An increasing amount of discrimination and violence is targeting Sudanese women.
Read MoreChad is the Country Most Vulnerable to Climate Change
In Chad, climate change creates new challenges for an already disadvantaged population.
Humanitarian aid in Chad. EU Civil Protection and Humanitarian Aid. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Due to its geography, Chad has experienced a temperature increase of 1.5 times higher than other places in the world. With additional disadvantages of poverty and political conflict, Chad has been ranked as the country most vulnerable to climate change. Here are some of the ways Chad is currently being affected by climate change, as well as current action against this crisis and ways you can help.
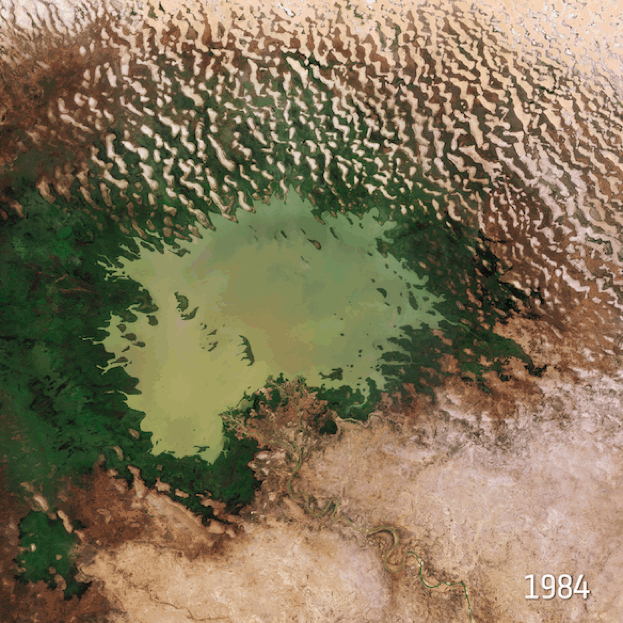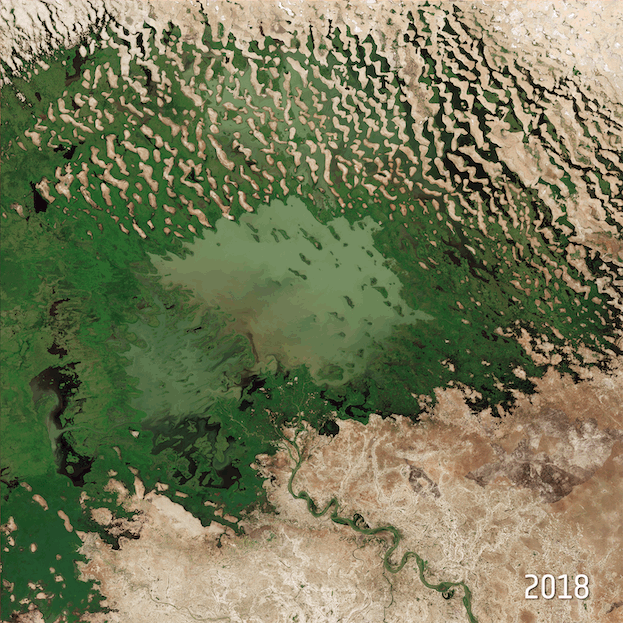
Lake Chad
Satellite images of Lake Chad’s shrinking waters between 1984 and 2018. Fae. CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO.
With a surface area of 2.3 million square kilometers, Lake Chad is the country’s reservoir. Climate degradation has taken a toll on this freshwater inland sea over the decades, resulting in its shrinkage of 90 percent within the past 60 years. Not only does this affect the country of Chad itself, but also surrounding nations that rely on Lake Chad, such as Nigeria, Niger, and Cameroon. The increasing lack of this water source reduces the availability of drinking water for both humans and animals, and also impacts irrigation and fishing. Access to clean water is an existing issue in Chad, with only 43 percent of the population able to obtain clean drinking water, forcing many to consume unsafe water that exposes them to diseases like cholera.
Flooding
Chari River. Afcone. CC BY-ND 2.0.
