sounds. In our room there was a list of rules, one of which was “no plastic bags”. Buying food, if caught without a bag became a game of smuggling. The fruit and vegetable trucks come every other day at random times. And when caught off guard, we would use plastic. As per request, after unpacking we would wash the plastic bags and hang them up to dry, to be reused. This was done in secret to try to avoid a punishing eye about bringing home more plastic bags. More often than not we would walk home with an assortment of items stacked awkwardly against our chest and were greeted with an approving smile or “what’s for dinner?”.
Lesson 3: Everything can be reused, recycled or up cycled.
SHIT!
“This is the bathroom”. Alex and I were getting the grand tour of her house. “It’s a composting toilet so you can throw your toilet paper inside the toilet” “ohhh” “ahhh”. For anyone else who has travelled through Latin America, you know this is kind of a big deal. All you do is chuck some sawdust in afterwards and let nature do its magic. Well, technically less magic from nature and more bugs digesting feces which is then shoveled to be used for compost in the garden. Ta-da! The garden gifted her back fruits, vegetables, herbs and an assortment of goodies she made into cleaning products, mosquito repellent, even gift wrapping.
Lesson 4: Literally, you can recycle anything.
Bliss Bombs
She told us that the government watches her because of her ‘bliss bombs’, a fruity protein ball of shredded coconut, almond meal chia seeds and dates. “If you google ‘bomb’, which I do because of ‘bliss bomb’ then the government puts you on a blacklist”. Once a chef and always an animal rights activist, I was amazed at what much she could make with just vegetables and a few grains. No gluten, no fats, no meat and “no fucking sugar” this was written on a whiteboard in the kitchen and repeated in all of her meals. Her chili sauce, a family recipe, was to die for and made an appearance in different restaurants in the town, in recycled Gatorade bottles she collected along the road.
Lesson 5: You are what you eat. Eat to reflect your ethics.
Admittedly, I’ve never been overly conscious of my waste more than the basic dabble in vegetarianism and using a recycle bin. But, since moving out I’ve seen little differences here and there in my dispositions towards conservation and sustainability in everyday activities. This eco-warrior/ witch/ woman taught me a lot.
JESS LEMIRE
Jess Lemire is a traveller, writer and social activist, sometimes simultaneously. I write about the things that I am passionate about and am passionate about what I write. I'm a cultural observer and linguist at heart.
I love good food and am a low key fruit juice enthusiast.
Fighting the Desert with Gardens in Senegal
This video follows a group of people in Senegal who are fighting deforestation. Due to extreme poverty, many people in Senegal result to cutting down trees to make money. This group is planting trees and gardens to help the environment.
VIDEO: A Fisherman's Freedom in Madagascar
Ravelo was trapped; He couldn't afford to continue paying the local loan shark to rent fishing equipment, because he couldn't catch fish to sell and make his payments. He couldn't catch fish because the mangrove estuaries had been depleted of wood for fire, in turn decimating the population of fish and seafood.
When Ravelo was hired by Eden Reforestation Projects, he was not only able to make an income planting trees, but his environment began to revitalize.
Eden Reforestation Projects hired Outskirt Films to tell this story on the remote coast of Madagascar. This powerful story was filmed in Madagascar by Outskirt Films.
VIDEO: Deep in Panama's Rainforest
Enrique Pacheco’s cinematography takes us on a journey through Panama’s lush landscape.
“Deep in the Rainforest” captures the density and beauty of this undisrupted natural space. Through Pacheco’s lens, we explore nature’s gentle power—torrential storms, vibrant light, and the intricate ecosystems that make up Panama’s environment.
VIDEO: The Social Enterprise Biji-Biji in Malaysia
The Biji-biji Initiative is a social enterprise that aims to share progressive ideas with everyone. In Kuala Lumpur the organization is a champion of sustainable living and by using discarded materials, basic electronics and passive building techniques to reuse waste in creative ways.
How many Gigatons of CO2?
Examine the CO2 data for yourself: http://bit.ly/Gigatons_C02
THIS IMAGE WAS CREATED BY DAVID MCCANDLESS AT INFORMATION IS BEAUTIFUL.
Regenerative Agriculture: our best shot at cooling the planet?
