In preparation for the Olympic Games, Paris invests in sustainable resources to minimize environmental impact.
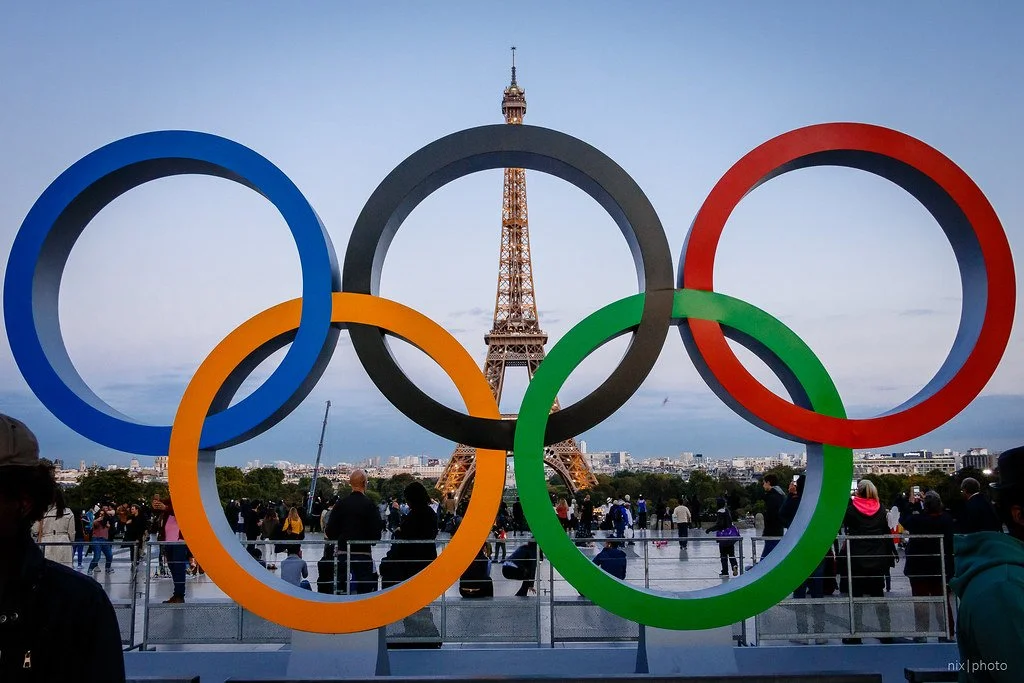
Paris Olympic Games. Nicolas Michaud. CC BY 2.0
Keeping up the momentum of its previous environmental ambitions, Paris has committed to complete environmental sustainability for the 2024 Olympic Games. This greener approach will be made possible through careful consideration of the event’s chosen venues, operations (catering and accommodation) and transportation.
As a city renowned for its architecture, Paris has addressed one major change that it can make to the games — using existing infrastructure to host events. As of now, 95% of the chosen venues are pre-existing or temporary structures.
The competition zones are divided into two main areas both inside and outside of Paris’ center. Universally connected by the Seine, 80% of the venues are within a 10 kilometer distance of the Olympic and Paralympic Zones, allowing 85% of athletes to stay less than 30 minutes away from their venue. Through the use of existing facilities that require minimal transportation, Paris can host an event that will aid in its goal to, hopefully, halve a previous carbon footprint of 3.86 million tons. The French aim for a decrease in emissions compared to that of the Tokyo Games in 2020. With Tokyo’s post-game estimation of 2.16 million tons of carbon dioxide, Paris has committed to a limit of 1.65 million tons and to offset any indirect impact with climate-positive projects. Meeting carbon emission goals for the games may prove challenging because of these indirect impacts, primarily the substantial travel emissions generated by spectators. This seems a daunting task when compared to the Tokyo games which managed to achieve low net emissions because of the lack of spectators due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
In accordance with the city’s holistic sustainability vision, Paris has placed emphasis on the importance of green catering. As an event that is responsible for serving 13 million meals, embracing sustainable food sources and partnerships now will set the city up for environmental prosperity even after the games.
In recognizing the environmental impact of certain food sources and resulting waste, Paris has quantified its objectives to reduce its carbon footprint. This eco-conscious catering approach is made up of 6 commitments: two times more plant-based food, 100% certified food (food that is sourced, produced and consumed in a responsible way), reduced plastic consumption, recycling of all uneaten food, reuse of all equipment and structures and hiring 10% of workers from professional integration programs. Athletes and spectators will have a wide variety of plant-based options at their disposal, with 60% of food and beverages available to spectators being vegetarian. With 80% of the total food supply being sourced from within France’s borders, the alternatives to traditional cuisine should hardly be noticed as food will be prepared by culinary professionals who are familiar with creating meals that make the best use of the seasonal menu. Expertise from the chefs and localized sourcing will leave little room for waste across both food and its packing. In its drive to cut down on single-use plastic, Paris’ catering teams will exercise the use of plastic alternatives and employ a “reducing, reusing, replacing and recycling” concept on drink and food containers.
Paris’ goal to minimize waste generation and increase localized food sourcing encourages a healthier lifestyle that will extend beyond the games and become a beacon for environmental change. Even during the 2016 Olympic Games in Rio de Janeiro, plastic in the Guanabara Bay made it difficult for sailing teams to compete. This problem only intensified after the games when produced waste registered at over 18,500 tons, most being non-renewables. Despite this, some of the food waste after those games was utilized by an Italian chef, who created meals for the homeless.
The Paris Olympics will not focus only on breaking athletic records, but on breaking new ground for environmental action, particularly in sustainable event management. Through reliance on a well-developed, effective public transit system and localizing operations within France to minimize travel distance, Paris is showcasing a dedication to environmental impact that will extend beyond the games. If successful, this will serve as an inspiring example for how a large-scale international event can align with sustainability goals to change not just experiences, but lifestyles.
Mira White
Mira is a student at Brown University studying international and public affairs. Passionate about travel and language learning, she is eager to visit each continent to better understand the world and the people across it. In her free time she perfects her French, hoping to someday live in France working as a freelance journalist or in international affairs.