In sharp contrast to the drought affecting Lake Chad, the rest of this Sahelian Republic has suffered flood damage over the past year, caused by its heaviest rain season in 30 years. In October of 2022, both the Chari and Logone rivers overflowed, causing 18 out of 23 Chadian provinces to flood. This flooding has affected more than 340,000 people, destroying thousands of homes and farmland. Though climate change has caused much drought in Chad, it is also a contributing factor to this flooding. As climate change causes temperatures to rise, it allows for more evaporation from the ground and water sources, leading to extended periods of drought and punctuated by bursts of extreme rainfall.
Illness
Medicine in Faya-Largeau, Chad. Gerhard Holub. CC BY-SA 4.0.
Another way climate change endangers Chadians is by increasing the probability of illness transmission. As mosquitoes are attracted to water, increased flooding could create a greater risk of malaria contraction. In 2022, there were 1.8 million cases of malaria in Chad, with over 2,500 fatalities. Though malaria cases have decreased over the last 20 years due to an increase in treatment and preventative measures, they have been rising within the last decade, with 190 cases per 1,000 at risk in 2014 versus 206 cases per 1,000 in 2021. An uptick in temperatures can also cause a greater risk of meningitis, an illness that is common in Southern Chad, which is part of a region known as the “Meningitis Belt.” Heatstroke is also a danger to Chadian people, as well as malnutrition, as crops are destroyed by drought and flooding. With only 1 in 17 children having access to soap and water to wash their hands with, there is already a public health crisis in Chad, and rising temperatures only exacerbate the problem.
Resolutions
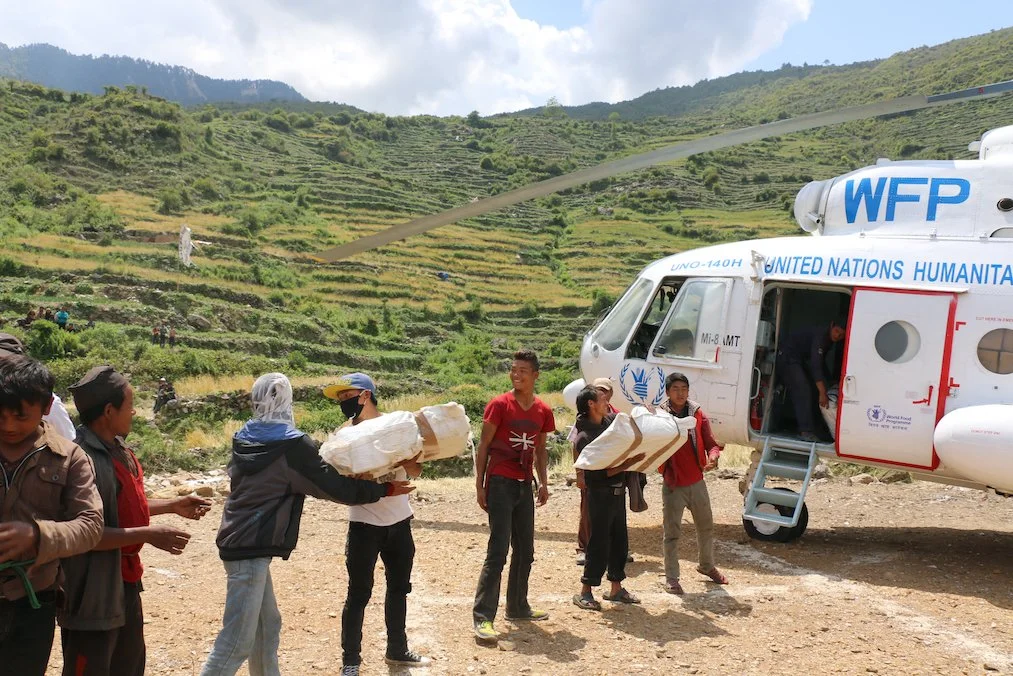
World Food Programme. Anjeli Mendoza. CC BY-SA 4.0.
Chad National Adaptation Plan Advancement Project (NAP)