It’s getting hot out there. For a stretch of 16 months running through August 2016, new global temperature records were set every month.[1] Ice cover in the Arctic sea hit a new low this past summer, at 525,000 square miles less than normal.[2] And apparently we’re not doing much to stop it: according to Professor Kevin Anderson, one of Britain’s leading climate scientists, we’ve already blown our chances of keeping global warming below the “safe” threshold of 1.5 degrees.[3]
If we want to stay below the upper ceiling of 2 degrees, though, we still have a shot. But it’s going to take a monumental effort. Anderson and his colleagues estimate that in order to keep within this threshold, we need to start reducing emissions by a sobering 8-10% per year, from now until we reach “net zero” in 2050.[4] If that doesn’t sound difficult enough, here’s the clincher: efficiency improvements and clean energy technologies will only win us reductions of about 4% per year at most.
How to make up the difference is one of the biggest questions of the 21st century. There are a number of proposals out there. One is to capture the CO2 that pours out of our power stations, liquefy it, and store it in chambers deep under the ground. Another is to seed the oceans with iron to trigger huge algae blooms that will absorb CO2. Others take a different approach, such as putting giant mirrors in space to deflect some of the sun’s rays, or pumping aerosols into the stratosphere to create man-made clouds.
Unfortunately, in all of these cases either the risks are too dangerous, or we don’t have the technology yet.
This leaves us in a bit of a bind. But while engineers are scrambling to come up with grand geo-engineering schemes, they may be overlooking a simpler, less glamorous solution. It has to do with soil.
Soil is the second biggest reservoir of carbon on the planet, next to the oceans. It holds four times more carbon than all the plants and trees in the world. But human activity like deforestation and industrial farming – with its intensive ploughing, monoculture and heavy use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides – is ruining our soils at breakneck speed, killing the organic materials that they contain. Now 40% of agricultural soil is classed as “degraded” or “seriously degraded”. In fact, industrial farming has so damaged our soils that a third of the world’s farmland has been destroyed in the past four decades.[5]
As our soils degrade, they are losing their ability to hold carbon, releasing enormous plumes of CO2 into the atmosphere.
There is, however, a solution. Scientists and farmers around the world are pointing out that we can regenerate degraded soils by switching from intensive industrial farming to more ecological methods – not just organic fertiliser, but also no-tillage, composting, and crop rotation. Here’s the brilliant part: as the soils recover, they not only regain their capacity to hold CO2, they begin to actively pull additional CO2 out of the atmosphere.
The science on this is quite exciting. A study published recently by the US National Academy of Sciences claims that regenerative farming can sequester 3% of our global carbon emissions.[6] An article in Science suggests it could be up to 15%.[7] And new research from the Rodale Institute in Pennsylvania, although not yet peer-reviewed, says sequestration rates could be as high as 40%.[8] The same report argues that if we apply regenerative techniques to the world’s pastureland as well, we could capture more than 100% of global emissions. In other words, regenerative farming may be our best shot at actually cooling the planet.
Yet despite having the evidence on their side, proponents of regenerative farming – like the international farmers’ association La Via Campesina – are fighting an uphill battle. The multinational corporations that run the industrial food system seem to be dead set against it because it threatens their monopoly power – power that relies on seeds linked to patented chemical fertilisers and pesticides. They are well aware that their methods are causing climate change, but they insist that it’s a necessary evil: if we want to feed the world’s growing population, we don’t have a choice – it’s the only way to secure high yields.
Scientists are calling their bluff. First of all, feeding the world isn’t about higher yields; it’s about fairer distribution. We already grow enough food for 10 billion people.[9] In any case, it can be argued that regenerative farming actually increases crop yields over the long term by enhancing soil fertility and improving resilience against drought and flooding. So as climate change makes farming more difficult, this may be our best bet for food security, too.
The battle here is not just between two different methods. It is between two different ways of relating to the land: one that sees the soil as an object from which profit must be extracted at all costs, and one that recognizes the interdependence of living systems and honours the principles of balance and harmony.
Ultimately, this is about more than just soil. It is about something much larger. As Pope Francis put it in his much-celebrated encyclical, our present ecological crisis is the sign of a cultural pathology. “We have come to see ourselves as the lords and masters of the Earth, entitled to plunder her at will. The sickness evident in the soil, in the water, in the air and in all forms of life are symptoms that reflect the violence present in our hearts. We have forgotten that we ourselves are dust of the Earth; that we breathe her air and receive life from her waters.”
