Rwanda's unwavering determination and spirit shine as a source of optimism for the rest of the world.
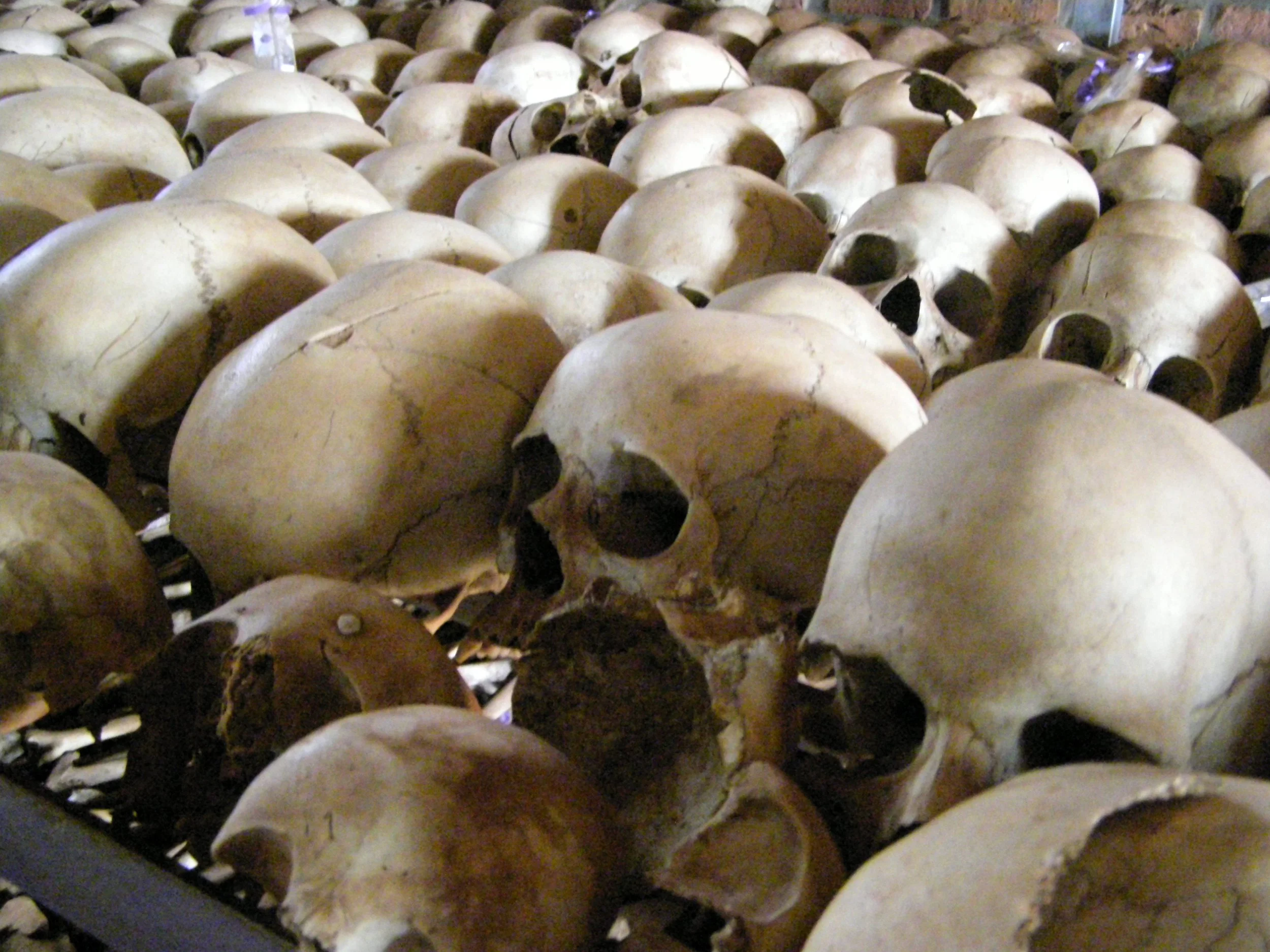
Rwanda Genocide Memorial. config manager.CC BY 2.0.
This week marks the 29th anniversary of the Rwandan Genocide, a 100-day period of violence in 1994 in which more than 800,000 people were killed. The repercussions of this tragedy continue to linger, leaving survivors and their family members with deep emotional traumas. Almost 30 years have passed since the devastating genocide in Rwanda, and the country has made some commendable progress in rebuilding its economy and mending its relationships with other nations, while also acknowledging its past mistakes and the sacrifices made during the massacre. The scars of the past may still be visible, but they no longer define Rwanda. Its developments shed light on the country’s journey toward healing and growth, with infrastructure, technology, and education driving its transformation.