Launched in 2018, the NAP was created as part of Chad’s national contribution to the Paris Climate Agreement. With this plan, eight areas are prioritized, including environmental subjects such as agriculture, forests, sanitation, water resources, and more. National planning and budgeting are being developed on these fronts, all aiming to improve conditions for the Chadian population.
United Nations (UN)
In April, the United Nations appealed for $674 million for a humanitarian response plan, in order to address climate, health, and food crises in Chad. The Sustainable Development Group of the UN also aims to aid the country in its struggles by helping the government enact national security, humanitarian and economic policies.
World Food Programme (WFP)
The WFP provides nutritional support to infants, young children, and pregnant women in order to combat malnutrition in Chad, helping 458,000 children and 235,400 nursing and pregnant women in 2021. WFP has also provided meals to schoolchildren and helped restore degraded land.
To Get Involved
Click here to donate to the World Food Programme.
Click here to donate to the International Committee of the Red Cross.
Click here to donate to UNICEF.
Alexandra Copeland
Alexandra Copeland is a student at The College of New Jersey studying psychology and journalism. She is a lover of coffee, dancing, and visiting new places. Being raised with her Greek culture has inspired her interest in cultural customs around the world. She is a passionate writer and hopes that her work will make an impact in the future.
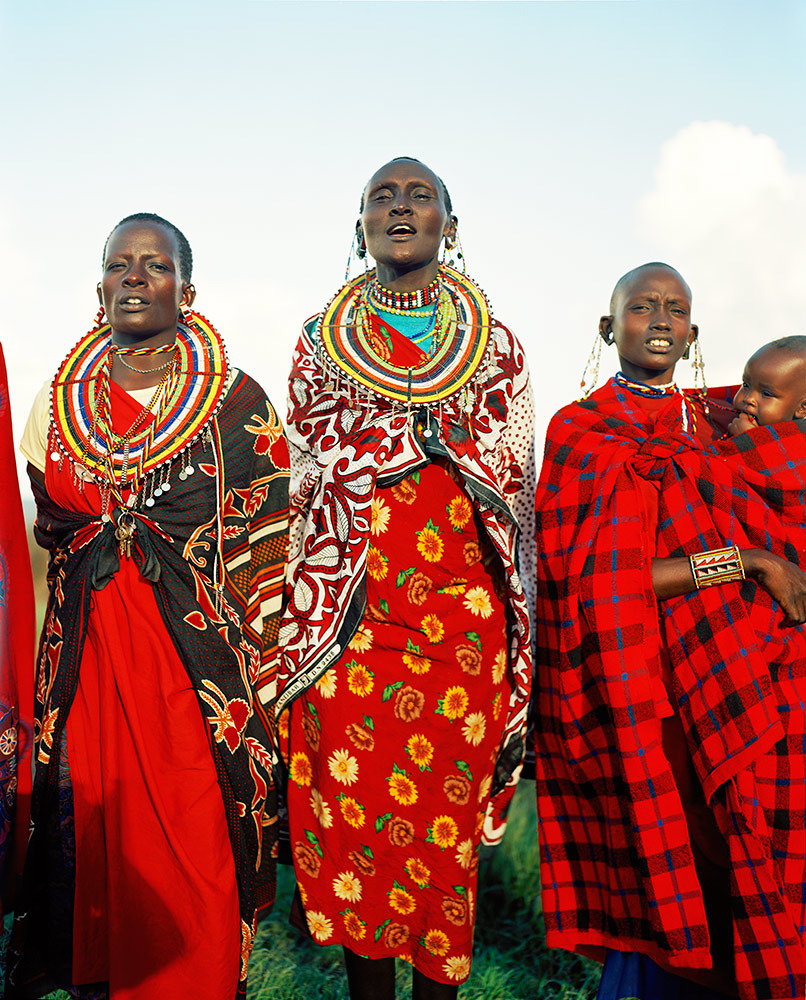
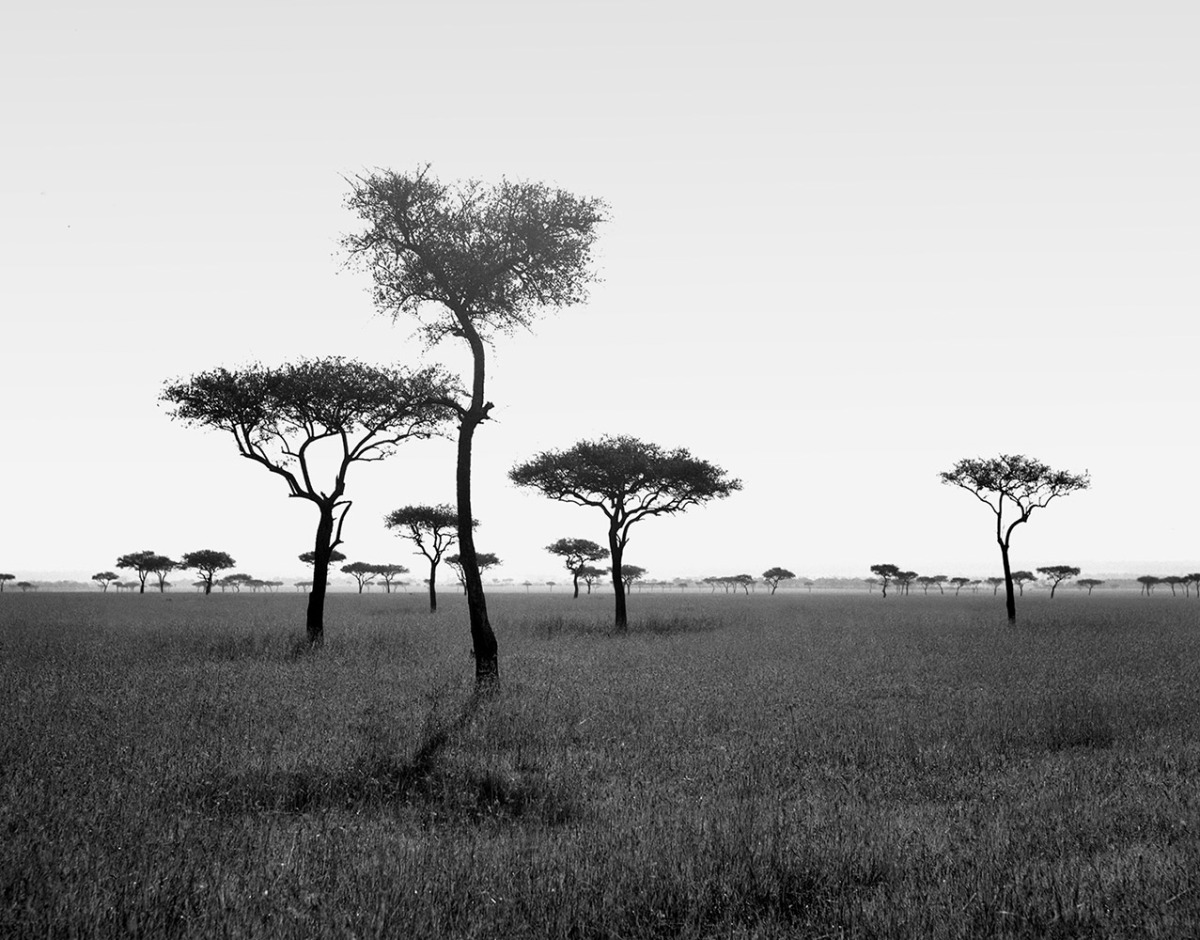
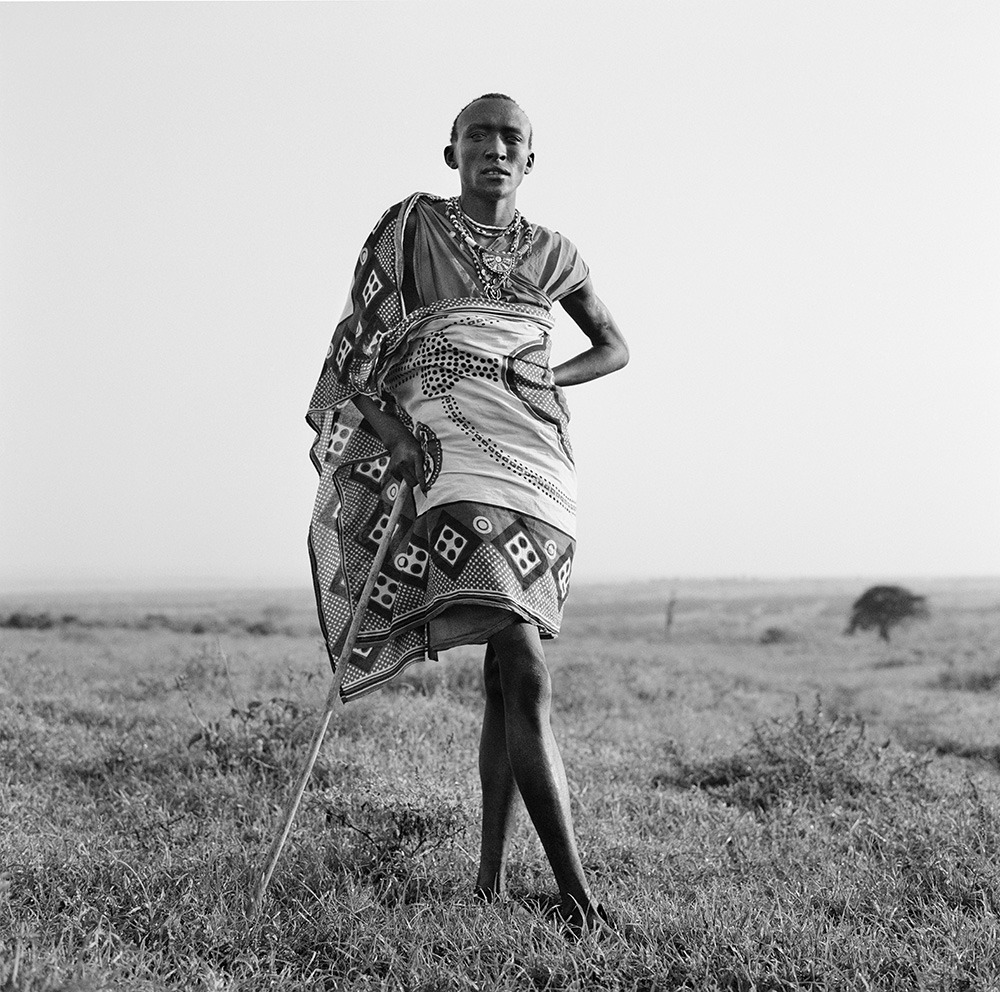
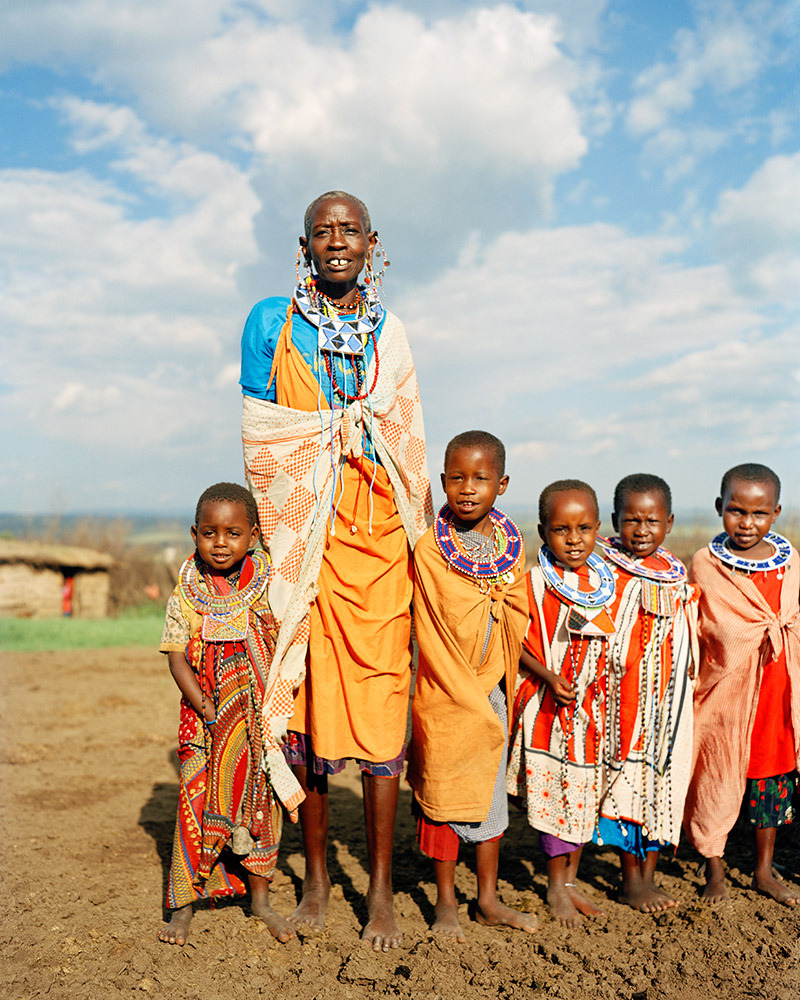
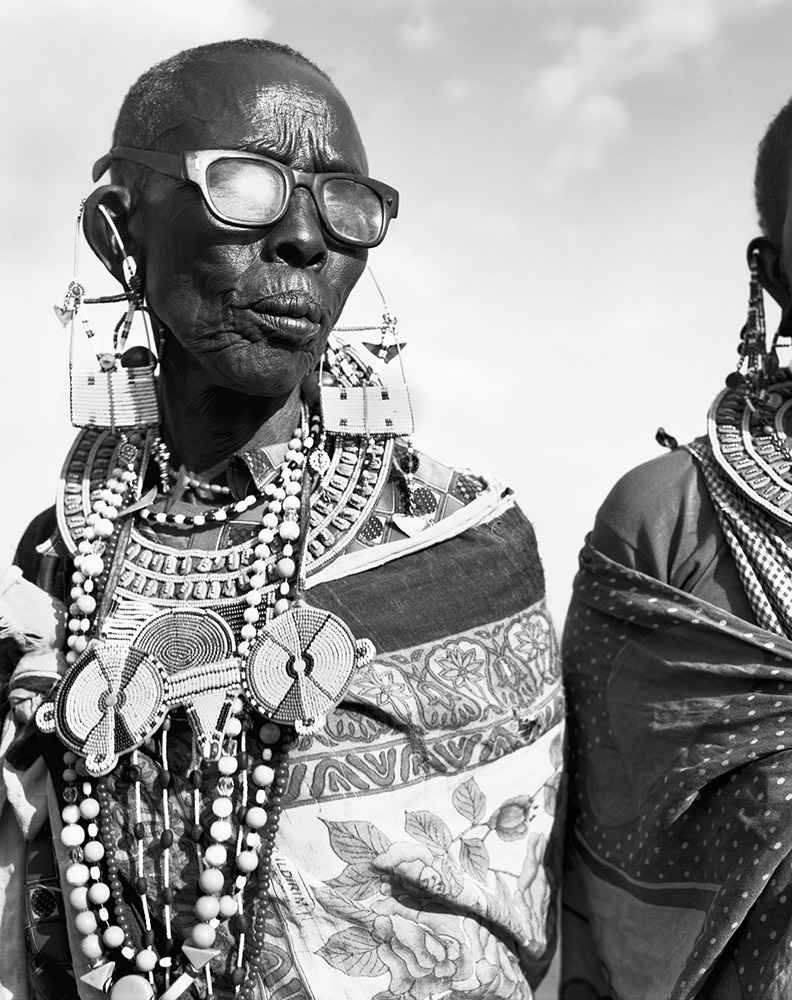
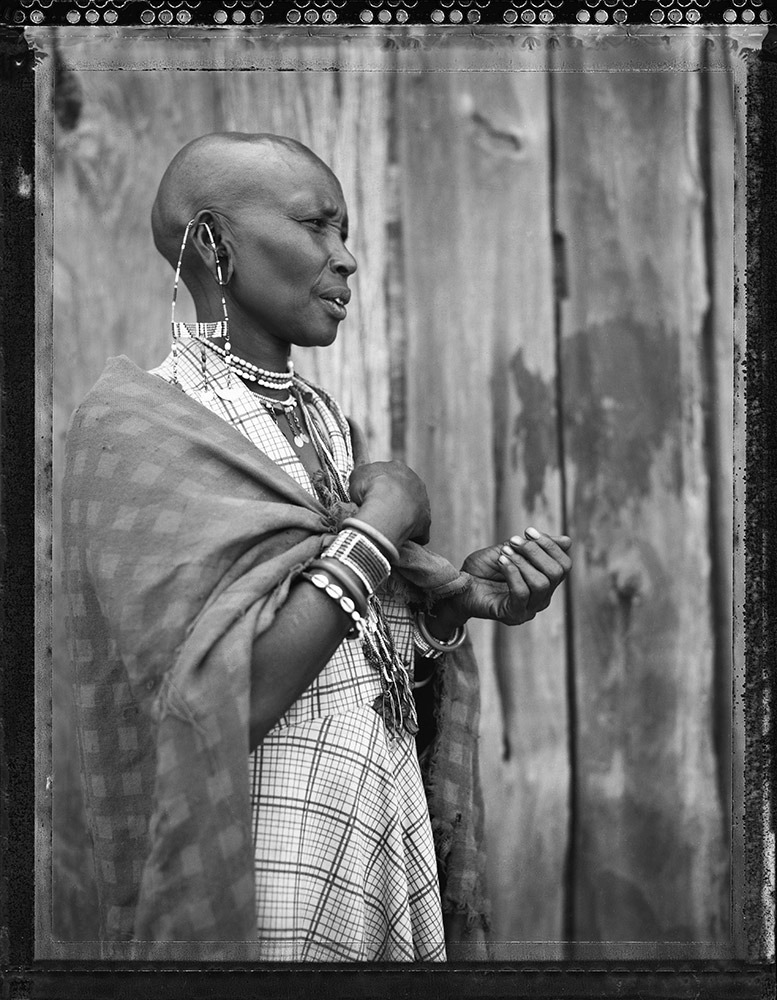
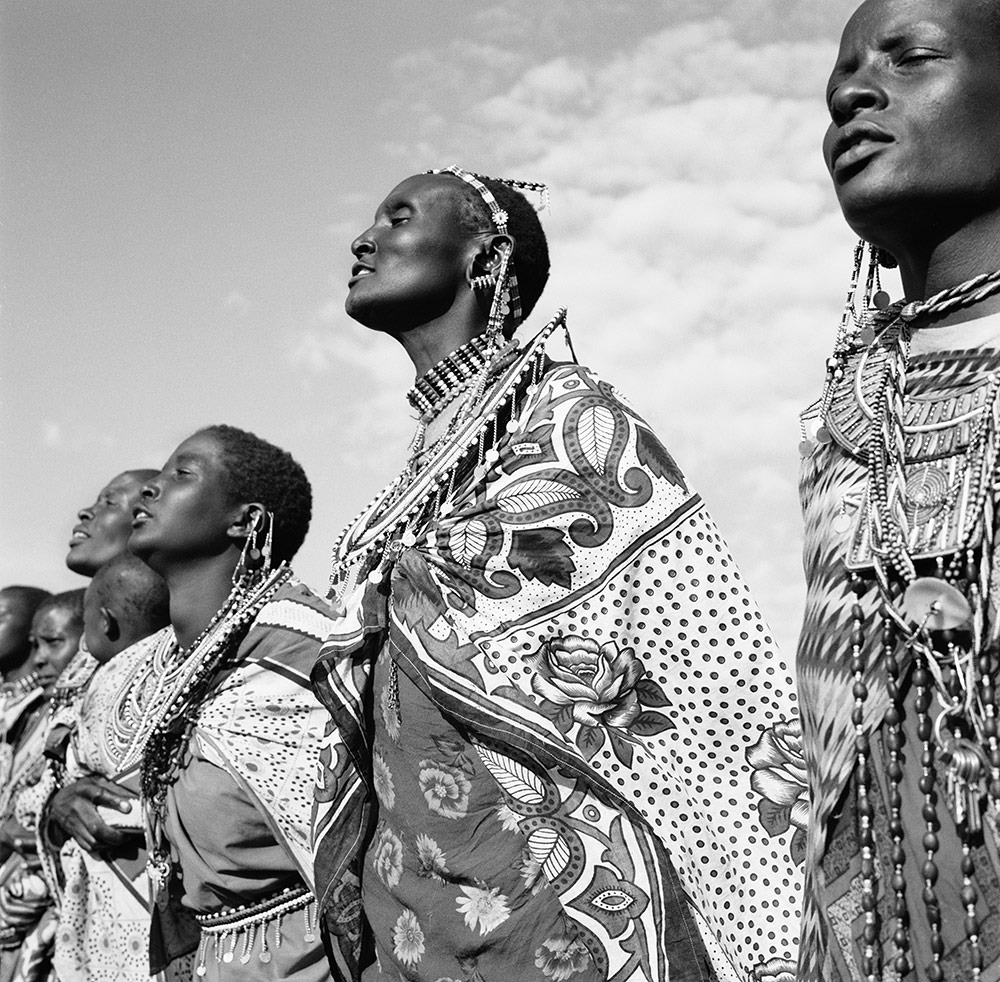
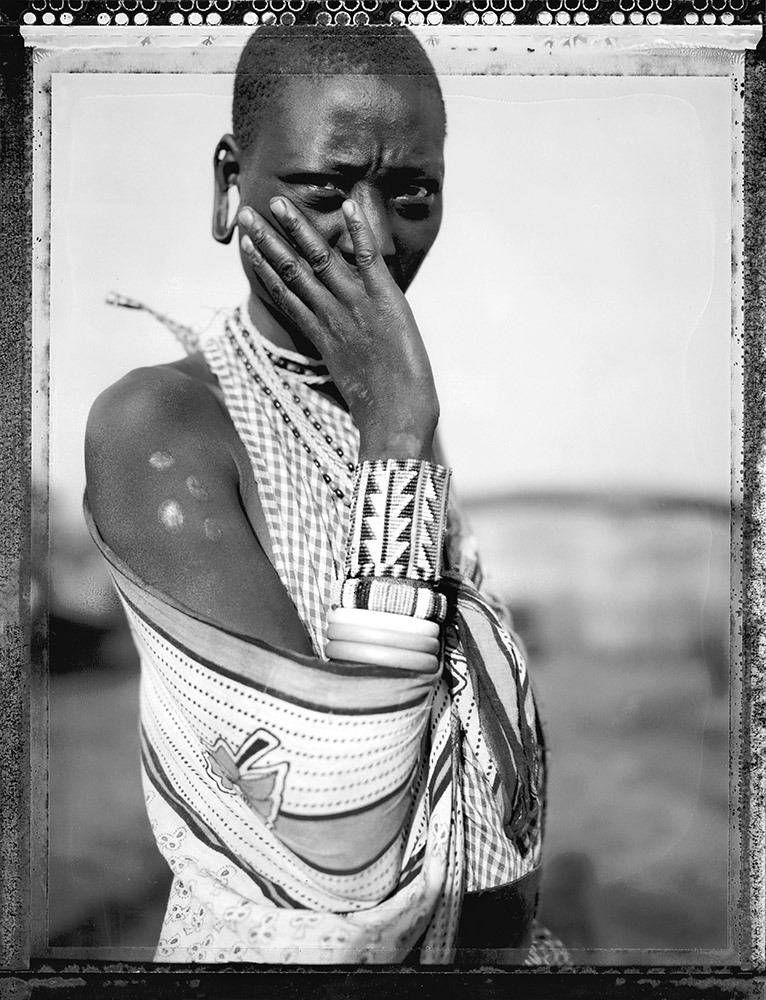