Maybe our engineers are missing the point. The problem with geo-engineering is that it proceeds from the very same logic that got us into this mess in the first place: one that treats the land as something to be subdued, dominated and consumed. But the solution to climate change won’t be found in the latest schemes to bend our living planet to the will of man. Perhaps instead it lies in something much more down to earth – an ethic of care and healing, starting with the soils on which our existence depends.
Of course, regenerative farming doesn’t offer a permanent solution to the climate crisis; soils can only hold a finite amount of carbon. We still need to get off fossil fuels, and – most importantly – we have to kick our obsession with endless exponential growth and downsize our material economy to bring it back in tune with ecological cycles. But it might buy us some time to get our act together.
[1] “August 2016 Global Temperatures Set 16th Straight Monthly Record”, weather.com, Sept. 20, 2016.
[2] “Arctic sea ice crashes to record low for June”, The Guardian, July 7, 2016.
[3] “Going beyond ‘dangerous’ climate change”, London School of Economics lecture, Feb 4, 2016.
[4] Anderson, Kevin, “Avoiding dangerous climate change demands de-growth strategies from wealthier nations”, Nov. 25, 2013.
[5] “Earth has lost 1/3 of arable land in last 40 years”, The Guardian, Dec. 2, 2015.
[6] Gattinger, Andreas, et al, “Enhanced topsoil carbon stocks under organic farming”, Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, vol. 109 no. 44.
[7] Lal, R., “Soil Carbon Sequestration Impacts on Global Climate Change and Food Security”, Science magazine, June 11, 2004.
[8] Rodale Institute, “Regenerative Organic Agriculture and Climate Change”, April 17, 2014.
[9] Altieri, Miguel et al, “We Already Grow Enough Food for 10 Billion People … and Still Can’t End Hunger”, Journal of Sustainable Agriculture, July, 2012.
THIS ARTICLE WAS ORIGINALLY PUBLISHED ON LOCAL FUTURES.
JASON HICKEL
Jason Hickel is an anthropologist at the London School of Economics. He specializes in globalization, finance, democracy, violence, and ritual, and is the author of "Democracy as Death: The Moral Order of Anti-Liberal Politics in South Africa".
VIDEO: Mothers Fight Against Monsanto in Argentina
Sofia Gatica led a grassroots movement of mothers to protest the spraying of monsanto pesticide products on genetically modified soy crops in her region of Ituzaingo, Argentina. Their efforts led to a study that determined the cancer rate in their area was 40x the national average. After 10 years, they succeeded and laws changed. Now they cannot spray within 2500 meters of homes. She is the winner of the Goldman Environmental Prize.
Kicking the Habit: Air Travel in the Time of Climate Change
Air travel is neither just nor sustainable. So how can environmental justice activists make a global difference?
We live in a time of far-flung relationships, our families, colleagues, and friends often spread out across continents. These relationships mirror the global nature of many of our most pressing problems, such as global climate change—and they also contribute to those problems.
In Eaarth: Making a Life on a Tough Planet, Bill McKibben likens the biosphere to “a guy who smoked for forty years and then he had a stroke. He doesn’t smoke anymore, but the left side of his body doesn’t work either.” This new world, he says, requires new habits.
And, no doubt, many of us have adopted new habits—trying to use public transportation, buying local foods, rejecting bottled water. But the “savings” from such practices are wiped out by a habit that many of us not only refuse to kick, but also increasingly embrace: flying, the single most ecologically costly act of individual consumption.
Flights of Privilege
A round-trip flight between New York and Los Angeles on a typical commercial jet yields an estimated 715 kilos of CO2 per economy class passenger, according to the International Civil Aviation Organization.
Only 2-3 percent of the world’s population flies internationally each year, but the climate impacts are felt by a much larger—and poorer—population.
But due to the height at which planes fly, combined with the mixture of gases and particles they emit, conventional air travel has an impact on the global climate that’s approximately 2.7 times worse than its carbon emissions alone, says the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. As a result, that roundtrip flight’s “climatic forcing” is really 1,917 kilos, or almost two tons, of emissions—more than nine times the annual emissions of an average denizen of Haiti (as per U.S. Department of Energy figures).