The genesis of the Rwanda Genocide three decades ago can be attributed to years of systemic oppression that eventually culminated in one of the most devastating conflicts in modern history. Surprisingly, the two primary ethnic groups involved in this conflict, the Hutus and Tutsis, shared no religious or linguistic differences at the outset. A deep dive into their origins reveals that the Hutus migrated to the Great Lakes region of Central Africa between 500 and 1000 BC, while the Tutsis arrived four centuries later, migrating from the highlands of Ethiopia. The Hutus primarily worked as land cultivators, while the Tutsis were cattle herders, thus creating an economic divide that eventually led to a hierarchical system. In a strange colonial mythology, Tutsi cattle herders were labeled Hamites — a separate and exceptional group — who hailed from an ancient Christian tribe supposedly linked to people of old Palestine. This system placed the Tutsis, as a minority ethnic group, in a position of disproportionate power over the majority Hutus.
Colonial powers subscribed to this concept of racial hierarchy and origin stories, believing the Tutsi to be natural leaders and granting them preferential treatment. After taking Rwanda as a colonial possession in 1897, the German Empire built a power structure that firmly established a hierarchy that favored the Tutsis. They bestowed upon the Tutsis a superior status, owing to their taller stature and lighter skin, giving them greater influence over the Hutus. However, in the aftermath of Germany’s defeat in World War I, Belgium took over the reins of Rwanda’s governance, and, rather than attempting to bridge the cultural divide, exacerbated it. The Belgian administration continued to uphold the Tutsis’ superior status while disregarding the Hutus, creating a further chasm of inequality that only grew wider with time. The introduction of identification cards during the 1930s that explicitly listed one’s ethnicity, for example, further polarized the population, and the stage was set for the tragic events that culminated in the Rwanda Genocide.
In 1973, Rwanda witnessed an event that would forever alter the course of its history. General Juvenal Habyarimana, a Hutu tribe member, rose to power and established the National Revolutionary Movement for Development (NRMD) party to secure his authority. Meanwhile, in Uganda, a group of Rwandan exiles in Uganda who had tasted victory in Yoweri Museveni’s National Resistance Army during the Ugandan Civil War formed the Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF). This organization was largely dominated by Tutsi figures and posed a challenge to the incumbent regime. The Rwandan Civil War began, which pitted the Hutu-dominated NRMD government against the primarily Tutsi RPF, while social tensions began to simmer. It was midsummer in 1993 when Hutu extremists hatched their plan, creating a platform for propagating their racist ideology and spewing hatred against the Tutsi people. Thus, Radio Télévision Libre des Mille Collines (RTLM) came into being, which soon became a tool to incite violence and hatred against the Tutsi, using propaganda and malicious rhetoric.
Radio Télévision Libre des Mille Collines broadcasted from this office during the Rwanda Genocide. kigaliwire.CC BY-NC 2.0.
April 6, 1994, was the beginning of a nightmare for Rwanda and Burundi. The presidential plane, which was carrying the heads of state of both countries, was hit by gunfire. The news of their deaths, broadcasted by the radical Hutu RTLM radio station, served as a call to arms, sparking a wave of violence against the Tutsi population. The initial attack was planned by a group of military leaders, politicians, and business owners, who were later joined by an increasing number of supporters. This resulted in a devastating genocide, with Tutsis flocking to ostensibly safe havens like churches and administrative centers only to find them transformed into places of horror. 75% of the Tutsi population was wiped out, including many children who were labeled “little rats” and killed alongside adults. The perpetrators killed people of all ages indiscriminately, committing rape and torture on a regular basis. With nowhere to call home, over 2 million people fled the country, including many Hutu ethnic group members, while a million more were internally displaced, leaving 75,000 children orphaned.
The aftermath was massive destruction, with infrastructure reduced to ruins and hundreds of thousands of citizens dead, dealt a crippling blow to progress and development. Rwanda, however, refused to give in to despair. The RPF won the Civil War and took power after four months of horror, ending the genocide. The nation embarked on a journey of healing and reconciliation by embracing a deliberate strategy of transitional justice and transformative programs, characterized by the visionary “Rwanda Vision 2020” campaign launched in 2000. Rwanda embraced a path of renewal through initiatives such as “I am Rwandan,” which encouraged deep reflection on the nation's painful history, acknowledgment of past atrocities, and promotion of healing and reconciliation among all its people. Another example is “Umuganda,” a day of community service in which people from all walks of life work together to improve their communities. Though challenges remained, these initiatives instilled a renewed sense of vigor and solidarity, bringing new life to the difficult task of rebuilding Rwanda.