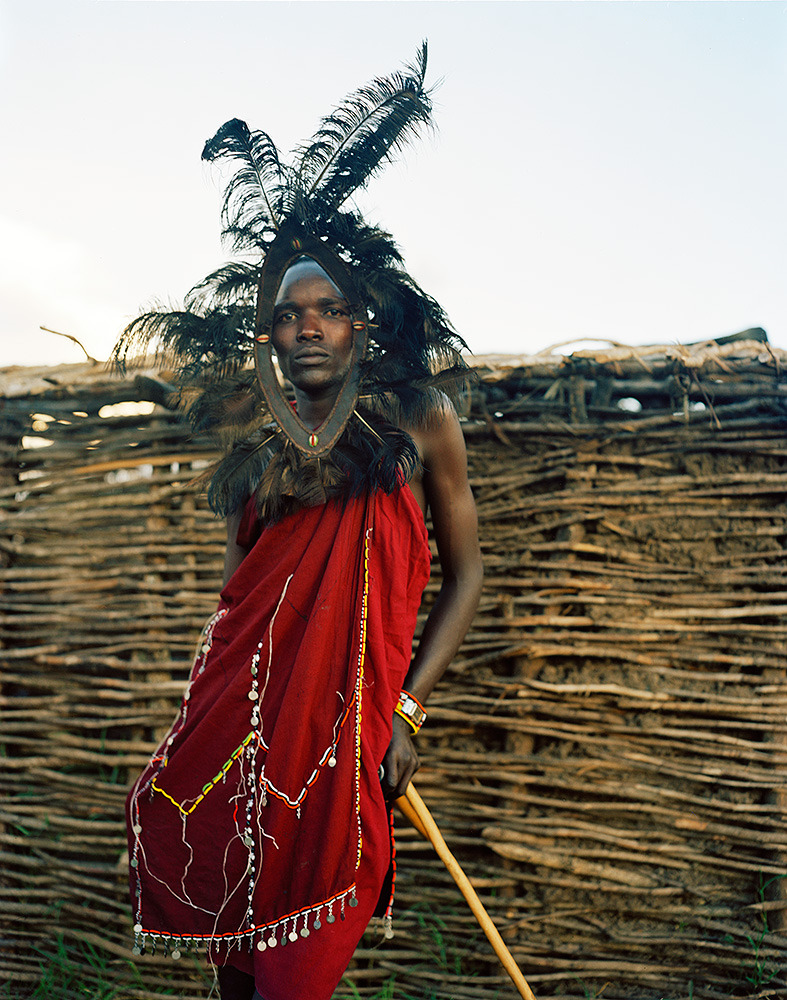
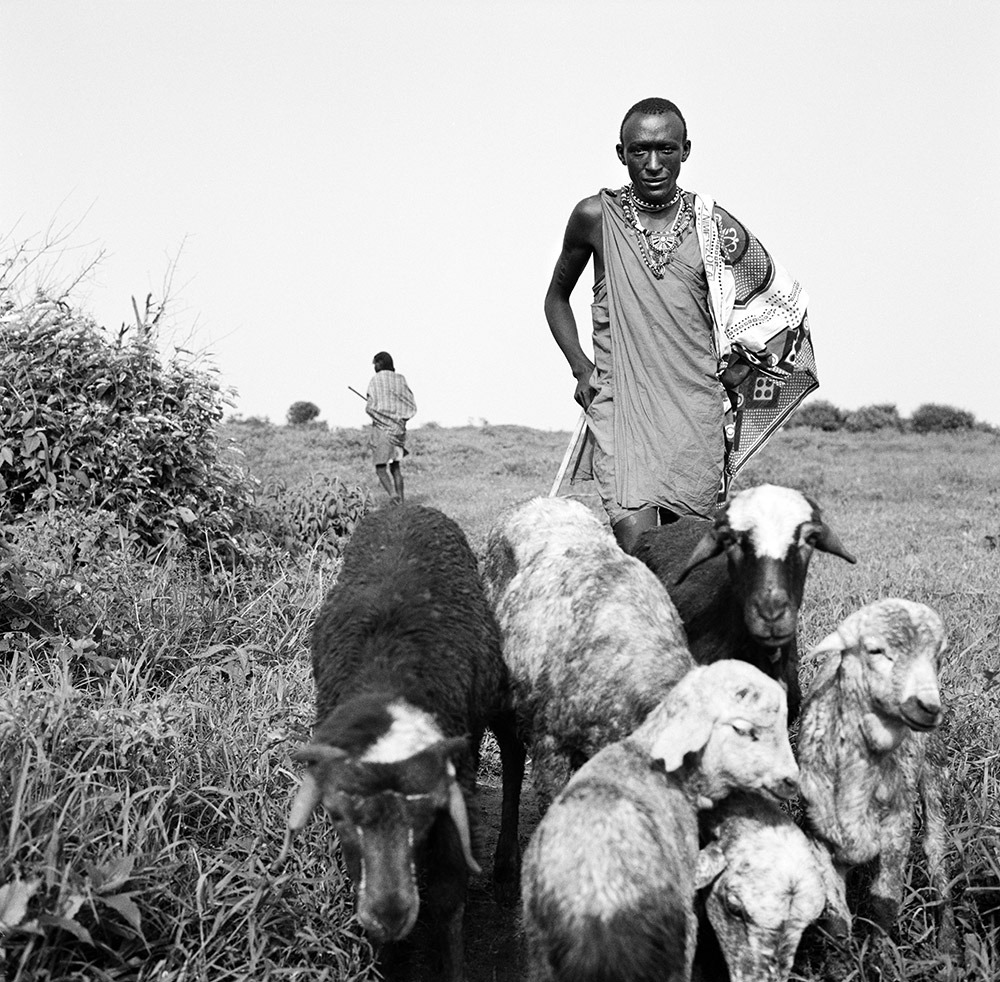
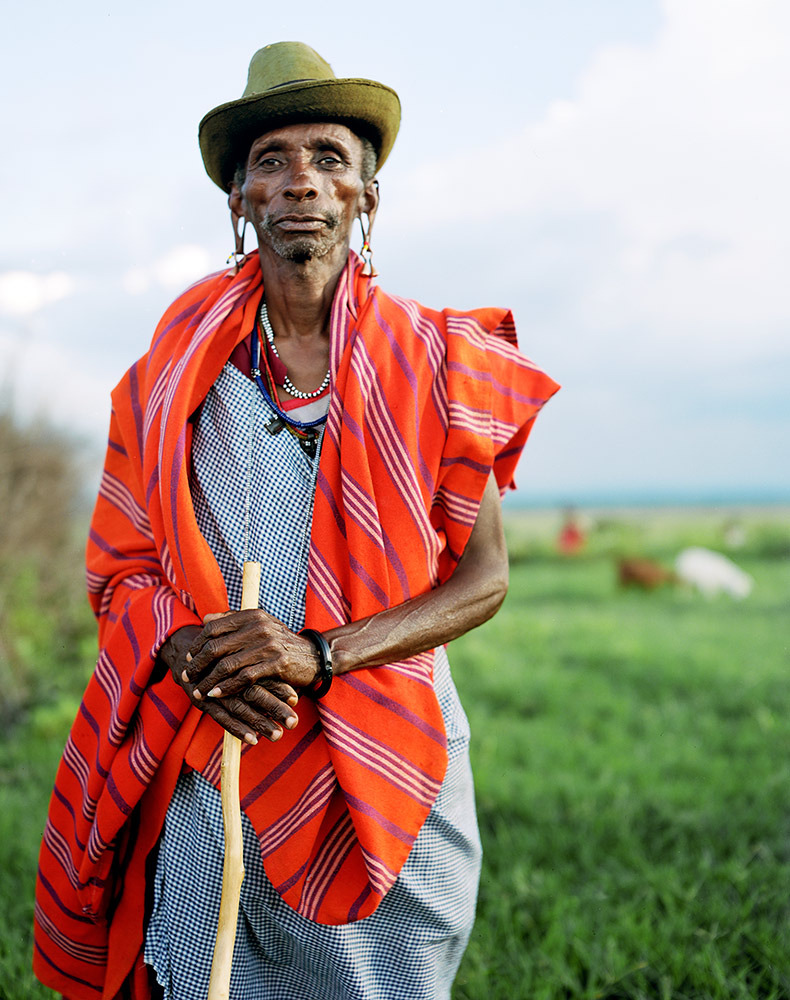
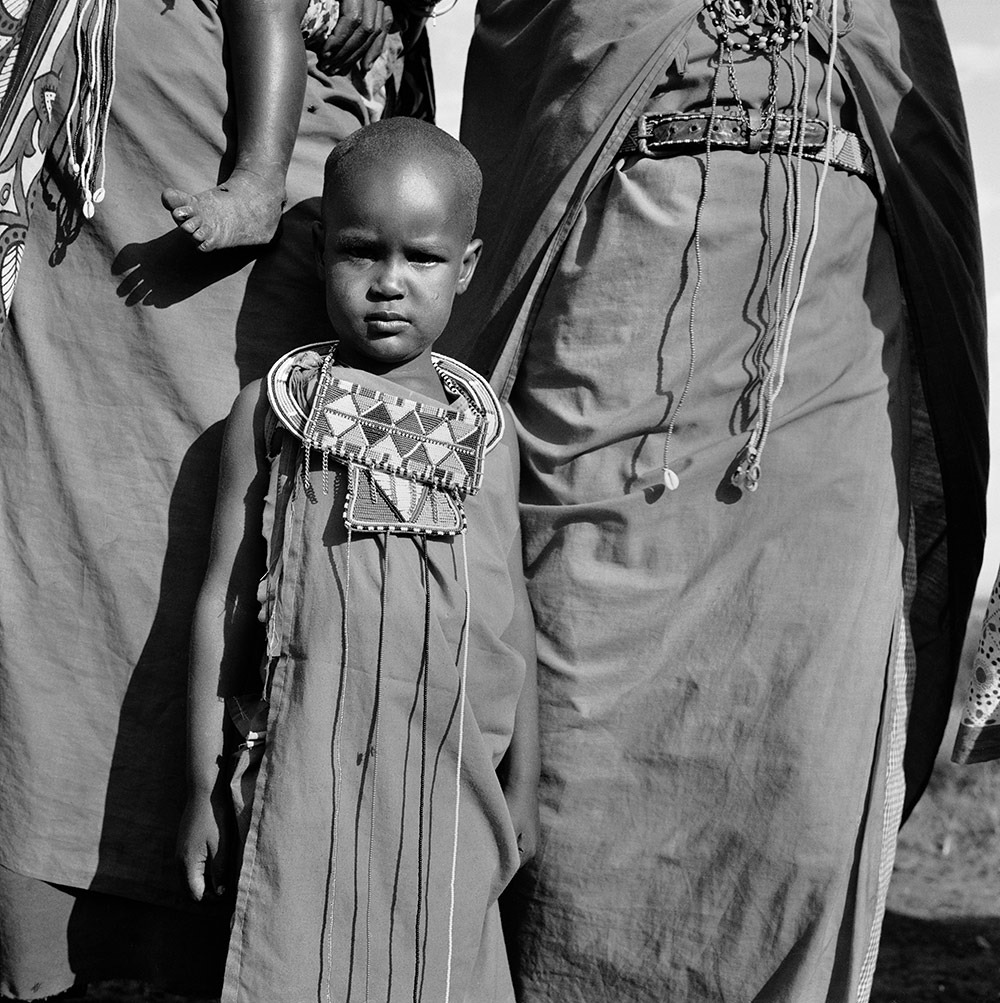
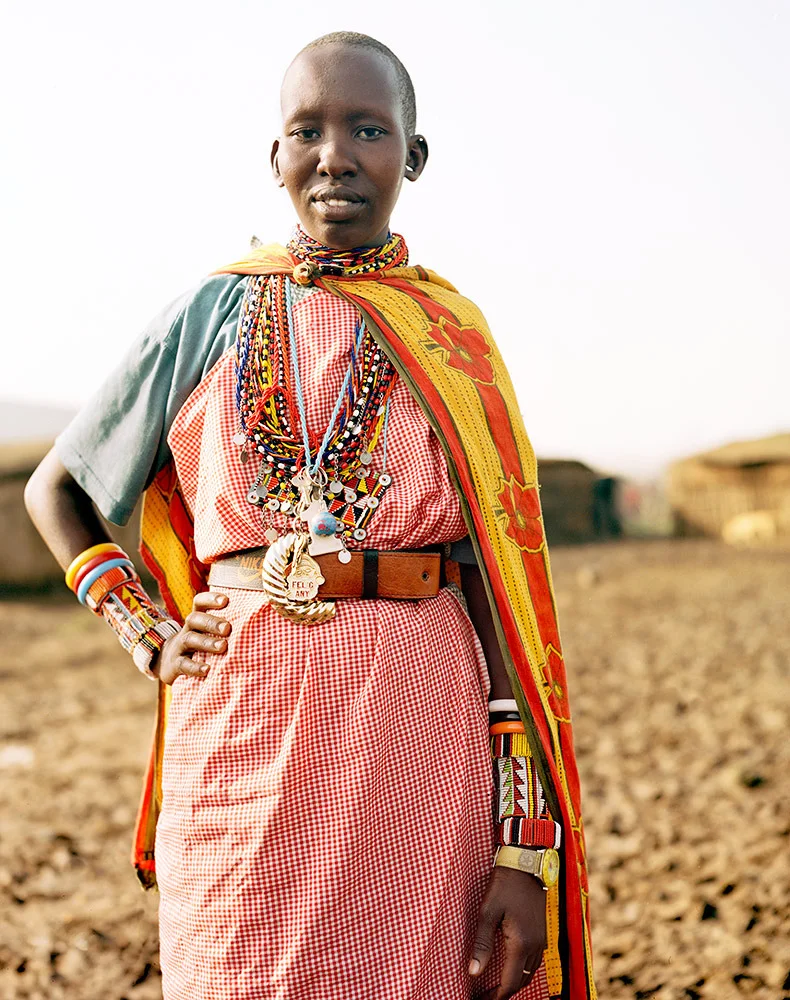
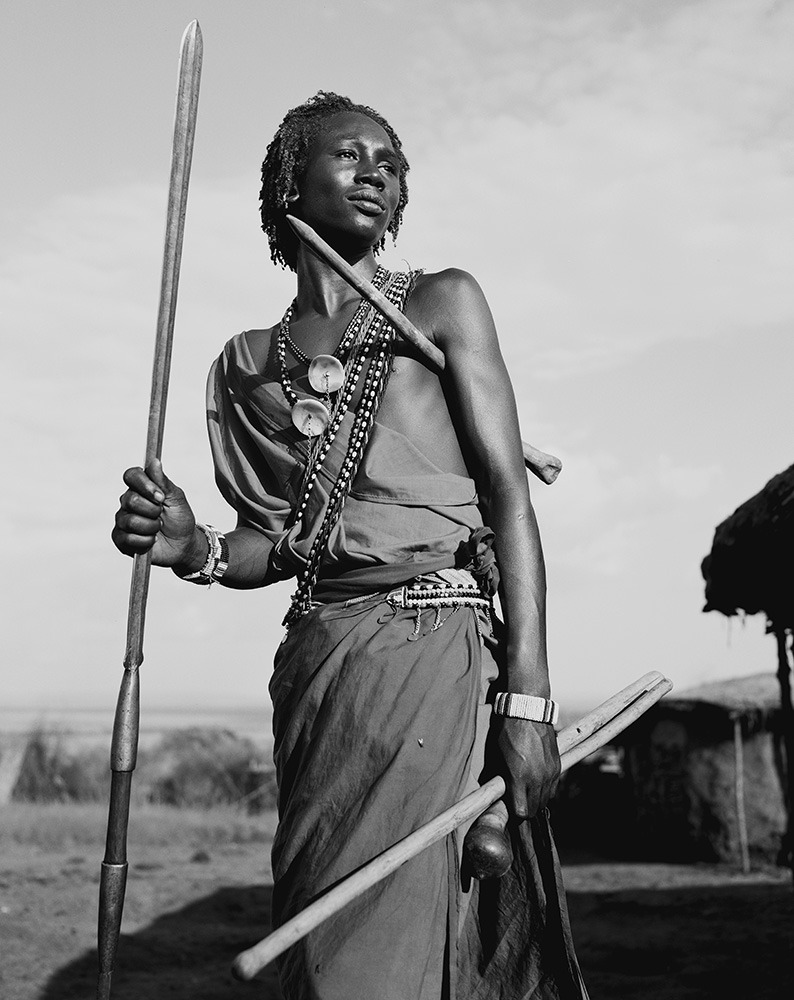
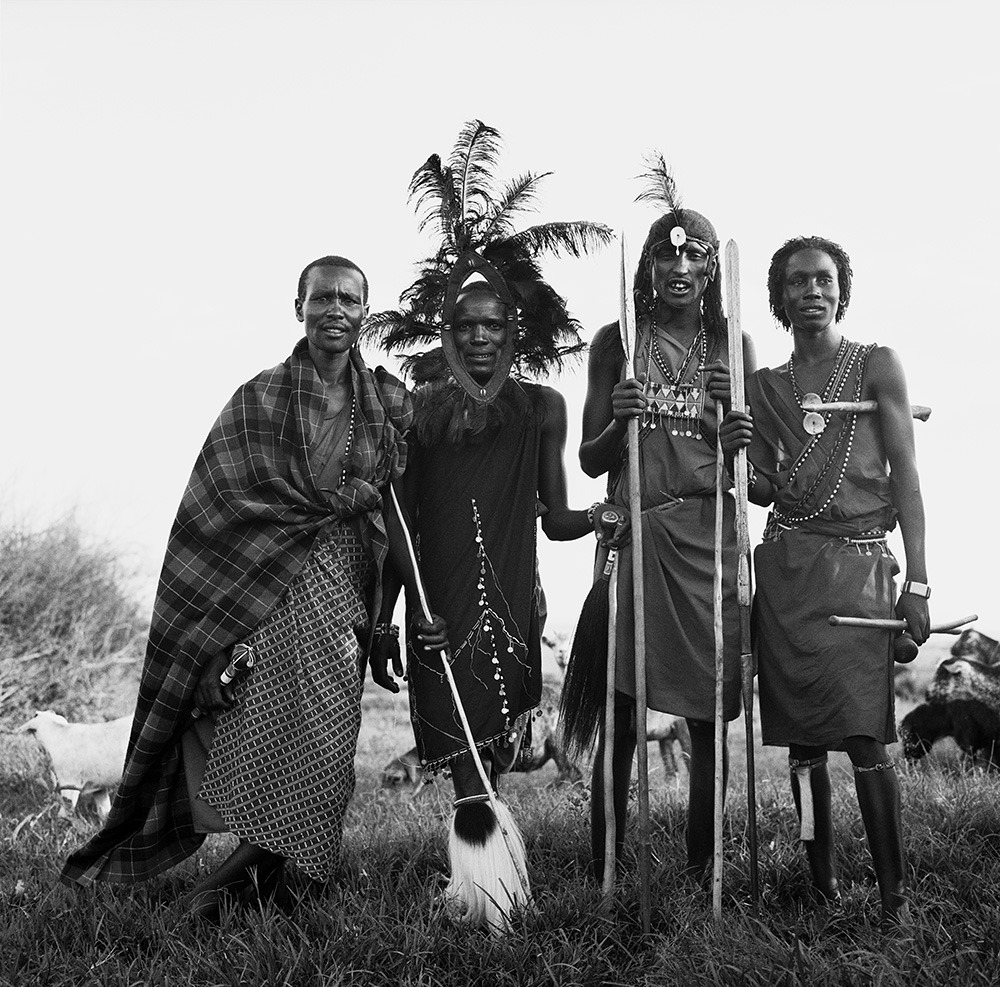
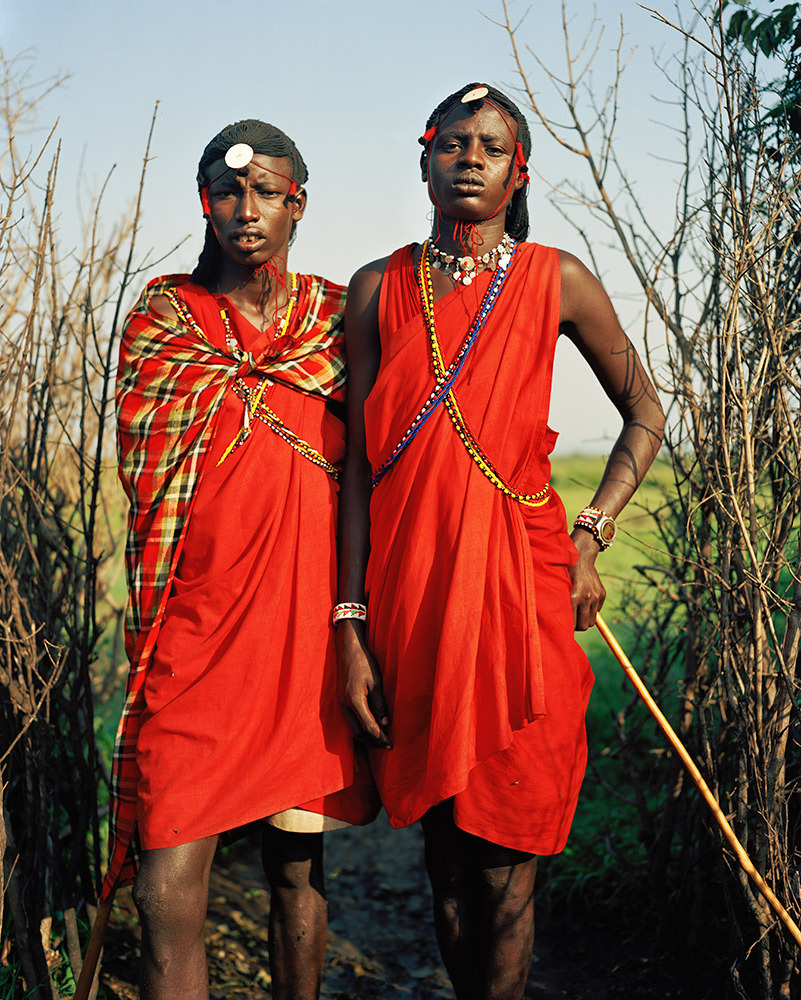
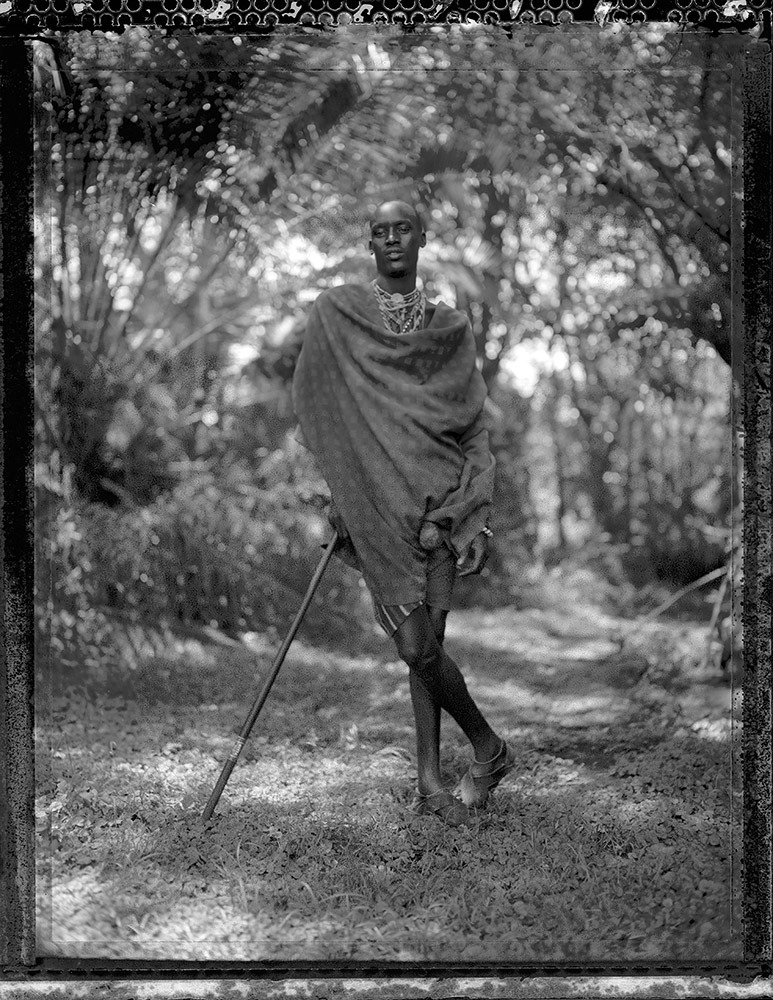
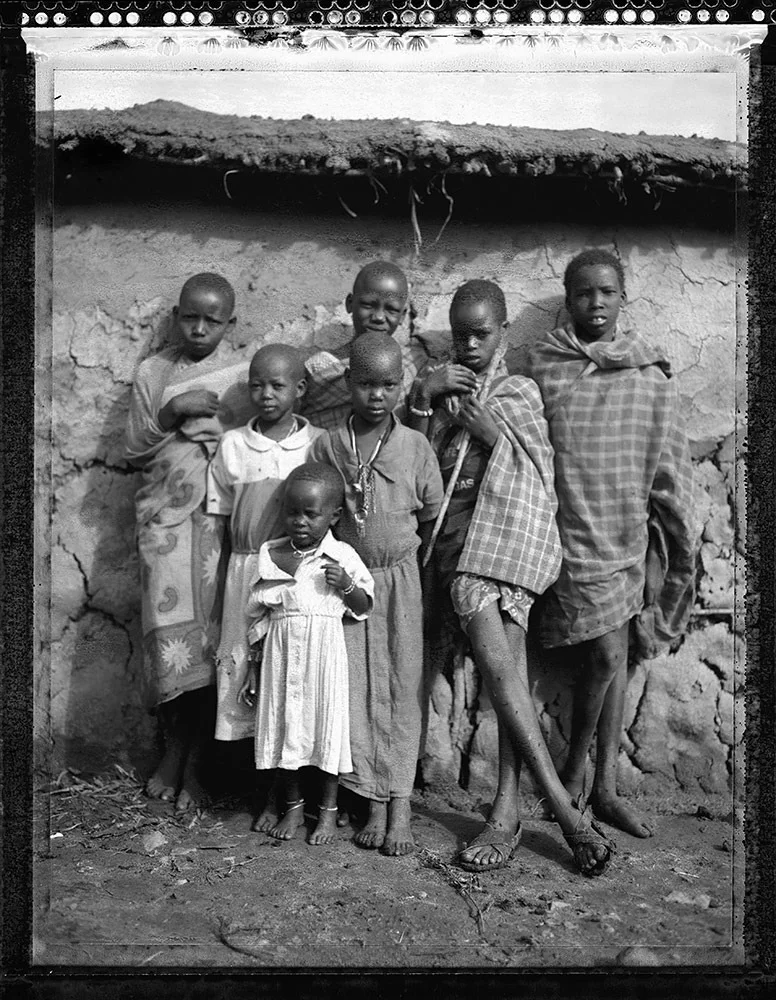


















Photo Essay: The Maasai Spirit
This series of images was taken while on assignment in the Maasai Mara Game Reserve in Kenya. As we were leaving the reserve one day our driver suggested we stop at a nearby Maasai village. I thought it would be just a quick stop and a chance to pickup some handmade souvenirs.
Knowing that the Maasai depend on tourists to supplement their subsistence farming, I didn't expect the warmth of our welcome and the genuine dialogue I would have with the chief. He introduced us to the village, showing every aspect of their daily life. Speaking passionately about the realities confronting the Maasai people and the hard choices they must make in order to preserve their cultural identity - from environmental issues threatening their homes and grazing lands, exposure to tourists and the lure of modern life.
He was an erudite speaker, having mastered English and more than 6 African languages. This worldliness empowered him to make mindful decisions governing the collective future of his tribe. All the while recognizing the hypocrisies of a first world existence. In his village no one went hungry, loneliness and depression did not exist and the elders were a revered and integral part of the social dynamic.
He encouraged me to take photos, wanting to share their simple but dignified life, beautiful aesthetic and overt happiness. I hope these images honor the chief's wishes and convey some of the Maasai spirit.
