Africa saw the rise and fall of diverse societies, cultures, and civilizations that thrived long before colonization.
A’it benhaddou. Toa Heftiba. Unsplash
Africa as a continent is of great diversity and complexity, with a rich history that spans millennia. It has seen ancient civilizations advance agriculture, science, technology, and political systems, all of it predating the European colonial era. However, the impact of colonialism on the continent cannot be ignored. Colonialism has distorted the development and history of Africa as we know it today. From the arbitrary borders drawn by European powers to political instability in certain regions, Africa has had to navigate numerous challenges. Despite this, Africa’s story is one not of despair but of resilience and hope. Nor does it begin with these themes; it has always been a vibrant and dynamic continent.
As we explore Africa’s past, it is essential to remember that no single narrative can capture an entire continent’s complexity. Instead, we must approach each story with an open mind, ready to learn from the diverse perspectives and experiences that make Africa the remarkable place it is today.
It is a continent home to many different cultures, beliefs, traditions, kingdoms, empires, and visionaries. It is rich with mineral red soil and oceans as blue as sapphires. It is a continent where the rhythmic beats from djembe drums reverberate across the nation for all ears to hear. It is a continent with traditions ancient and beloved by many. It is a peaceful continent that many people call home. The story of pre-colonial Africa has been kept hidden, but it deserves to be uncovered for all its glory.
Empires, tribes, notables
Let’s start with the fact that “Africa” isn’t a native name for the continent , but a name the Romans gave to the provinces they conquered from Carthage. It is unclear what indigenous Africans called their continent before this European appellation, but so vast a land mass may have defied conceptualization to the ancients. The Roman term initially applied to only a portion of what we would now call North Africa. Today, some refer to the continent as a “garden of Eden” and the “cradle of humankind,” as it is the origin of our species, homo sapiens.
As we know, there is power to a name; it solidifies identity. Now that we know more about where the name Africa comes from, let’s explore more about its people and their cultures.
Malian Empire (Mansa musa)
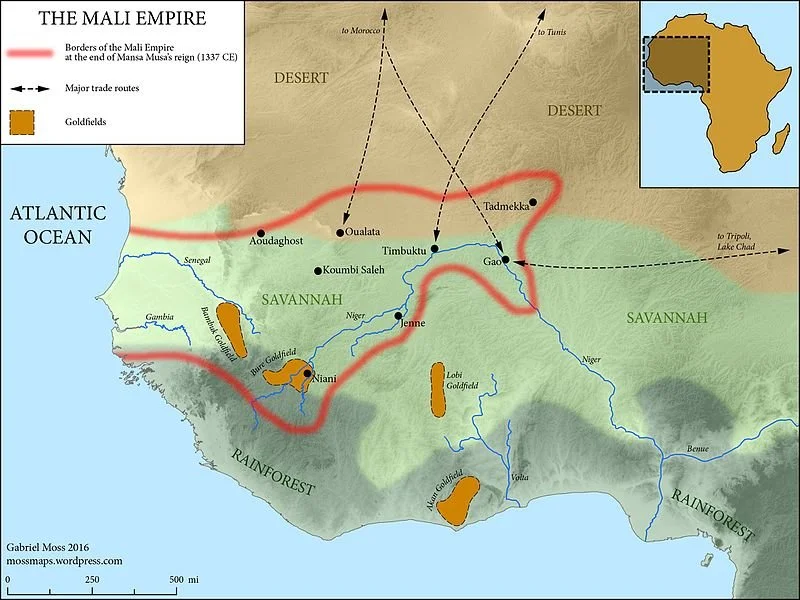
A map of the Malian Empire during its reign. Gabriel Moss. CC BY-SA 4.0
The Malian empire (13th-16th century) was an empire that spanned a multitude of present-day West African countries, in particular its present-day namesake, the Republic of Mali. During the reign of its emperors, this kingdom was widely known as a trading empire, driving the international trade in gold and salt. A notable figure who helped Mali become one of the wealthiest empires at the time was a king named Mansa Musa. He was known to be one of the richest men on earth, and during his pilgrimage to Mecca, he took tons of gold with him and shared his wealth with the people there. Under his leadership, the Malian empire excelled in education, navigation, and more.
Education
Sankore mosque, one of the largest universities in the world. upyernoz. CC by 2.0
Under Mansa Musa’s reign, his Empire built many of the most reputable philosophical schools of the age. The most well-known one is the University of Sankoré. This particular university had one of the largest libraries since the library of Alexandria – it could house 200,000 students and preserved a collection of 400,000-700,000 manuscripts. Many astronomers, mathematicians, and philosophers called this institution home.