Only 2-3 percent of the world’s population flies internationally on an annual basis, but the climate impacts of air travel are felt by a much larger—and poorer—population. It is difficult to illustrate the meaning of such numbers in terms of who among the planet’s citizens pays the costs.
But this is exactly what the 2009 German short film The Bill does in powerfully demonstrating the ecological privilege and disadvantage embodied by flying. In doing so, it shows aviation to be a classic example of how the comparatively well-off privatize benefits of environmental resource consumption (the ability to travel quickly and afar) while socializing the detriments. By making a disproportionate contribution to climate destabilization and associated forms of environmental degradation—biodiversity loss, rising sea levels, and desertification, for instance—air travelers exacerbate the precarious existence of the most vulnerable. In doing so, they contribute to unjust hierarchies (e.g. racism and imperialism) that reflect a world of profound inequality.
Global Organizing—Without Planes
Clearly this presents a huge challenge to social and environmental justice advocates, activists, and organizers from the planet’s relatively wealthy areas who often connect to distant peoples and places by flying. Because the institutions and individuals most responsible for our global predicaments typically exercise mobility and exert their power across great distances, those of us who want to challenge their practices often must also do so. So what to do?
One option is to use transportation that stays on the Earth’s surface, to accept traveling more slowly, and to make flying a very rare exception instead of the rule. Throughout North America, buses—and, in many places, trains—are viable options. And for transoceanic voyages, ships (including freight ones) are a possibility—albeit not typically inexpensive or as common as they need be.
In an increasingly vulnerable world, we’re searching for rooted communities—and what we can learn from them.
Another option—indeed an obligation in a time of growing ecological destruction and a degraded resource base—is to stay home more often. Given that “jet travel can’t be our salvation in an age of climate shock and dwindling oil,” McKibben writes, “the kind of trip you can take with a click of a mouse will have to substitute.” In other words, we have to become much better at exploiting the “trips” that the Internet and related technologies afford—by videoconferencing, for example.
While such options present numerous challenges, not least logistical ones, perhaps the biggest obstacle is the particular way of seeing and being common to the small slice of the world’s population that flies regularly. Traveling long distances by bus, train, or ship, for example, necessitates time—and a willingness to expend it in manners that those from the world’s privileged parts and sectors are not used to doing. It doesn’t necessarily entail doing less, but it does mean doing things in different ways.
A New Normal
It also calls for new mechanisms and institutions—and some organizing to bring them about. Take long-distance travel by ship. Less than a century ago, many regular folks traversed the seas—think of immigrants to Angel and Ellis islands. And many well-known organizers and activists—Gandhi, Helen Keller, and W.E.B. Dubois, to name just three—journeyed extensively by ship.
To do so today, of course, is far more difficult as jet travel has greatly weakened the passenger ship option. But what if, for instance, U.S. and Canadian activists and advocates going to Denmark for the Dec. 2009 climate summit had, instead of booking individual flights, organized to travel together by ship—with all promising to get to and from their ports of call by surface-level transportation? And what if they had publicized this effort as a way of setting an example for, and challenging, others?
That such a suggestion will seem unrealistic, if not foolhardy, to many illustrates the way that what we’re used to thinking of as normal can stifle our imaginations, and let us off the political, ecological, and ethical hook. The option is as “realistic” as we make it. In this regard, we need to push and support one another in the effort to make far-reaching alternatives viable.
What we’re used to thinking of as normal can stifle our imaginations, and let us off the political, ecological, and ethical hook. The option is as "realistic" as we make it.
Climate science tells us that we need a 90 percent cut in greenhouse gas emissions over the next few decades to keep within a safe upper limit of atmospheric carbon. In light of the great changes such a reduction demands, what is unrealistic and foolhardy is the notion that we can continue flying with abandon.
Interested?
• We thought we had 20, 30, 50 years to take on the climate crisis. We were wrong. The scary science, smart policies, and critical actions that could still avert disaster.
• Bill McKibben imagines himself in the year 2100, looking back at a century of climate chaos and asking: What did it take to save the world?
THIS ARTICLE WAS ORIGINALLY PUBLISHED ON YES MAGAZINE.
JOSEPH NEVINS
Joseph Nevins wrote this article for YES! Magazine, a national, nonprofit media organization that fuses powerful ideas with practical actions. Joseph is a geography professor at Vassar College. Among his books is Dying to Live: A Story of U.S. Immigration in an Age of Global Apartheid (City Lights Books/Open Media).