PHOTO + TEXT: JULIEN CAPMEIL
Julien Capmeil is an Australian born photographer living in New York. His work has appeared in many publications worldwide including Vogue, GQ and Conde Nast Traveler.
You can view more of his work online at: www.juliencapmeil.com
For print purchases Email: info@juliencapmeil.com
PHOTO ESSAY CURATED BY NELIDA MORTENSEN
An Ethiopian’s Path to From Refugee Camp to College Campus
How a refugee survived genocide and rebuilt a life in the United States.
Omot retelling his journey coming to the U.S. during our interview. Image courtesy of Ojullu Omit.
This semester, I had the privilege of connecting with Ojullu Omot, whose life was forever altered by tragedy. On December 13, 2003, when he was just 14 years old, Omot experienced a massacre at his hometown in south-west Ethiopia. As part of a Wake Forest University project to raise awareness about the challenges faced by refugees, a team made up of me and my classmates produced a 10-minute advocacy film that aims to shed light on the often-overlooked struggles refugees encounter while adapting to life in the United States. Omot’s story is a testament to the blend of heartbreak and perseverance that characterizes the ongoing global refugee crisis, capturing the resilience and fortitude of those seeking haven away from home.
Omot’s story began with displacement, as he fled the 2003 massacre in the remote Gambella region of southwestern Ethiopia. From December 13-15, in a reprisal against a small ambush against Ethiopian federal government officials, ethnically Amhara, Oromo, and Tigrayan soldiers and rioters murdered hundreds of minority Anuak civilians. Human Rights Watch’s report suggests that these atrocities should be considered crimes against humanity. . The Ethiopian government claimed that only 57 were killed and that the violence resulted from ethnic tensions between rival Anuak and Nuer groups, in contrast to the claims of international human rights groups and the Anuak themselves. Human rights NGOs have called for a thorough investigation into the incident, with concerns that others like it could occur. Despite facing deadly tragedy along with the immense challenges of settling into a new society as a refugee, Omot has found a new home in the United States, where he serves as a living witness to the egregious human rights abuses of his homeland. He remains committed to starting a new chapter in life.
By now Omot has gotten used to retelling the story of how he left his home in Ethiopia in the midst of genocidal violence, and his journey from there to become an international politics student in the United States. The three-day-long massacre in Gambella town of southwestern Ethiopia was an outburst of ethnic conflict between the indigenous Anuak group and members of the Ethiopian military. As the situation in Ethiopia deteriorated, Omot moved to Sudan when he was a teenager, with the hope that things would get better in a year or two.
But they didn’t. The military confrontation neither started, nor ended with the massacre. More than 10,000 Anuak people were forced to leave Ethiopia in 2004, the year after the massacre took place.
Omot left Sudan for Kenya after two years of waiting. The unrest had separated him from his family, and he lacked many colorful memories about his childhood in Ethiopia, Sudan and Kenya. What he remembered is playing football with his friends in refugee camps everyday; many of those eventually being sent to Canada, Australia and other developed nations. Omot remembers planes from the United Nation hovered above their heads in refugee camps, dropping food and supplies and people hurrying to grab them. “We were dependent on the refugee program,” Omot said, “Resettlement in the United States was not a typical solution for refugees living in the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees(UNHCR) camp.”
Omot never dreamed about coming to the United States then. He was invested in the idea that everything will go back to normal in Ethiopia, and that he could then return home. Yet Omot’s life took a major turn in the year 2016. He was called for an interview, which he later found out was part of the application process by U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services employees concerning whether he is eligible for resettlement in the United States as a refugee. The approval rate for a refugee status in the United States is 27%, according to World Data.
Omot waited for roughly six months until he was called for a series of security checks, examinations and orientation. In February 2016, International Organization for Migration contacted Omot, telling him that his case is ready. He then boarded a plane to the United States on April 4th, 2016, his first ever flight. When he landed in Miami, Florida, it was like landing on a new planet- the shock of the novel language and lifestyle almost dazzled the then 28 year old.
“There was something change, [such as] the day became longer, I was not even comfortable, and I cannot see where I come from, ” Omot recalled his initial exposure to the United States, “The first question I asked myself [was], is this the U.S. [as] I expected it?”
And the first few months continued to affirm to him that starting anew wasn’t easy. Omot often found himself alone in his house assigned by the government, since his roommates busied themselves working in the daytime, and went straight to sleep not long after walking in the door at night. Comparing the situation to the community life in Ethiopia, where everyone would sit down and share stories after a day’s work, filled Omot with homesickness at night.
Language is also a major challenge to Omot. Going to a university was at the top of his wish list when he came to the United States, but he couldn’t even understand people’s accents when he asked for directions on his way to school. He had no idea how to open emails during his first semester at a community college. When one of his classmates finally taught him how to view the inbox, he found emails from professors flooded in there. In winter, the temperature dropped so low that Omot, who used to live near the equator, had to drop his English as Second language (ESL) classes to avoid traveling in freezing weather.
But Omot is determined to realize his dream. Instead of “wasting time” in ESL classes, he decided to push himself, taking the General Educational Development (GED) tests directly. He works as a hospital janitor in the daytime for living; in the evening and before dawn, he dives into his study. Whenever he had free time, Omot would peruse his textbooks, went up to the library of the community college he attended everyday, asking every librarian what GED looks like, and tips and tricks to score higher.
The global refugee population has reached crisis proportions, with more than 30 million refugees displaced in 2022, signaling a significant surge from the previous year's level. The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) has reported a staggering total of 103 million people forcibly displaced as of mid-2022. In response, President Joe Biden has committed to revamping America’s current “inhumane” immigration policy. However, the administration's effort to admit refugees has fallen significantly short of its goal, with only 25,465 individuals granted admission by the end of the previous fiscal year on September 30, 2022, a mere 20% of the objective. The number of refugees received by the United States still remains one of the lowest among all nations, and the number continues to decrease.
Refugees face a plethora of challenges when they resettle in a foreign country, with attaining secure housing among the most pressing. Asylum seekers in particular struggle to obtain temporary housing due to a lack of government support and unfamiliarity with the US housing system. Non-profit organizations and shelters provide vital assistance to these individuals. Despite this aid, refugee and asylum seekers are disproportionately at risk for health problems, both physical and mental. They are more susceptible to severe mental health conditions like PTSD and depression, while chronic illnesses like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease exacerbate their already challenging circumstances.
In 2017, Omot took the GED for the first time. And hard work pays off — he passed the test.
“It [passing the test] gives me hope that I could continue to do all of them,” said Omot, breaking into a smile. And he did. After he finished with GED, Omot is currently pursuing a bachelor degree in international politics at University of North Carolina Greensboro. When asked why he could recall his story in astonishingly clear detail, Omot answered, “I think my story is important because if other people, other refugees heard about it, they would think, oh, this guy did that and starting his new life. Maybe I could do the same.”
To Get Involved:
While Omot is navigating through his new life in the United States, it is not without support from various refugee organizations, such as Every Campus a Refugee (ECAR), an organization aiming to mobilize colleges and universities to host refugees on campus grounds and support them in their resettlement. ECAR provided nearly 4 years free housing and accessories to Omot, and provides several other services to refugees in the North Carolina region. Learn more about ECAR here.
Hope Zhu
Hope is a Chinese international student at Wake Forest University in North Carolina studying sociology, statistics, and journalism. She dreams of traveling around the globe as a freelance reporter while touching on a wide range of social issues from education inequality to cultural diversity. Passionate about environmental issues and learning about other cultures, she is eager to explore the globe. In her free time, she enjoys cooking Asian cuisine, reading, and theater.
Africa’s History Before Colonialism
Africa saw the rise and fall of diverse societies, cultures, and civilizations that thrived long before colonization.
A’it benhaddou. Toa Heftiba. Unsplash
Africa as a continent is of great diversity and complexity, with a rich history that spans millennia. It has seen ancient civilizations advance agriculture, science, technology, and political systems, all of it predating the European colonial era. However, the impact of colonialism on the continent cannot be ignored. Colonialism has distorted the development and history of Africa as we know it today. From the arbitrary borders drawn by European powers to political instability in certain regions, Africa has had to navigate numerous challenges. Despite this, Africa’s story is one not of despair but of resilience and hope. Nor does it begin with these themes; it has always been a vibrant and dynamic continent.
As we explore Africa’s past, it is essential to remember that no single narrative can capture an entire continent’s complexity. Instead, we must approach each story with an open mind, ready to learn from the diverse perspectives and experiences that make Africa the remarkable place it is today.
It is a continent home to many different cultures, beliefs, traditions, kingdoms, empires, and visionaries. It is rich with mineral red soil and oceans as blue as sapphires. It is a continent where the rhythmic beats from djembe drums reverberate across the nation for all ears to hear. It is a continent with traditions ancient and beloved by many. It is a peaceful continent that many people call home. The story of pre-colonial Africa has been kept hidden, but it deserves to be uncovered for all its glory.
Empires, tribes, notables
Let’s start with the fact that “Africa” isn’t a native name for the continent , but a name the Romans gave to the provinces they conquered from Carthage. It is unclear what indigenous Africans called their continent before this European appellation, but so vast a land mass may have defied conceptualization to the ancients. The Roman term initially applied to only a portion of what we would now call North Africa. Today, some refer to the continent as a “garden of Eden” and the “cradle of humankind,” as it is the origin of our species, homo sapiens.
As we know, there is power to a name; it solidifies identity. Now that we know more about where the name Africa comes from, let’s explore more about its people and their cultures.
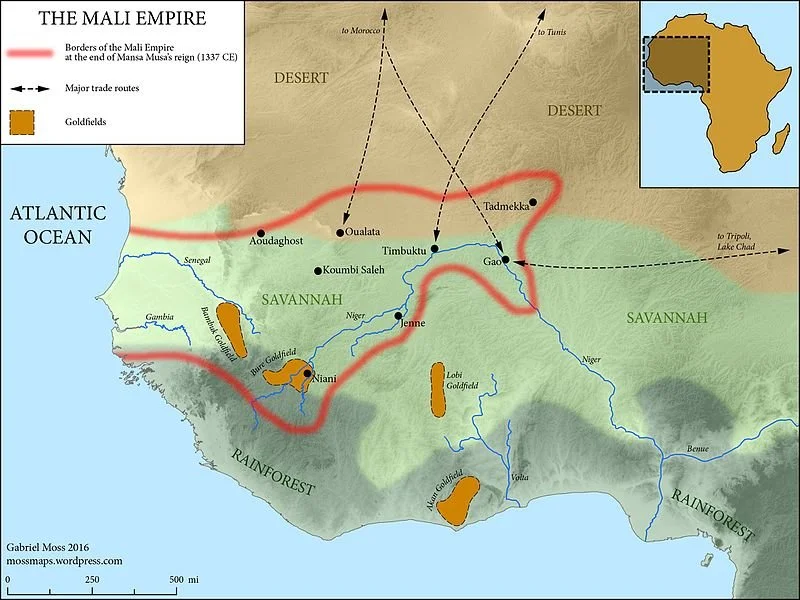
Malian Empire (Mansa musa)
A map of the Malian Empire during its reign. Gabriel Moss. CC BY-SA 4.0
The Malian empire (13th-16th century) was an empire that spanned a multitude of present-day West African countries, in particular its present-day namesake, the Republic of Mali. During the reign of its emperors, this kingdom was widely known as a trading empire, driving the international trade in gold and salt. A notable figure who helped Mali become one of the wealthiest empires at the time was a king named Mansa Musa. He was known to be one of the richest men on earth, and during his pilgrimage to Mecca, he took tons of gold with him and shared his wealth with the people there. Under his leadership, the Malian empire excelled in education, navigation, and more.
Education
Sankore mosque, one of the largest universities in the world. upyernoz. CC by 2.0
Under Mansa Musa’s reign, his Empire built many of the most reputable philosophical schools of the age. The most well-known one is the University of Sankoré. This particular university had one of the largest libraries since the library of Alexandria – it could house 200,000 students and preserved a collection of 400,000-700,000 manuscripts. Many astronomers, mathematicians, and philosophers called this institution home.
Additionally, the Malian empire is home to the famous educational and trading city of Timbuktu. Mansa Musa, having built and cultivated this city, opened the doors for trading across north and west Africa. As more Muslim Tuareg (northern African nomads) traders made their way to the city, spreading Islam, Timbuktu became an epicenter for Maktab’s (Muslim schools).
Amazigh Indigenous
The Amazigh are Indigenous people from all over northern Africa. Often these people are called ‘Berber,’ which is a harmful exonym, as literally derived from the same root as ‘barbaric.’ They have been fighting for cultural recognition and acceptance since the Arab conquests in North Africa, eroding their existence.
Traditions
The Amazigh have a deep and profound love for the earth and for their natural lands, and they believe their mountains (Aakal) protected them from Arab invasions. They even have annual festivals celebrating the land’s fertility called Bou-Irmawen.
Another tradition they have is tattooing, which came about as an act of rebellion against Arab rulers, who banned the practice. Amazigh men tattooed Amazigh symbols and tribal affiliations onto the backs of their hands.
Lastly, Amazigh families are by tradition matriarchal. This system, coming long before colonialism and lasting many years, speaks volumes. In Amazigh families, the mother is considered the head of the family.
The Amhara people of the Abyssinian empire (Ethiopia)
Collage photo of what the Amhara people looked like. Middayexpress. CC BY-SA 3.0
One interesting thing about Ethiopia is that it was never officially colonized, only briefly occupied by Fascist Italy during WWII, meaning the nation/empire retains much of its traditions and culture. The Amhara people are among the oldest indigenous groups in the Abyssinian empire. As one of the country’s largest ethnic groups, the Amhara have given their language of Amharic to be Ethiopia’s official language. A proud and ancient people, the Amhara have many fantastic fables, stories, and myths that help define their way of life and culture.
Myths and Culture
Starting with an interesting fact, the Amhara people believe that they share ancestry with Shem, eldest son of biblical Noah, and can even trace it all the way back to King Solomon and Queen Sheba. Ethiopia is one of the oldest epicenters of Christianity in Africa (and, indeed, the world).
While the Amhara have a strong connection to religion, they also have a tie to their spirituality. They have a myth about a being called Buda, which is believed to use evil eyes and possess humans, making them partake in malicious activities. To protect yourself against these spirits, wearing a blue glass eye is believed to ward off the evil spirits and protect you.
Bunyoro-Kitara Kingdom- Eastern Uganda
A photo of what the ancient kingdom’s capital looked like. Harry johnston. CC BY-SA 4.0
Bunyoro was a kingdom in East Africa whose kings reigned from the 16th to the 19th centuries. The kingdom was infamous for its fortified military unit and its trade of fish and salt. Its economy relied heavily on agriculture and succeeded due to a surplus of fertile soils.
Reproductive health
Not only were these people excellent in agriculture, but they were excellent midwives and performed one of the first successful c-sections. They are noted to be the origin or birthplace of the c-section, as many western researchers would come here to see how they had achieved this feat. To perform these c-sections, the midwives would use banana wine as an anesthetic, fire to sterilize their tools and for cauterization, and salves and stitches for healing. These c-sections would rarely result in complications and most were successful.
