Human rights organizations report on dire humanitarian conditions in Israel and Palestine, alleging violations of international law.
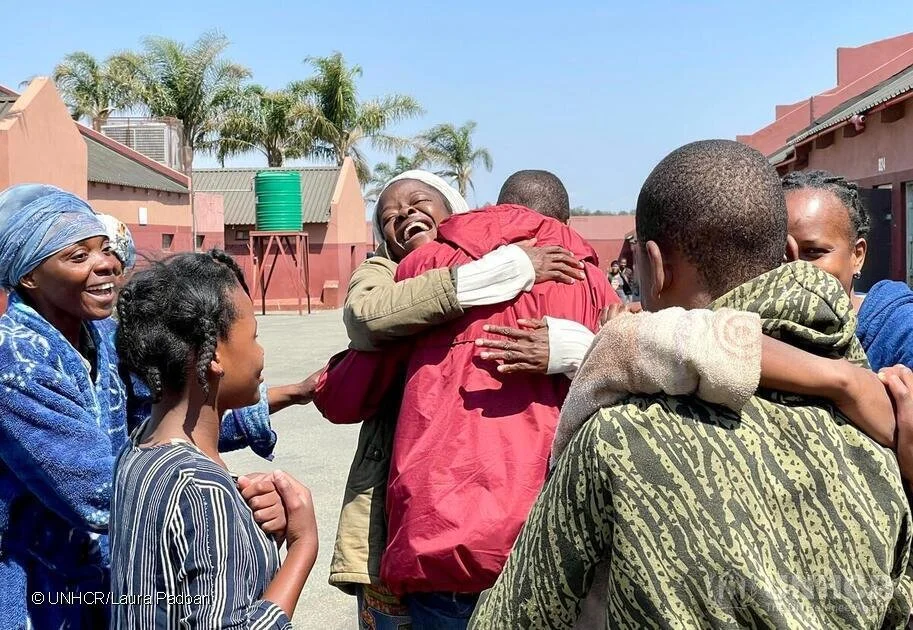
London Demonstration for Palestine. Alisdare Hickson. CC BY-SA 2.0 DEED
Since the escalation of violence in the conflict between Israeli forces and Palestinian armed factions, alleged violations of International Humanitarian Law (IHL) have surfaced. Both sides have faced criticism regarding allegations that may constitute a breach of IHL.
The United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) describes IHL law designed to safeguard civilians and prohibit indiscriminate attacks against them. This provision is binding on all armed groups involved in a conflict, regardless of reciprocal actions. The OCHA, with this law in mind, has drawn up potential allegations against Israeli and Palestinian combatants, which take aim at Israeli military tactics and use of prohibited weapons as well as Palestinian armed groups’ conduct.
With the intensification of the violence and the number of Palestinians who have been displaced, there has been rising criticism regarding the weaponry and tactics that Israel has employed against Palestine. More serious allegations include the use of white phosphorus in well-populated areas of Gaza, which has harmful effects on human tissue. This, among other tactics such as blockades and airstrikes, have resulted in high civilian casualties, raising questions with regard to the potential for indiscriminate suffering and collective punishment.
Palestinian actors have also breached rules of IHL. Human Rights Watch reports that armed groups, such as Hamas, have used indiscriminate rocket firing into Israeli territories, giving reason to accuse those involved of targeting Israeli civilians specifically, warranting a war crime.
Apart from OCHA, other human rights organizations have also begun to contend the violence as war crime and collective punishment. Amnesty International, an organization focused on human rights, has found Israel’s system of governing Palestinians in Israel and the Occupied Palestinian Territories to be oppressive and discriminatory. Citing the forced eviction of thousands of Palestinians, use of arbitrary detention by Israeli authorities and torture or ill-treatment of civilians, Amnesty has expressed the belief that Israel’s actions constitute a system of aparthied under international law.
The International Federation For Human Rights (FIDH) has additionally expressed concern over the targeting of civilians and human rights violations in Israel and the occupied territories. From the gathered evidence of human rights abuses, FIDH has acknowledged a tightened system of apartheid by Israel, involving the displacement of Palestinians in the West Bank, denial of freedom of movement and incidents of torture, all amounting to crimes against humanity. As of November 2023, Israel held close to 7,000 Palestinians that, with restrictions on water and overcrowded conditions, subjected detainees to what is now being considered ill-treatment and collective punishment. Tal Steiner, executive director of the Public Committee Against Torture in Israel, commented on the treatment of Palestinian detainees, saying that “Punitive detention conditions, arbitrary violence and humiliation of detainees and the intentional infliction of torture, should all be absolutely prohibited and unacceptable.”
The International Criminal Court (ICC) has become involved with the conflict as a potential route for prosecuting those accused of war crime and human rights abuses. Israel has argued that the ICC does not have jurisdiction because of its views regarding Palestine’s statehood, however, the mandate by ICC has gathered international support as viable protection against war crimes. The collection of evidence gathered by human rights organizations has aided in the investigation by the ICC, and the pursuit of accountability in this current situation has been viewed as one of the most crucial steps in ending the violence.
Both the Israeli and Palestinian governments and terrorist organizations like Hamas are responsible for upholding human rights, regardless of the applicability of international law in the case of the conflict between the two. Those infractions adjudicated as war crimes may be subject to legal repercussions, but as the international community awaits further development, accountability as an avenue for resolution remains integral.
Mira White
Mira is a student at Brown University studying international and public affairs. Passionate about travel and language learning, she is eager to visit each continent to better understand the world and the people across it. In her free time she perfects her French, hoping to someday live in France working as a freelance journalist or in international affairs.