Recording the Sounds of Extinction
Bernie Krause has been recording wildlife sounds, or "soundscapes," for over forty years. He's amassed the largest archive in the world, and in doing so, can chart how wildlife sounds have changed over the course of climate change. Listen for yourself: the rising silence speaks volumes.
A design of the 110 meter long ocean-going vessel of change
A Carbon Neutral Alternative to Flight
VoyageVert, a Bristol, UK based company, is raising funds to begin a transatlantic ferry service that will operate entirely under sail and renewable energy.
The pilot project will ferry 26 passengers from Bristol to Boston in around seven days, with the eventual aim of scaling up to 200 passengers at a time on custom built catamarans.
“Quite simply, there is absolutely nothing like this at all,” says Ross Porter, VoyageVert's founder, “which is really, really exciting, and quite daunting.”
The company aims to attract those who are looking for a sustainable alternative to flying, as well as those looking for adventure. Passengers will also have the opportunity to participate in a unique experience, living on board as part of a community and taking their place as part of the crew if they wish. They can learn about navigation, meteorology, marine biology and more. Guest speakers will lecture on aspects of the marine environment, one of the world's last remaining wildernesses.
Ross Porter began sailing in Torbay at the age of eight. He spent many years working on boats throughout Greece, the Caribbean and New Zealand. By his own count he has notched up enough miles to take him around the world more than one and a half times. He then returned to England to set up a company delivering yachts for clients. This led to him being contacted so many times by people asking if he could take them from one place to another that he realised there was a market for transporting not just boats but people too.
“I thought: I’m a marine engineer, a captain and a project manager. I could deliver a project that would mean that people could buy a ticket on a sailing boat and get themselves from A to B. All I need is a sailing boat,” says Porter.
The past few years has seen a growing movement for transporting goods under sail. There are now more than ten large boats and many smaller ones in Europe and North America, trading everything from chocolate to rum, from cider to salt cod, in a way which is completely carbon free. With 120,000 available seats on planes, every day, to cross the Atlantic, Porter believes that there is a very viable market for passengers looking to make the crossing by other means.
VoyageVert has one month to raise the funds to launch the pilot project, which would mean that the first trip could come as early as 2018. “The vision is for a truly global passenger transport network, one that’s totally sustainable and high speed,” says Porter. “Cheap and fast has had its day, and it's now really becoming a problem. We’ve got to do away with cheap and fast, and start travelling with intention. If the public wants this, then it’s going to happen.”
To see how the project is getting on, go to: http://www.crowdfunder.co.uk/voyagevert-crowdfunder
VIDEO: Samuel in the Clouds of Bolivia
In Bolivia, the glaciers are melting. Samuel, an old ski lift operator, is looking out of a window on the rooftop of the world. Through generations his family lived and worked in the snowy mountains, but now snow fails. While scientists are discussing and measuring ominous changes Samuel honors the ancient mountain spirits. Clouds continue to drift by.
What You Need to Know About Water and Sanitation
Water, Sanitation and Hygiene, or WASH, are issues that affect the health and wellbeing of every person in the world. Everyone needs clean water to drink. Everyone needs a safe place to pee and poop. And everyone needs to be able to clean themselves. For many people, WASH concerns are taken for granted and their combined impact on life isn’t always appreciated.
But for hundreds of millions of others, water, sanitation and hygiene are constant sources of stress and illness. The quality of water, sanitation and hygiene in a person’s life is directly correlated to poverty, as it is usually joined by lack of education, lack of opportunity and gender inequality.
What's the scope of the problem?
780 million people do not have regular access to clean water.
2.4 billion people, or 35% of the global population, do not have access to adequate sanitation.
Photo credit: Flickr - Gates Foundation
Inadequate sanitation generally means open defecation. When people defecate in the open without a proper waste management system, then the feces generally seeps into and contaminates water systems. Just standing in an open defecation zone can lead to disease, if, for instance, the person is barefoot and parasites are there.
The problem is concentrated in Sub-Saharan Africa, Southern Asia and Eastern Asia. The country with the most people lacking adequate WASH is India.