Fulbe Nomad tribe–Wodaabe in Chad
The Wodaabe men dressed in their Gerewol attire and makeup. Dan Lundberg. CC By-NC-S.A 2.0
The Fulbe people, also called the Fulani, are a widely dispersed and often nomadic ethnic group across Africa. It is under debate where they originate from, and, due to their lifestyle, they are very diverse people. The Fulbe people are known to be merchants and herders. An interesting fact about them is that they were among the first people to adopt Islam after the conquests.
Gender Roles
The Wodaabe people in Chad, an extension of the Fulani, are one of the remaining groups that have stuck to their traditional religion instead of converting to Islam. They subscribe to the belief of Animism– the idea that every living thing (including trees) has a soul. Something unique about these people is that they have an annual Gerewol festival, which showcases a male beauty pageant to find a wife. In this society, despite general patriarchy, women get to choose their partners. The festival unfolds with the Wodaabe men painted in yellow with makeup wearing elaborate jewelry and sweet perfume dancing the night away.
Africa is a continent that so many call home, and for its true history to be unearthed authentically speaks volumes. Africa was often portrayed as backward or barbaric during the colonial era, and because of this, diverse and advanced ancient cultures were erased in the process. This is only a glimpse of what pre-colonial Africa was like, and there are so many more cultures that deserve recognition.
Kadija Diallo
Kadija is a student at Georgia State in Atlanta, Ga. She is a creative spirit who loves traveling and seeing new places. She also enjoys using her love for writing/storytelling to make an impact on the world. One day she hopes to make new connections and share stories as she travels to every continent.
Uncovering the Diversity of African Music
If you are a music buff looking to expand your horizon, check out these 5 African music genres.
African drums. Lee Pigott. Unsplash.
People all across the African diaspora share a love for music, which connects everyone to the same frequency. Many are familiar with Afrobeats, a style of music from Nigeria, but there are many different and diverse genres to explore the sounds of, from the likes of Amapiano to Chimurenga.
Amapiano
Two people singing Amapiano together.. The Charles Gallery. Unsplash
Amapiano is a genre of music originating from South Africa characterized by a mixture of jazz, house and Gospel music. Amapiano is composed heavily of synthesizers, percussion, soulful vocals, and repetitive melodies. This genre of music is relatively new, coming into being in the early 2010’s. Amapiano is a Zulu word meaning “the pianos.” Amapiano is a form of music South Africans believe can bridge people together, and a musical escape for the younger generations.
Listen to a Youtube playlist of Amapiano music
Juju
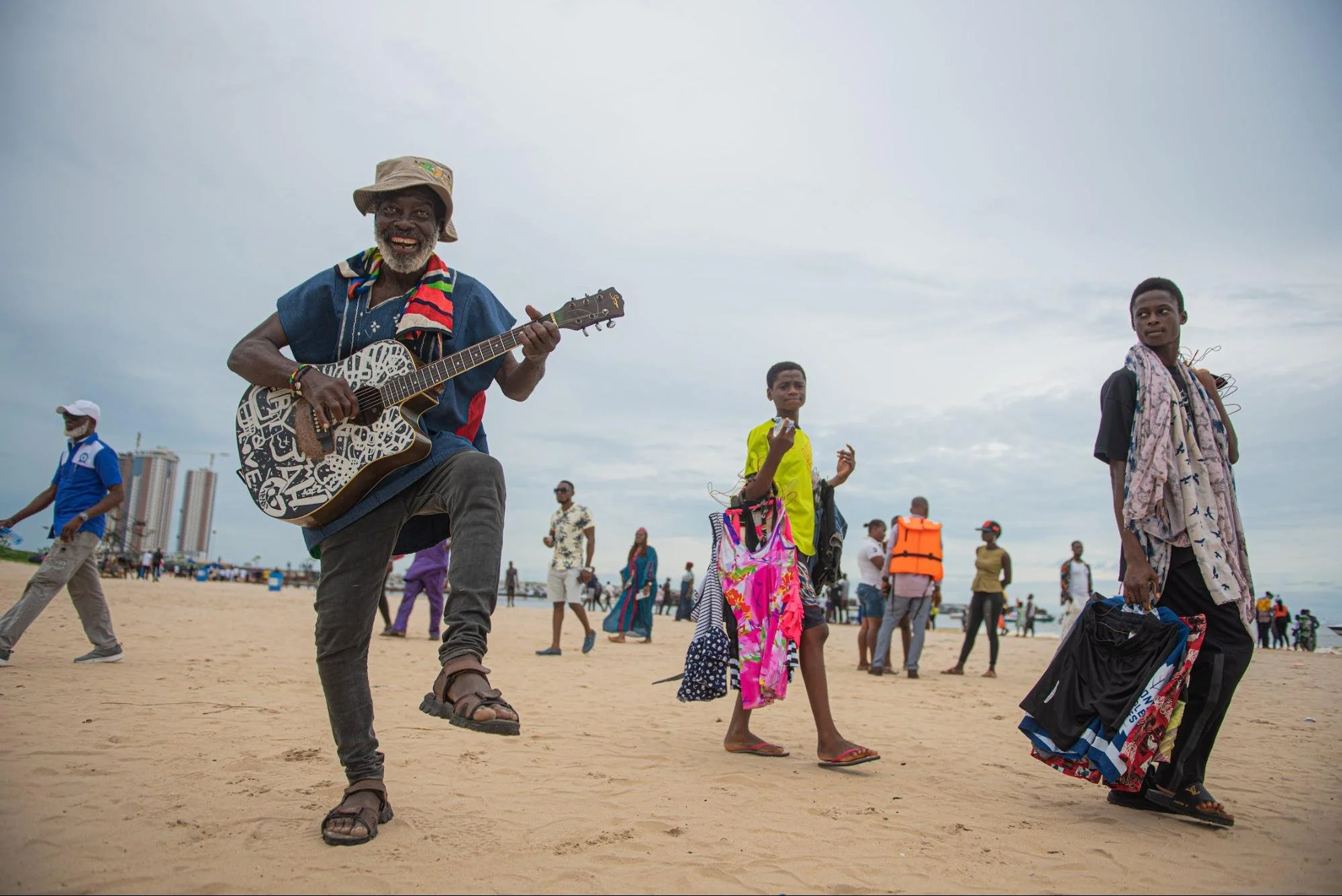
Man playing music on the beach. Seun Adeniyi-CCO.
Juju is a genre of music that originates from Nigeria, specifically its Yoruba region. It’s a musical style that is composed of praise-singing accompanied by a guitar or banjo and a gourd shaker. This genre of music was traditionally played in taverns or during festivals as dance music, but became modernized and generally popular by the 1980’s. As it grew in popularity, it led to the birth of many other genres of music like Highlife or Afrobeats, as we know of them today.
Listen to a Youtube playlist of Juju music
Coupe decale
A group dances to Coupe Decale. Tommy. CC 2.0
Coupe Decale is a genre of music created by Cote D'ivoirians living in France in the early 2000’s. It’s a musical style composed of ‘computerized circular beats’ mixed with Ivorian rhythms . The lyrics themselves are inspired by the West African griot tradition of story-telling, and the genre’s primary message focuses on providing a space for many people to dress nice, go clubbing, and forget their problems during a time of economic and political crisis.
Listen to a Youtube playlist of Coupe Decale music
Gnawa–saharan Folk music
Man playing Moroccan bass lute. Marrakech Riad-CCO.
Gnawa is a folk genre that originates from Morocco. It’s a musical style that has its roots in ancient African tradition, as it’s the result of formerly enslaved black Africans integrating into Moroccan life. It serves as a preservation of the folkloric music of their ancestors, as well as a means to heal from collective trauma. Interestingly it is also said to have healing properties for those that are possessed by ‘genie spirits.’ Its musical style is composed of African percussion, metallic castanets, and bass lutes.’ Gnawa at its core is a combination of poetry, music and dancing. This genre shares many similarities with its American counterparts Jazz and the Blues, as all three share the same purpose. The genre’ songs consist of references to the singer’s origins and history regarding enslavement.
Listen to a Youtube playlist of Coupe Decale music
Chimurenga
Thomas Mapfumo, the creator of Chimurenga music performs. Cultrvultr-CC BY NC-SA 2.0
Chimurenga is a genre of music that was developed in Zimbabwe. It was used to protest colonial rule in the 70s, and more generally is used to discuss and inform on societal issues and movements important to the singer. Because of this, it is recognized as ‘music for the people’s struggle’. This musical genre can be accredited to the Shona musician Thomas Mapfumo. He was inspired by the rock bands he heard playing growing up and his Shona background to create a political movement through music.
Listen to a Youtube playlist of Chimurenga music
Kadija Diallo
Kadija is a student at Georgia State in Atlanta, Ga. She is a creative spirit who loves traveling and seeing new places. She also enjoys using her love for writing/storytelling to make an impact on the world. One day she hopes to make new connections and share stories as she travels to every continent.
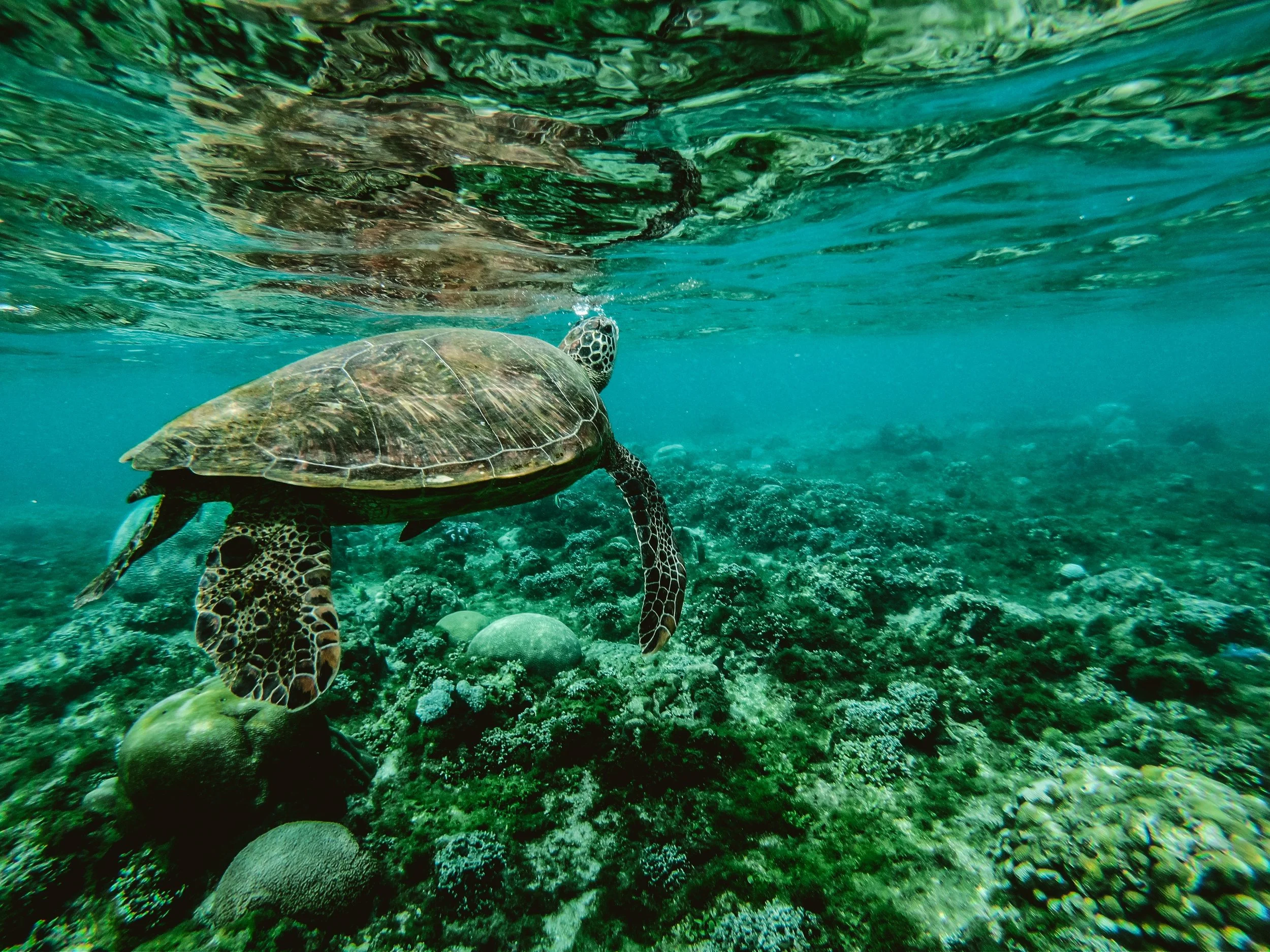
How Ancient Ghanaian Culture Shapes Sea Turtle Conservation
Ghana’s ancient admiration for sea turtles has inspired a modern conservation movement to protect these ecologically vital animals.
Sea turtle swimming in the ocean. Belle Co. CC0.
Ghana is a vibrant country located in West Africa, bordered by Côte D’Ivoire, Burkina Faso and Togo. It is known for its rich culture, stunning beaches, and diverse wildlife. As a traveler, you would likely find Ghana to be a lively country, full of colorful markets, bustling streets, and a unique mix of traditional and modern cultures. Perhaps most importantly, Ghana is known for the warmth and hospitality of its people, where you’ll be met with a welcoming and friendly nature.
Ghanaian people are also very spiritually attuned, whether it’s native African spirituality or more newly introduced Christianity. They are very fond of their cultural and religious traditions, one of which is long-standing is their long standing connection to sea turtles.
Sea turtles have been a part of Ghana’s culture and folklore for centuries, with oral literature depicting these animals as protectors, helpers or even guides. Moreover, the reptiles are integral to Ghana’s ecology, as they help to maintain coral reefs and seagrass, which in turn ensure continued biodiversity.
It wasn’t always this way, as with Urbanization came poverty, and with poverty came poachers. These poachers saw the Sea turtles not as protectors but as a source of profit. Now, having returned to their traditions, Ghanaians are more determined than ever to protect and conserve these animals in hopes to prevent their extinction.
All over Ghana, there are different recorded myths and stories that show the ancient connection between Ghana and sea turtles.
The Ga and Akan ethnic groups of central Ghana have a story about their ancestors and how they once were caught in a storm while fishing, in which their boat had sunk. It is said that as the men were struggling in the choppy waters, the sea turtles arrived and helped them get back to shore.
The Dange people of eastern Ghana have a story in which their ancestors were trying to retreat after Ashanti armies had them cornered against the Volta River. They recount how both the crocodiles and the sea turtles helped them safely cross the river, by having the crocodiles form a bridge, while sea turtles helped heal the injured and guided the elderly across. It is said that to this day, both animals are fully protected in this region of Ghana.
