Canada has announced their plans to decriminalize small amounts of illicit drugs in British Columbia by January of 2023. They are hopeful this will lower high rates of overdoses.
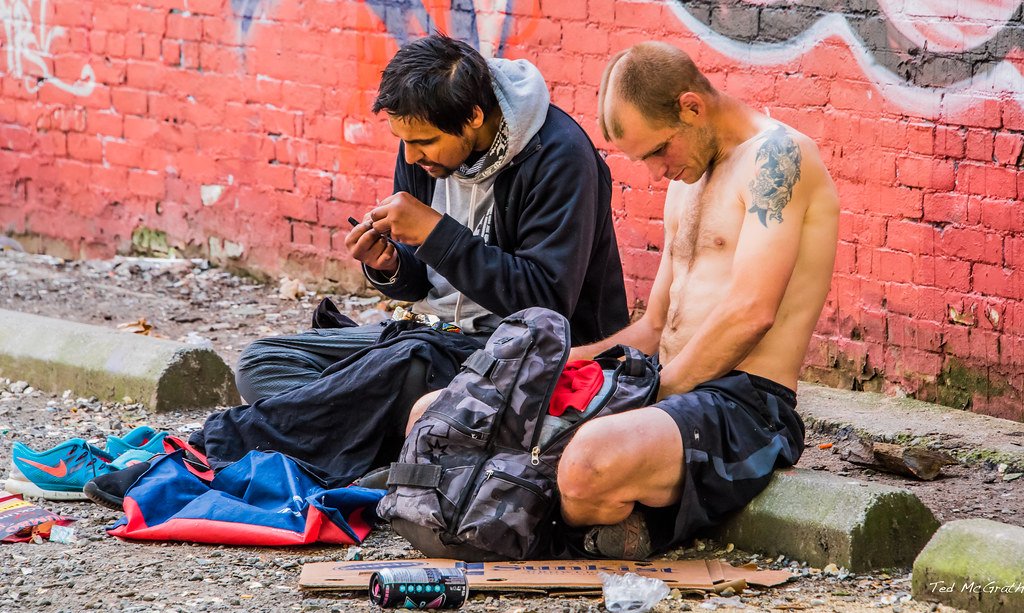
Graffiti about drug decriminalization. Ted’s Photos. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0.
In British Columbia, Canada, where thousands of overdose deaths occur each year, officials have decided to try decriminalizing small amounts of illicit drugs. The illicit drugs in question include heroin, cocaine, opioids, methamphetamine and more. Residents of British Columbia 18 years or older will be allowed to possess a maximum of 2.5 grams of these drugs without penalty, a policy that will take effect in January of 2023. This policy comes from an exemption from the Controlled Drugs and Substances Act that makes these drugs illicit, which was granted to British Columbia for a three-year trial run.
Officials hope that by decriminalizing small amounts of these drugs, dependent users will feel less afraid of prosecution and stigmatization if they do decide to seek drug-related help. Further, by tackling rates of drug deaths as a public health issue, BC Government News says “the Province will create new pathways to support those seeking treatment.”
Since the height of the pandemic in 2020, British Columbia has struggled with high rates of illicit drug abuse and overdose deaths. In 2020, drug-related death rates rose into the two-thousands, a problem that since 2016 had been declared a public health crisis. Most of these deaths occur when drug users hide their addiction from friends and family, fearing the reaction or stigmatization that will come from their loved ones learning of their addiction.
By decriminalizing these drugs, Canada hopes to reverse this effect; Dr. Theresa Tam, Canada’s chief public health officer, wrote in a tweet: “Stigma and fear of criminalization cause some people to hide their drug use, use alone, or use in ways that increase the risk of harm. This is why the Government of Canada treats substance use as a health issue, not a criminal one.”
Street use in Vancouver. Ted’s Photos. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0.
The exemption to be instituted in 2023 has found support from family and friends of deceased drug users and was even supported by the police associations and chief coroner. Though some call for even further decriminalization – a policy that would expand the 2.5 gram limit to larger amounts – health officials in Canada believe 2.5 grams is a good trial starting point. Harm reduction is their main goal; British Columbia’s Provincial Health Official Dr. Bonnie Henry stated, “This is not one single thing that will reverse this crisis but it will make a difference.”
In requesting an exemption from the Controlled Drug and Substances Act, British Columbia also stated that drug-related felonies and arrests disproportionately affect already marginalized communities. In decriminalizing small amounts of drugs, the authorities will reduce punitive actions and may help to decrease the stigmas around drug use that cause people to hide their addictions.
Turning Point of Tampa has also stated that experts on drug incarceration have stated that imprisonment does not deter drug use, and problems such as substance abuse, mental health issues and fear of open drug use worsen when sentenced to prison time. Peer clinical adviser Guy Felicella told the New York Times, “Arresting me and incarcerating me for all those years for using drugs never stopped me once from using drugs — even when I went to prison. It didn’t do anything except create stigma and discrimination, shame,” which is the exact thing Canada is trying to end through decriminalization.
Hoping to reduce the stigma surrounding drug use that leads to deaths due to fear of judgment and sequentially more dangerous usage, Canada is waiting to see how this exemption in 2023 will reduce rates of drug-related deaths, and whether further decriminalization is needed.
To Get Involved:
The Canadian Drug Policy Coalition (CDPC) is an advocacy organization that is fighting against the harm caused by drug prohibition laws. Campaigning with a platform centered on decriminalization, the Coalition strives to reduce the high rates of drug overdose deaths in Canada. To learn more about the CDPC’s mission and to support their work, click here.
Ava Mamary
Ava is an undergraduate student at the University of Illinois, double majoring in English and Communications. At school, she Web Writes about music for a student-run radio station. She is also an avid backpacker, which is where her passion for travel and the outdoors comes from. She is very passionate about social justice issues, specifically those involving women’s rights, and is excited to write content about social action across the globe.