Julia Kelley
While Indonesia’s government seeks to build a large sea wall to protect Jakarta from detrimental floods, criticism in the name of environmental and economic loss urges them to look for other solutions.
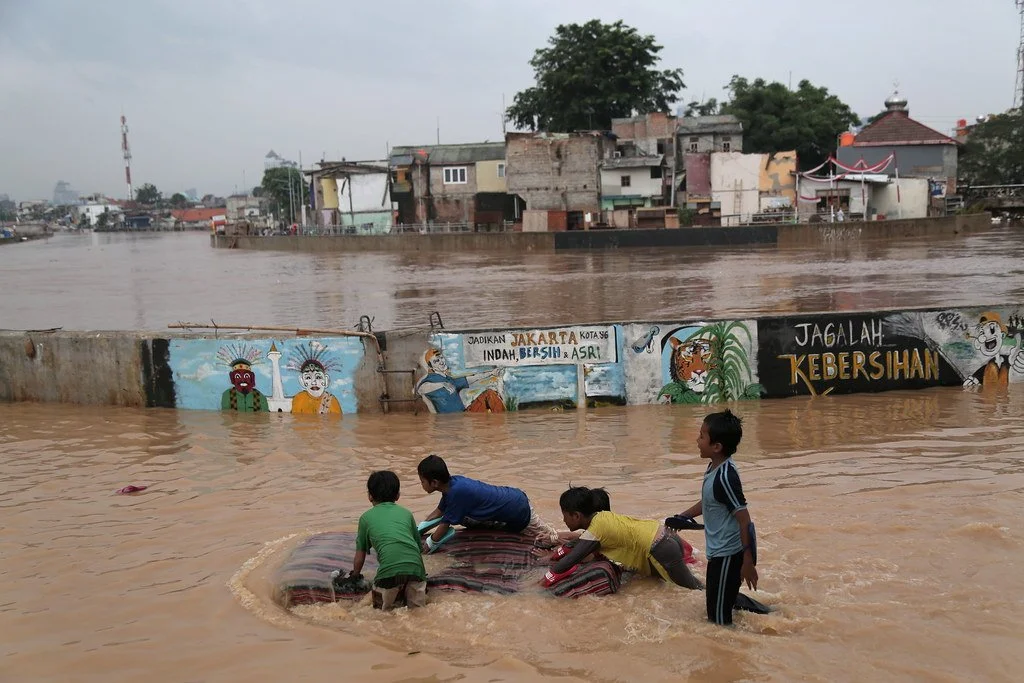
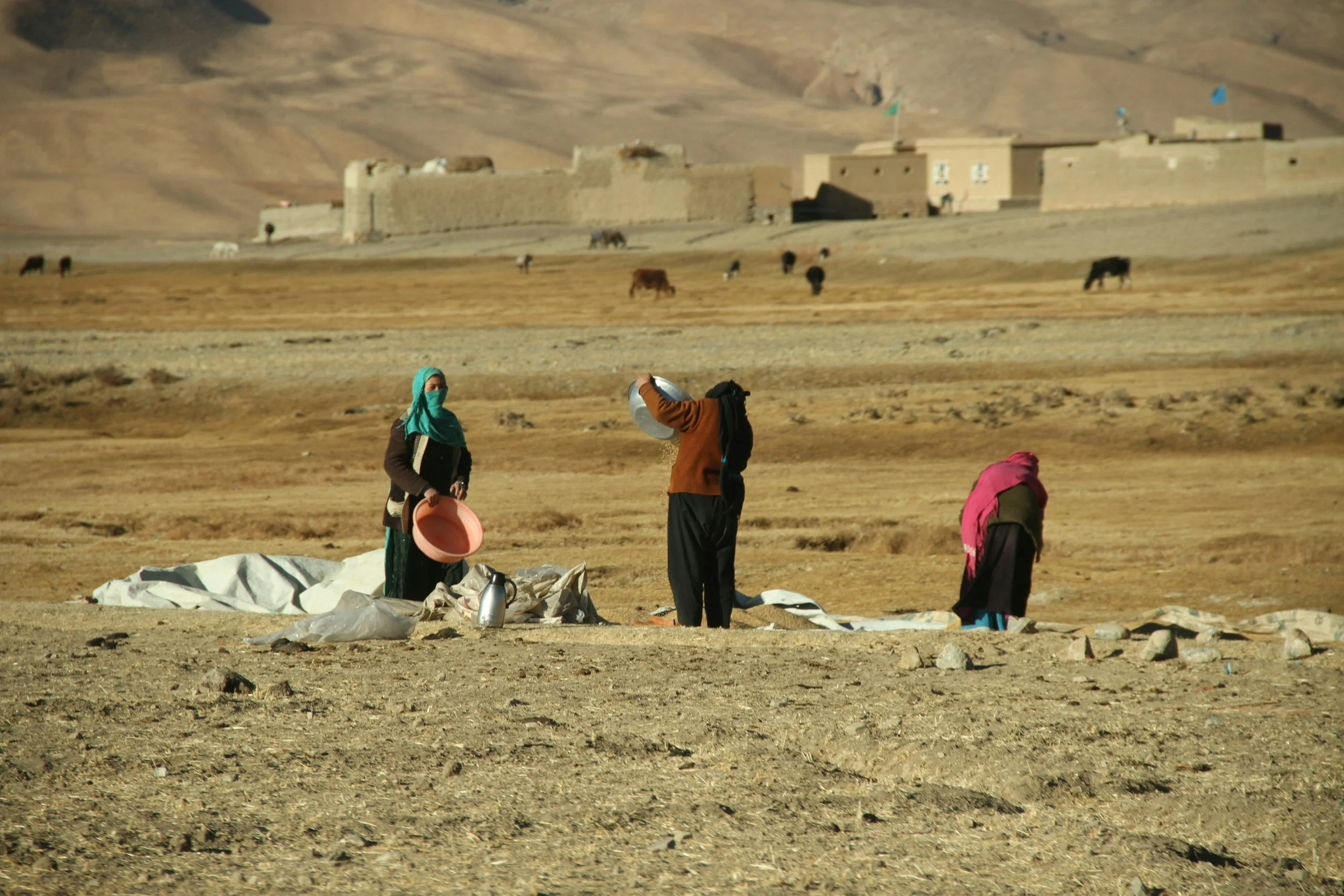
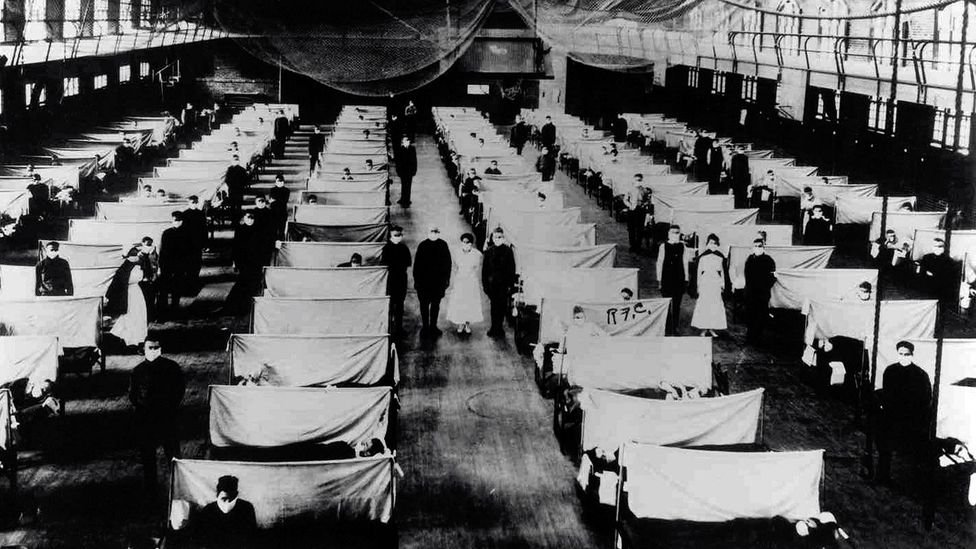
Flooding Ciliwung River in Jakarta Region. World Meteorological Organization. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
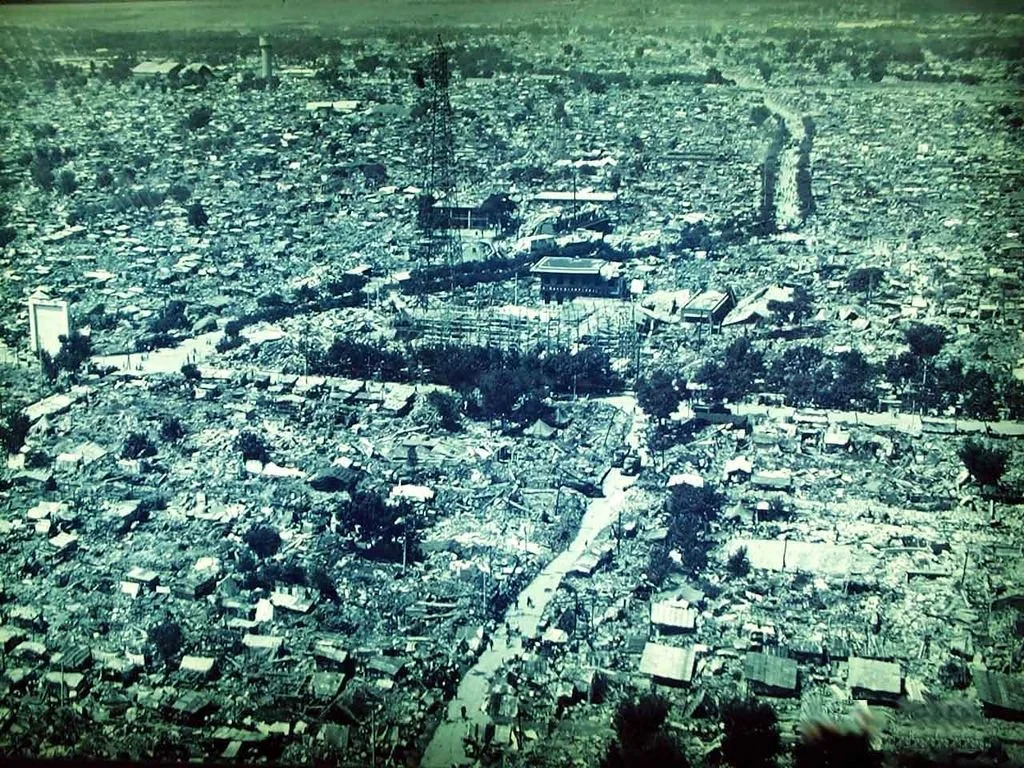
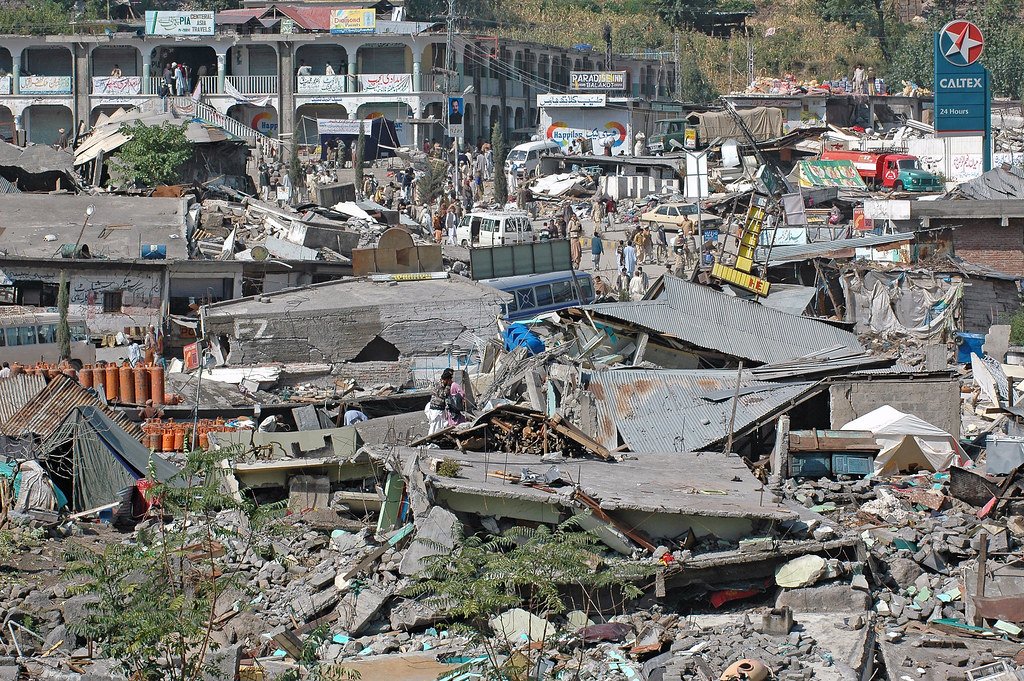
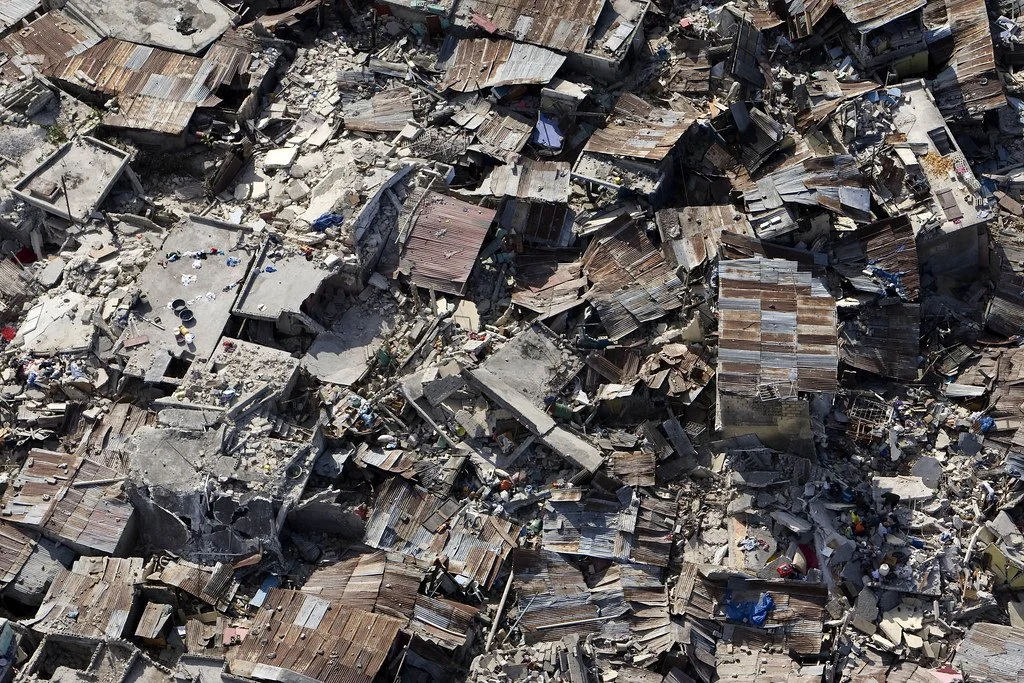
On the northwest coast of Indonesia stands Jakarta, the country’s capital and largest city. Sitting upon a low, flat alluvial plain with swampy areas, Jakarta is notably susceptible to major floods every few years from its multiple rivers and the adjoining Java Sea. This is made worse by excessive groundwater extraction and rising global sea levels, which have seen a worldwide mean increase of about eight to nine inches since 1880 due to global warming. Rapid urbanization, population growth and a change in land use have crowded more and more people into high-risk floodplain areas, leaving thousands displaced and large parts of the city submerged underwater during these natural