Sea turtles in Ghana have been protected by law since 1971. Even then, there are still poachers, so just that isn’t enough. The Ghana Turtle Research Project (GTRP) has been around for more than 10 years. The organization encourages community members to participate in sea turtle conservation and to embrace their culture and traditions. By doing so they were able to get more than fifty community members to form a volunteer network. They also helped to tag and identify where turtle species reside most often in order to make sure that fishermen avoid those areas and to ensure they are safe-guarded.
Additionally, the Environmental Justice Foundation (EJF) is an organization that was focused on protecting nesting sites in the fishing communities of central Ghana. In 2019, during the first turtle nesting season (of that year), they were successfully able to deter poachers from the Goma Fetteh region.
As more and more Ghanaian communities return to their traditional and spiritual beliefs, more people are caring about the sea turtles. It’s due to the oral traditions in Ghanaian culture that these conservation efforts were possible, as they make people care more about these creatures of the sea. They helped form an everlasting connection between the sea turtle and man.
Kadija Diallo
Kadija is a student at Georgia State in Atlanta, Ga. She is a creative spirit who loves traveling and seeing new places. She also enjoys using her love for writing/storytelling to make an impact on the world. One day she hopes to make new connections and share stories as she travels to every continent.
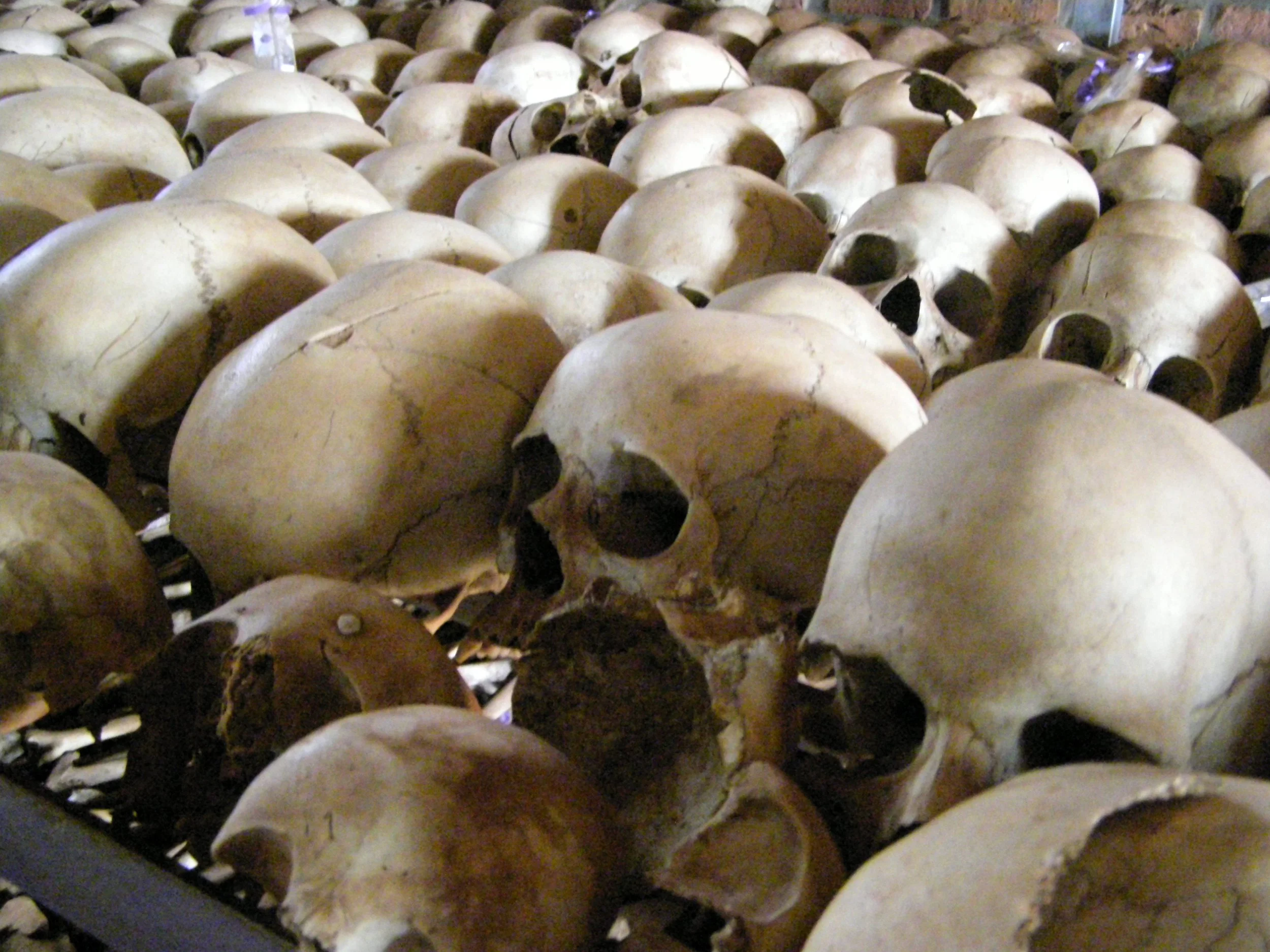
A Brighter Future Emerges 29 Years After Rwanda's Genocide
Rwanda's unwavering determination and spirit shine as a source of optimism for the rest of the world.
Rwanda Genocide Memorial. config manager.CC BY 2.0.
This week marks the 29th anniversary of the Rwandan Genocide, a 100-day period of violence in 1994 in which more than 800,000 people were killed. The repercussions of this tragedy continue to linger, leaving survivors and their family members with deep emotional traumas. Almost 30 years have passed since the devastating genocide in Rwanda, and the country has made some commendable progress in rebuilding its economy and mending its relationships with other nations, while also acknowledging its past mistakes and the sacrifices made during the massacre. The scars of the past may still be visible, but they no longer define Rwanda. Its developments shed light on the country’s journey toward healing and growth, with infrastructure, technology, and education driving its transformation.
The genesis of the Rwanda Genocide three decades ago can be attributed to years of systemic oppression that eventually culminated in one of the most devastating conflicts in modern history. Surprisingly, the two primary ethnic groups involved in this conflict, the Hutus and Tutsis, shared no religious or linguistic differences at the outset. A deep dive into their origins reveals that the Hutus migrated to the Great Lakes region of Central Africa between 500 and 1000 BC, while the Tutsis arrived four centuries later, migrating from the highlands of Ethiopia. The Hutus primarily worked as land cultivators, while the Tutsis were cattle herders, thus creating an economic divide that eventually led to a hierarchical system. In a strange colonial mythology, Tutsi cattle herders were labeled Hamites — a separate and exceptional group — who hailed from an ancient Christian tribe supposedly linked to people of old Palestine. This system placed the Tutsis, as a minority ethnic group, in a position of disproportionate power over the majority Hutus.
Colonial powers subscribed to this concept of racial hierarchy and origin stories, believing the Tutsi to be natural leaders and granting them preferential treatment. After taking Rwanda as a colonial possession in 1897, the German Empire built a power structure that firmly established a hierarchy that favored the Tutsis. They bestowed upon the Tutsis a superior status, owing to their taller stature and lighter skin, giving them greater influence over the Hutus. However, in the aftermath of Germany’s defeat in World War I, Belgium took over the reins of Rwanda’s governance, and, rather than attempting to bridge the cultural divide, exacerbated it. The Belgian administration continued to uphold the Tutsis’ superior status while disregarding the Hutus, creating a further chasm of inequality that only grew wider with time. The introduction of identification cards during the 1930s that explicitly listed one’s ethnicity, for example, further polarized the population, and the stage was set for the tragic events that culminated in the Rwanda Genocide.
In 1973, Rwanda witnessed an event that would forever alter the course of its history. General Juvenal Habyarimana, a Hutu tribe member, rose to power and established the National Revolutionary Movement for Development (NRMD) party to secure his authority. Meanwhile, in Uganda, a group of Rwandan exiles in Uganda who had tasted victory in Yoweri Museveni’s National Resistance Army during the Ugandan Civil War formed the Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF). This organization was largely dominated by Tutsi figures and posed a challenge to the incumbent regime. The Rwandan Civil War began, which pitted the Hutu-dominated NRMD government against the primarily Tutsi RPF, while social tensions began to simmer. It was midsummer in 1993 when Hutu extremists hatched their plan, creating a platform for propagating their racist ideology and spewing hatred against the Tutsi people. Thus, Radio Télévision Libre des Mille Collines (RTLM) came into being, which soon became a tool to incite violence and hatred against the Tutsi, using propaganda and malicious rhetoric.
Radio Télévision Libre des Mille Collines broadcasted from this office during the Rwanda Genocide. kigaliwire.CC BY-NC 2.0.
April 6, 1994, was the beginning of a nightmare for Rwanda and Burundi. The presidential plane, which was carrying the heads of state of both countries, was hit by gunfire. The news of their deaths, broadcasted by the radical Hutu RTLM radio station, served as a call to arms, sparking a wave of violence against the Tutsi population. The initial attack was planned by a group of military leaders, politicians, and business owners, who were later joined by an increasing number of supporters. This resulted in a devastating genocide, with Tutsis flocking to ostensibly safe havens like churches and administrative centers only to find them transformed into places of horror. 75% of the Tutsi population was wiped out, including many children who were labeled “little rats” and killed alongside adults. The perpetrators killed people of all ages indiscriminately, committing rape and torture on a regular basis. With nowhere to call home, over 2 million people fled the country, including many Hutu ethnic group members, while a million more were internally displaced, leaving 75,000 children orphaned.
The aftermath was massive destruction, with infrastructure reduced to ruins and hundreds of thousands of citizens dead, dealt a crippling blow to progress and development. Rwanda, however, refused to give in to despair. The RPF won the Civil War and took power after four months of horror, ending the genocide. The nation embarked on a journey of healing and reconciliation by embracing a deliberate strategy of transitional justice and transformative programs, characterized by the visionary “Rwanda Vision 2020” campaign launched in 2000. Rwanda embraced a path of renewal through initiatives such as “I am Rwandan,” which encouraged deep reflection on the nation's painful history, acknowledgment of past atrocities, and promotion of healing and reconciliation among all its people. Another example is “Umuganda,” a day of community service in which people from all walks of life work together to improve their communities. Though challenges remained, these initiatives instilled a renewed sense of vigor and solidarity, bringing new life to the difficult task of rebuilding Rwanda.
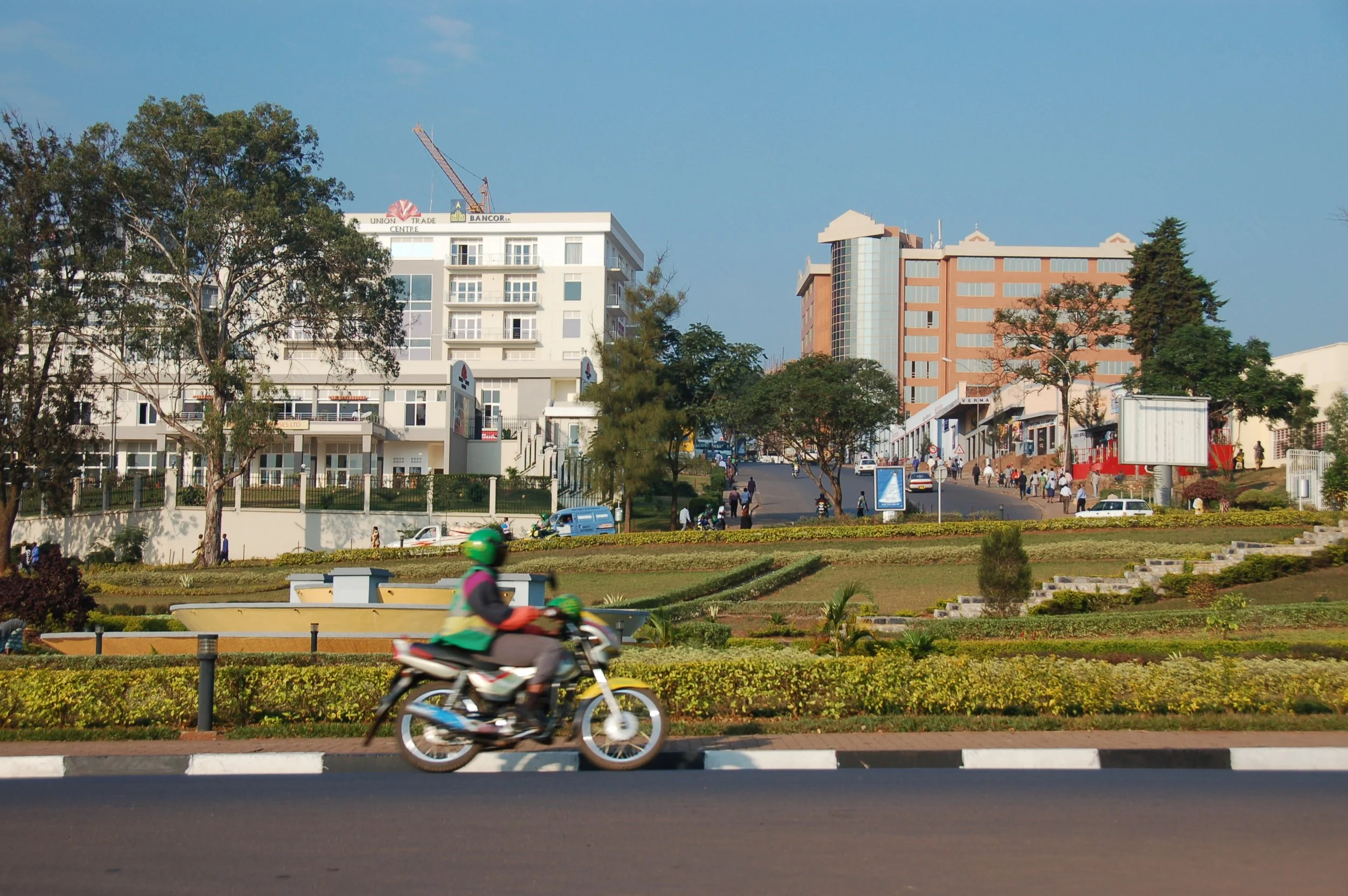
The modern capital of Kigali is safe, clean, and orderly. Dylan Walters. CC BY 2.0.
Rwanda also undergoes significant changes in its economy. The government has introduced the “Girinka” program, which provides one cow per poor family to combat poverty, with the first female calf being passed on to another family. Poverty has decreased by 23.8 percent from 2000 to 2010, and Rwanda has emerged as one of the fastest-growing economies in Central Africa, with four years of eight percent GDP growth between 2011 and 2014. These developments are positive indicators for Rwanda’s future.
Despite the indelible mark of shame left by the horrific acts, Rwanda has sought reconciliation by embracing its rich heritage of traditional pre-colonial Rwandese customs and values, while also welcoming contributions from the international community. The genocide has prompted profound reflections on critical issues such as the efficacy of peace operations, the urgency of ending international crimes, and the delicate nature of maintaining civility. These pressing issues necessitate international attention and are still relevant today.
TO GET INVOLVED:
World Help: Over the last decade, World Help has worked to bring healing and restoration to Rwandan communities through initiatives like trauma counseling, children’s homes, child sponsorship, construction projects, clean-water wells, sustainable agriculture, vocational training, and more. To learn more and get involved, click here.