Additionally, the Malian empire is home to the famous educational and trading city of Timbuktu. Mansa Musa, having built and cultivated this city, opened the doors for trading across north and west Africa. As more Muslim Tuareg (northern African nomads) traders made their way to the city, spreading Islam, Timbuktu became an epicenter for Maktab’s (Muslim schools).
Amazigh Indigenous
The Amazigh are Indigenous people from all over northern Africa. Often these people are called ‘Berber,’ which is a harmful exonym, as literally derived from the same root as ‘barbaric.’ They have been fighting for cultural recognition and acceptance since the Arab conquests in North Africa, eroding their existence.
Traditions
The Amazigh have a deep and profound love for the earth and for their natural lands, and they believe their mountains (Aakal) protected them from Arab invasions. They even have annual festivals celebrating the land’s fertility called Bou-Irmawen.
Another tradition they have is tattooing, which came about as an act of rebellion against Arab rulers, who banned the practice. Amazigh men tattooed Amazigh symbols and tribal affiliations onto the backs of their hands.
Lastly, Amazigh families are by tradition matriarchal. This system, coming long before colonialism and lasting many years, speaks volumes. In Amazigh families, the mother is considered the head of the family.
The Amhara people of the Abyssinian empire (Ethiopia)
Collage photo of what the Amhara people looked like. Middayexpress. CC BY-SA 3.0
One interesting thing about Ethiopia is that it was never officially colonized, only briefly occupied by Fascist Italy during WWII, meaning the nation/empire retains much of its traditions and culture. The Amhara people are among the oldest indigenous groups in the Abyssinian empire. As one of the country’s largest ethnic groups, the Amhara have given their language of Amharic to be Ethiopia’s official language. A proud and ancient people, the Amhara have many fantastic fables, stories, and myths that help define their way of life and culture.
Myths and Culture
Starting with an interesting fact, the Amhara people believe that they share ancestry with Shem, eldest son of biblical Noah, and can even trace it all the way back to King Solomon and Queen Sheba. Ethiopia is one of the oldest epicenters of Christianity in Africa (and, indeed, the world).
While the Amhara have a strong connection to religion, they also have a tie to their spirituality. They have a myth about a being called Buda, which is believed to use evil eyes and possess humans, making them partake in malicious activities. To protect yourself against these spirits, wearing a blue glass eye is believed to ward off the evil spirits and protect you.
Bunyoro-Kitara Kingdom- Eastern Uganda
A photo of what the ancient kingdom’s capital looked like. Harry johnston. CC BY-SA 4.0
Bunyoro was a kingdom in East Africa whose kings reigned from the 16th to the 19th centuries. The kingdom was infamous for its fortified military unit and its trade of fish and salt. Its economy relied heavily on agriculture and succeeded due to a surplus of fertile soils.
Reproductive health
Not only were these people excellent in agriculture, but they were excellent midwives and performed one of the first successful c-sections. They are noted to be the origin or birthplace of the c-section, as many western researchers would come here to see how they had achieved this feat. To perform these c-sections, the midwives would use banana wine as an anesthetic, fire to sterilize their tools and for cauterization, and salves and stitches for healing. These c-sections would rarely result in complications and most were successful.
Fulbe Nomad tribe–Wodaabe in Chad
The Wodaabe men dressed in their Gerewol attire and makeup. Dan Lundberg. CC By-NC-S.A 2.0
The Fulbe people, also called the Fulani, are a widely dispersed and often nomadic ethnic group across Africa. It is under debate where they originate from, and, due to their lifestyle, they are very diverse people. The Fulbe people are known to be merchants and herders. An interesting fact about them is that they were among the first people to adopt Islam after the conquests.
Gender Roles
The Wodaabe people in Chad, an extension of the Fulani, are one of the remaining groups that have stuck to their traditional religion instead of converting to Islam. They subscribe to the belief of Animism– the idea that every living thing (including trees) has a soul. Something unique about these people is that they have an annual Gerewol festival, which showcases a male beauty pageant to find a wife. In this society, despite general patriarchy, women get to choose their partners. The festival unfolds with the Wodaabe men painted in yellow with makeup wearing elaborate jewelry and sweet perfume dancing the night away.
Africa is a continent that so many call home, and for its true history to be unearthed authentically speaks volumes. Africa was often portrayed as backward or barbaric during the colonial era, and because of this, diverse and advanced ancient cultures were erased in the process. This is only a glimpse of what pre-colonial Africa was like, and there are so many more cultures that deserve recognition.
Kadija Diallo
Kadija is a student at Georgia State in Atlanta, Ga. She is a creative spirit who loves traveling and seeing new places. She also enjoys using her love for writing/storytelling to make an impact on the world. One day she hopes to make new connections and share stories as she travels to every continent.