disaster events. Although the Indonesian government built a coastal wall in 2002 to combat this, its collapse in a storm only five years later renewed the call for protective measures against destructive flooding. A new mega-project began in 2014, outlining both the construction of a new 29-mile-long sea wall and the so-called “Giant Sea Wall.” This “Giant Sea Wall,” a 20-mile-long artificial island shaped like a Garuda bird, Indonesia’s national symbol, will not only block storm surges but is also planned to contain homes, offices and recreational facilities.
This massive undertaking officially kicked off in February 2025 and is said by supporters to be key in dealing with the country’s land subsidence and flooding. Both President Prabowo Subianto and Minister of Infrastructure and Regional Development Agus Harimurti Yudhoyono claim that the project could save the government billions of dollars in disaster mitigation over the following 30 years. Despite this optimism, critics have come out against the large project, citing an array of detrimental economic and environmental issues that could result from construction. For example, many have noted how the proposed solution does not address the over-extraction of groundwater, which comes from excessive use by industrial and economic activities. In addition, the sea wall could disrupt marine biodiversity and, subsequently, the fishing industry, one of Indonesia’s strongest monetary sources. According to Maleh Dadi Segoro, a coalition of environmental and social groups, the sea wall would potentially narrow and close fishing catch areas, disrupting marine ecosystems and threatening the livelihoods of those who depend on them for food and income. Jakarta already faces low water quality in its rivers and canals, causing sewage and a lack of proper sanitation. Closing off Jakarta Bay for this sea wall, critics say, would turn the water into a “septic tank” or “black lagoon,” which necessitates a stronger water sanitation system immediately.
Controversy stirred up by the sea wall proposal has thus solicited alternative solutions. There has been an interest in using the water to its advantage, rather than working against it. This would entail diverting surplus waters, including that from floods, to surrounding farm areas where it could be stored. Restoration has also been widely proposed, as described by professor of oceanography Alan Koropitan for The Guardian: “If, instead, we can restore the bay and its polluted waters, that would mean something good for civilization in Indonesia.” Among all these suggested plans, environmental, social and economic protection are set at the center, urging the Indonesian government to rethink its monumental and costly plan.
GET INVOLVED:
Those looking to help support those affected by floods and flood prevention in Indonesia can do so by checking out relief organizations, such as The International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies’ Disaster Response Emergency Fund, Peace Winds and Mercy Corps, all of which provide immediate and long-term support. Furthermore, individuals interested in combating sea level rise can look into taking actions that counter global warming, including using renewable energy, reducing greenhouse gas usage, considering electric vehicles, recycling, decreasing food waste, keeping the environment clean, or getting involved with local communities and government to organize plans and legislation.
Julia Kelley
Julia is a recent graduate from UC San Diego majoring in Sociocultural Anthropology with a minor in Art History. She is passionate about cultural studies and social justice, and one day hopes to obtain a postgraduate degree expanding on these subjects. In her free time, she enjoys reading, traveling, and spending time with her friends and family.