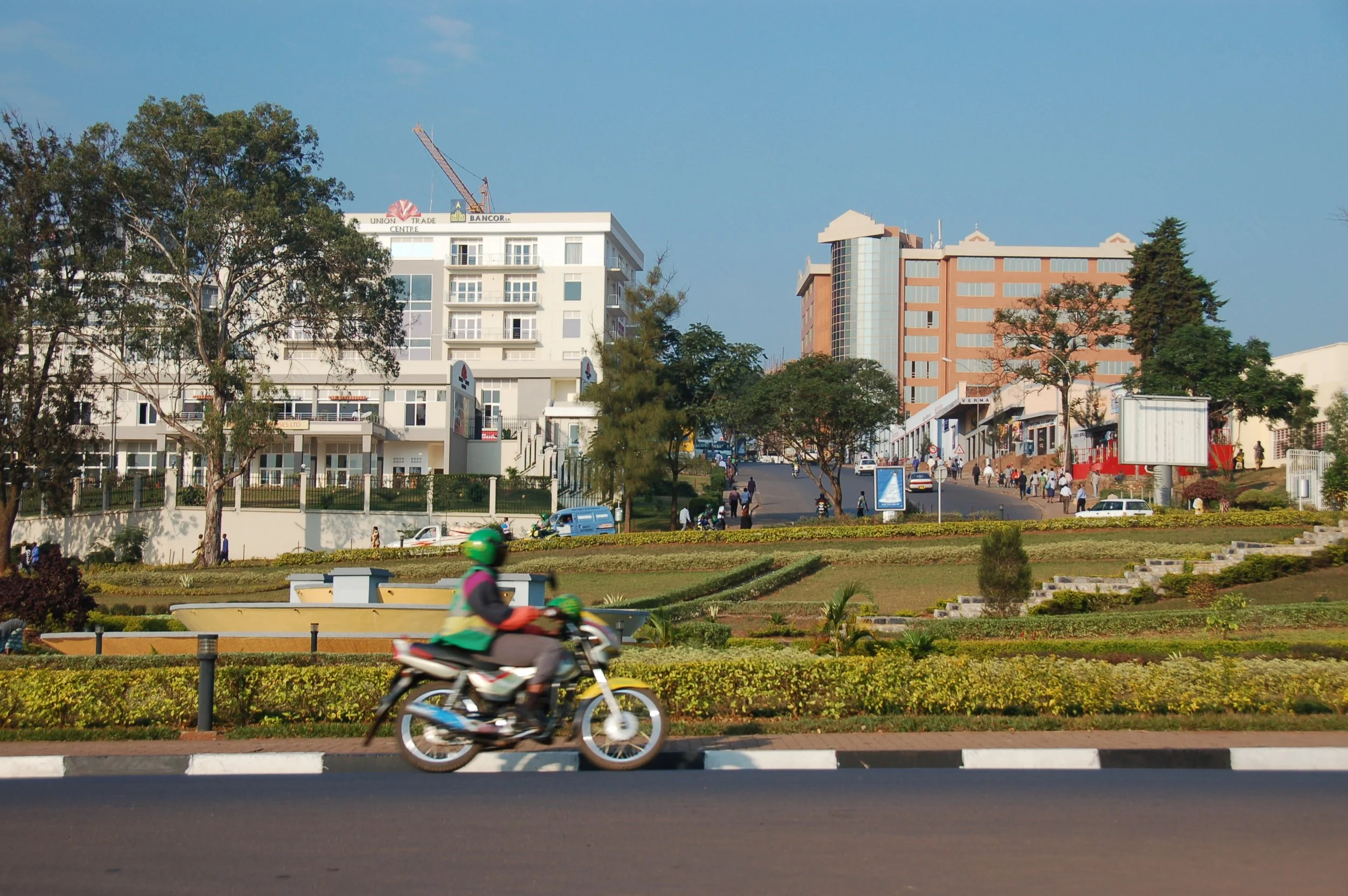
The modern capital of Kigali is safe, clean, and orderly. Dylan Walters. CC BY 2.0.
Rwanda also undergoes significant changes in its economy. The government has introduced the “Girinka” program, which provides one cow per poor family to combat poverty, with the first female calf being passed on to another family. Poverty has decreased by 23.8 percent from 2000 to 2010, and Rwanda has emerged as one of the fastest-growing economies in Central Africa, with four years of eight percent GDP growth between 2011 and 2014. These developments are positive indicators for Rwanda’s future.
Despite the indelible mark of shame left by the horrific acts, Rwanda has sought reconciliation by embracing its rich heritage of traditional pre-colonial Rwandese customs and values, while also welcoming contributions from the international community. The genocide has prompted profound reflections on critical issues such as the efficacy of peace operations, the urgency of ending international crimes, and the delicate nature of maintaining civility. These pressing issues necessitate international attention and are still relevant today.
TO GET INVOLVED:
World Help: Over the last decade, World Help has worked to bring healing and restoration to Rwandan communities through initiatives like trauma counseling, children’s homes, child sponsorship, construction projects, clean-water wells, sustainable agriculture, vocational training, and more. To learn more and get involved, click here.
IBUKA: IBUKA is an umbrella organization supporting survivors in Rwanda. Representatives from institutions like IBUKA and the National Commission for the Fight Against Genocide are invited to speak at commemorations to provide expert histories and testimonies. To learn more and get involved, click here.
Hope Zhu
Hope is a Chinese international student at Wake Forest University in North Carolina studying sociology, statistics, and journalism. She dreams of traveling around the globe as a freelance reporter while touching on a wide range of social issues from education inequality to cultural diversity. Passionate about environmental issues and learning about other cultures, she is eager to explore the globe. In her free time, she enjoys cooking Asian cuisine, reading, and theater.