Girls are the hardest hit by lack of clean water and sanitation for a few reasons. When schools lack functional toilets or latrines, girls often drop out because of the stigma associated with periods. Also, when families don’t have enough water, girls are generally forced to travel hours to gather some, leaving little time for school. This lack of education then contributes to higher poverty rates for women.
What are the health risks?
There are a lot of health risks associated with inadequate WASH. Just imagine what it would be like if you were drinking contaminated water and everyone in your community defecated in the open.
801,000 kids under the age of 5 die each year because of diarrhea. 88% of these cases are traced to contaminated water and lack of sanitation.
More than a billion people are infected by parasites from contaminated water or open defecation. One of these parasites is called the Guinea Worm Disease, which consists of worms up to 1 meter in size that emerge from the body through blisters.
Photo credit: Flickr - Andrew Moore
The bacterial infection Trachoma generally comes from contaminated water and is a leading cause of blindness in the world.
Other common WASH-related diseases include Cholera, Typhoid and Dysentery.
And, again, step back to consider what life without clean water and adequate sanitation would be like. A lot of your time would be spent trying to get clean water and avoid sanitation problems in the first place. And the hours not revolving around these concerns would probably be reduced quality of life because of the many minor health problems associated with poor water quality. Ultimately, inadequate WASH leads to reduced quality of life all the time.
What's being done?
For every $1 USD invested in WASH programs, economies gain $5 to $46 USD. In the US, for instance, water infrastructure investments had a 23 to 1 return rate in the 20th century. When people aren’t always getting sick, they’re more productive and everyone benefits.
While the numbers are daunting, a lot is being done. And the economic benefits of WASH investments make the likelihood of future investments and future progress much higher.
Some investments are small-scale, others are large-scale. On the smaller side of the spectrum, investments can go toward water purification methods, community wells or sources of water and the construction of community latrines.
Photo credit: Michael Sheldrick
For instance, in a slum in Nairobi, Kenya, the government recently installed ATM-style water dispensers that provide clean water to the whole community.
Larger scale investments include piped household water connections and household toilets with adequate sewage systems or septic tanks.
An often overlooked aspect of WASH involves behavioral hygiene, and, more specifically, hand washing. Simply washing your hands with soap can reduce the risk of various diseases, including the number 1 killer of the world’s poorest children: pneumonia.
What progress has been made?
In 1990, 76% of the global population had access to safe drinking water and 54% had access to adequate sanitation facilities.
In 2015, even though the population had climbed by more than 2 billion people, 91% of people had access to safe drinking water and 68% had access to improved sanitation.
That means in 25 years, 2.6 billion people gained access to safe drinking water and 2.1 billion gained access to improved sanitation.
India is currently in the process of an unprecedented WASH investment program. At the 2014 Global Citizen Festival, Prime Minister Narendra Modi committed to end open defecation in the country and has since mobilized substantial resources with the help of The World Bank.
What role does Global Citizen play in all this?
Global Citizen puts pressure on world leaders to focus on and direct money to poverty solutions around the world. When it comes to WASH, global citizens have helped raise awareness of the various associated problems and motivate politicians to invest in specific programs.
ORIGINALLY PUBLISHED ON GLOBAL CITIZEN
JOE MCCARTHY
Joe McCarthy is a Content Creator at Global Citizen. He believes apathy is the biggest threat to creating a more just world and tries his hardest to stay open-minded and curious. Living in New York keeps him aware of how interconnected our world is, how every action has ripples.
Photo credit: Wikipedia Commons - scdnr
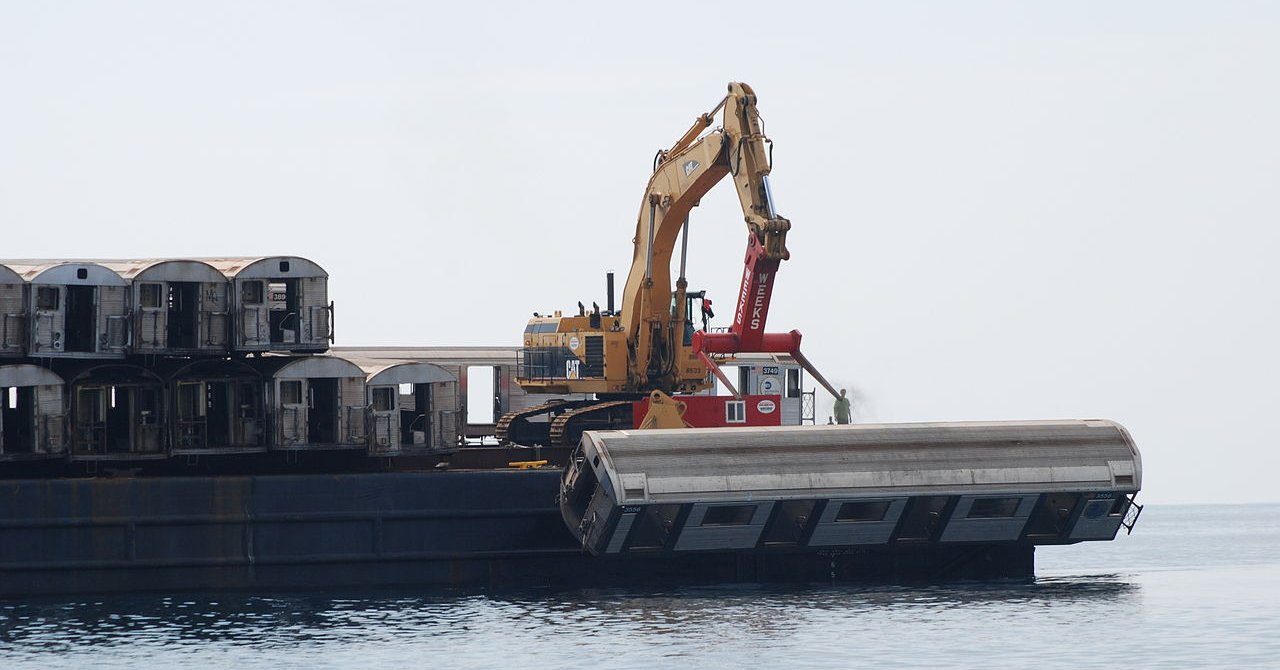
VIDEO: Old Subway Cars and Planes Get a Second Chance Underwater as Thriving Ecosystems in the USA
We’ve have all heard the phrase, “one man’s trash is another man’s treasure,” but New York's Metropolitan Transit Authority has turned their trash into a marine treasure.
Over 2,500 retired New York City subway cars have been hauled out to the the deepest, coldest parts of the Atlantic ocean and thrown overboard one by one into the ocean using a hydraulic lift. But before you panic, it’s okay. It’s actually a good thing!
As these stripped carbon steel subway cars reach the darkest lows of the ocean floor they are warmly welcomed by their soon-to-be marine life inhabitants. Over time, the cars become part of the underwater ecosystem, creating an artificial reef system, providing surfaces for invertebrates to live on and shelter for fish playing hide and seek with their predators.
The Subway cars act as “luxury condominiums for [the] fish,” providing more surface area for food and marine life to grow and flourish.
Though the project ended in 2010 and no new cars have been taken to sea, the Delaware Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control has reported a 400% increase in the amount of marine food available per square foot. While this particular project only ran for 10 years, the changes it sparked are self-sustaining and the benefits will last much longer than that.
Restoring the ocean’s reefs helps to restore balance to marine ecosystems that have been damaged by pollution, coral bleaching, and overfishing which can allow algae to overtake and smother reefs.
Oceans make up 97% the world’s water, produce half of its oxygen, provide food and livelihoods, and regulate climate. But we’re damaging reefs and polluting the water. It’s important that we work towards restoring our oceans and reefs to preserve marine life and return balance to the system.
The benefits of creating artificial reefs from retired subway cars are two-fold. Sinking these cars is a great way to recycle them, without sinking the MTA’s budget, and goes a long way toward restoring reefs.
It’s worked so well that Turkey just put a plane into the water in the hopes of creating a thriving artificial reef and capturing the attention of experienced divers.
Now don’t you wish you could get a little subway car or plane for your fishbowl?
ORIGINALLY PUBLISHED ON GLOBAL CITIZEN
ZAIMAH ABBAS
Zaimah Abbas is a social media associate at Global Citizen.
DANIELE SELBY
Daniele Selby is a freelance writer for Global Citizen. She is currently a Master's of International Affairs candidate focusing on human rights and humanitarian policy at Columbia's University's School of International and Public Affairs. She believes that education and equal provision of human rights will empower change.