IBUKA: IBUKA is an umbrella organization supporting survivors in Rwanda. Representatives from institutions like IBUKA and the National Commission for the Fight Against Genocide are invited to speak at commemorations to provide expert histories and testimonies. To learn more and get involved, click here.
Hope Zhu
Hope is a Chinese international student at Wake Forest University in North Carolina studying sociology, statistics, and journalism. She dreams of traveling around the globe as a freelance reporter while touching on a wide range of social issues from education inequality to cultural diversity. Passionate about environmental issues and learning about other cultures, she is eager to explore the globe. In her free time, she enjoys cooking Asian cuisine, reading, and theater.
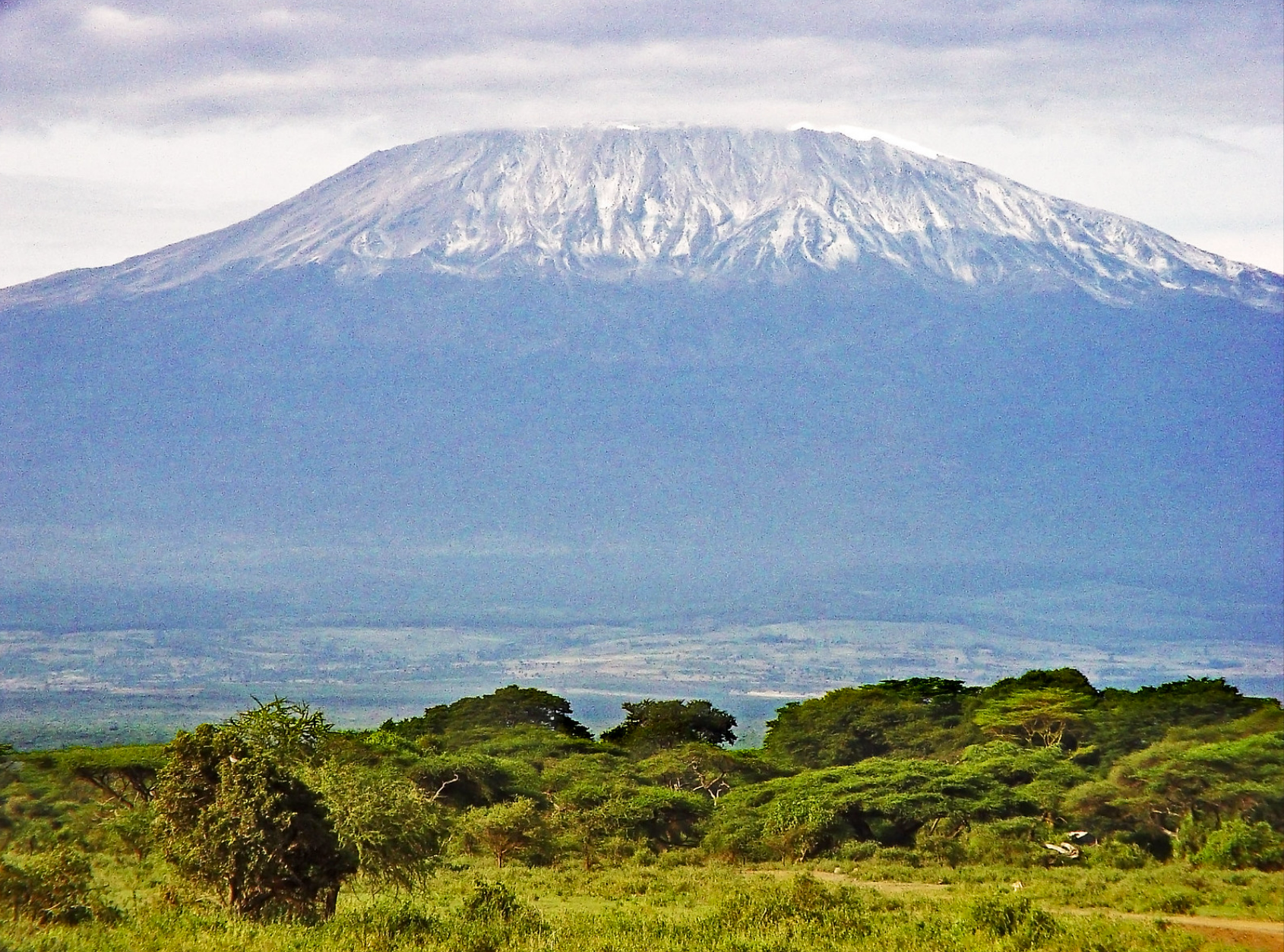
The Disappearing Snows of Mt. Kilimanjaro
As the mountain's snow melts, its ecosystem faces escalating pressures from tourism, climate change, and deforestation.
Mt Kilimanjaro. Tambako the Jagua. CC BY-ND 2.0.
If you have perused Ernest Hemingway’s “The Snows of Kilimanjaro,” you'd be moved by the writer's introspection and memories, and no doubt recall its breathtaking descriptions of Mount Kilimanjaro’s wintery peaks. Nestled in Southeastern Africa, where temperatures often soar to scorching heights, a mountain graced with a frozen crest appears as a natural wonder. Nevertheless, before many have had the opportunity to appreciate its miraculous summit, the pristine snow has begun to melt at an alarming speed.
Rising above the plains of Africa, Kilimanjaro is a dormant volcano and the highest free-standing mountain in the world. Its snow-capped peak is created through a combination of freezing temperatures and precipitation at high altitudes, where the mercury can drop to a frigid 15.98 F, calculated according to the linear relationship between altitude and temperature. Long-term averages indicate that, in the middle of February, snowfall occurs three days per week on Mount Kilimanjaro.
The captivating ice-capped peak of Mount Kilimanjaro renders it a highly coveted destination for tourists visiting Tanzania, with many foreigners and locals flocking to the site each year. As far back as the 1860s, Europeans had launched their quest to summit Kilimanjaro. In 2006, Kilimanjaro National Park Authorities (KINAPA) registered 40,701 climbers on the mountain, with the Machame trail reigning supreme, welcoming 15,879 adventurers. Today, numerous guiding companies, including the African Zoom and Abercrombie & Kent, offer luxury expeditions and comprehensive travel guides for those seeking to conquer the “roof of Africa.”
While Hemingway’s story may have brought Kilimanjaro to the attention of the world, the mountain has long been revered by locals who have given it names like “Mountain of Greatness” in Swahili and “That which defeats the caravan” in Chagga. The Maasai, who have a deep appreciation for Kilimanjaro, affectionately refer to it as the “Mountain of Water” due to its crucial function as the primary source of water for the surrounding area.
Regrettably, as mentioned above, generations to come might be deprived of the privilege of admiring the captivating natural beauty of Mount Kilimanjaro. Several complicated factors contribute to the rapid disappearance of its ice cap. Scientists have established a link between global climate change and variations in greenhouse gasses, along with transformations in land cover. The consequences of climate change loom over developing nations, and Tanzania is no exception. Additionally, glaciers located in tropical regions are more vulnerable to the impact of climate change, and they can only be sustained at exceptionally high altitudes, where the weather is colder than regional averages.
A recent study by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in late 2022 suggests that 1/3 World Heritage glacier sites will disappear by 2050 due to global warming, including Mount Kilimanjaro. Even if global greenhouse gas emissions are reduced, the melting is unlikely to be reversed.
The danger to Kilimanjaro’s ecosystem has not only inspired a widespread climate advocacy campaign but also sparked controversy. In 2002 a group of scientists led by Ohio State’s Lonnie Thompson published a paper predicting that Kilimanjaro would be devoid of ice by 2020. This claim was picked up in 2006 by former Vice President Al Gore in his documentary film “An Inconvenient Truth,” designed to raise awareness about global warming, emphasizing the melting glacier as a potent symbol of the impending environmental catastrophe. A decade later, the World Mountain Forum in Uganda saw the release of a report by the United Nations, revealing that the warming of the Earth’s temperature, caused by climate change, has led to a marked increase in the occurrence of wildfires on Mount Kilimanjaro, which has resulted in a hastened loss of forest cover. The report stressed the gravity of the situation and called upon Tanzania to protect Mount Kilimanjaro’s water catchment area, including reforestation, early warning systems, and climate adaptation strategies.
It’s obvious by now that Thompson et al. and Gore overestimated the future decline of Kilimanjaro’s glaciers. This has led websites such as Climate Realism and The Climate Record, as well as anti-regulation groups, to attempt to use Kilimanjaro’s lingering snow and ice to discredit climate science and Al Gore’s environmentalist stance. H. Sterling Burnett, a senior fellow, and head of environmental programs at the National Center for Policy Analysis criticized the Kilimanjaro snow melting prediction, stating that it is just one of many scare stories that scientists have had to revise or abandon in the face of significant counter-evidence. Although these specific predictions were false, the result of extrapolating past data far into the future, overgeneralization of a complex system, and neglecting the impact of yearly fluctuations in precipitation, this does not mean that Kilimanjaro or the planet at large are safe from the effects of climate change.
Although perhaps relieved by the presence of snow on Kilimanjaro’s ice cap in 2023, residents of nearby settlements confront other severe environmental problems such as dried streams during the sowing season and deforestation, problematic for a country that is heavily reliant on wood products. Additionally, even if the melting of the snow cap is not affected as much as predicted by Thompson and Gore, the vegetation communities’ altitudinal zonation will inevitably change in the medium-to-long term as the climate warms.
Ultimately, it is crucial to prioritize safeguarding the closely-knit ecosystem that surrounds Kilimanjaro’s snow-covered peak by taking necessary steps to bolster its resistance to the escalating pressures from tourism, climate change, and deforestation.
To Get Involved:
If you are looking to explore Kilimanjaro, there are various sustainable approaches to consider. Visit the site of Responsible Travel to learn more.
Mount Kilimanjaro is managed by Tanzania’s Kilimanjaro National Park, which strives to protect wildlife and provide eco-friendly tourism services around the mountain’s local community. Visit the site of Mount Kilimanjaro National Park to learn more.
The African Blackwood Conservation Project (ABCP) focuses on replanting the tree species Dalbergia melanoxylon, also known as grenadilla, African blackwood, or mpingo, in eastern Africa, including the Kilimanjaro area. The ABCP has played a significant role in Mount Kilimanjaro reforestation efforts. Visit the ABCP website to learn more.
Hope Zhu
Hope is a Chinese international student at Wake Forest University in North Carolina studying sociology, statistics, and journalism. She dreams of traveling around the globe as a freelance reporter while touching on a wide range of social issues from education inequality to cultural diversity. Passionate about environmental issues and learning about other cultures, she is eager to explore the globe. In her free time, she enjoys cooking Asian cuisine, reading, and theater.
7 Reasons Why Kenya Should Be On Your Ecotourism Travel List
As eco-consciousness grows among travelers, Kenya welcomes them as a beacon of sustainability and natural wonder.
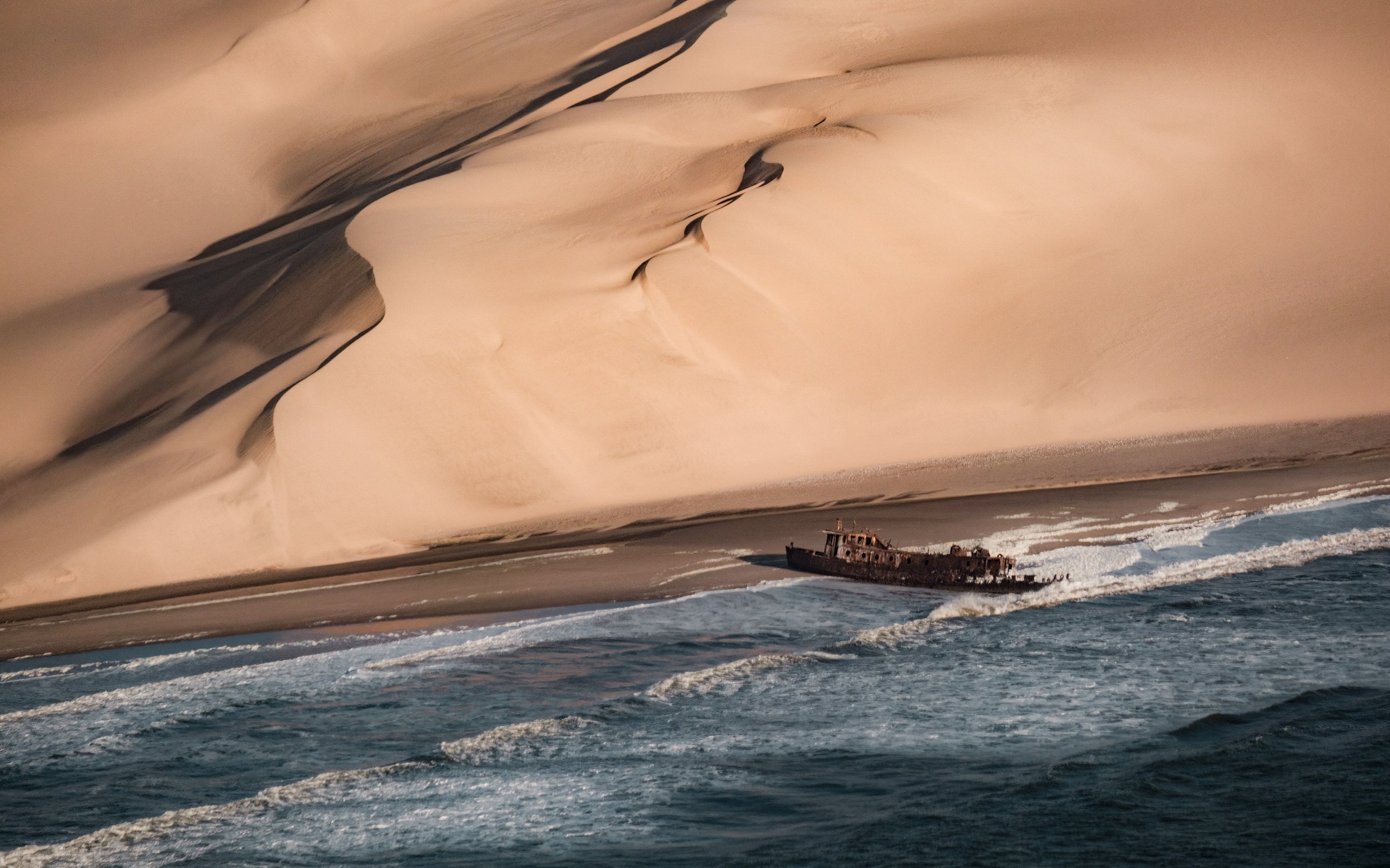
Read MoreThe Ghostly Shores of the Namib Desert’s Skeleton Coast
Bones and wreckage meet biodiversity on the Skeleton Coast of the world's oldest desert.
A ship wreckage by the red, sandy dunes along the Skeleton Coast. op23 | Unsplash
A map highlighting the Namib Desert in red along the coast of Africa.
Home to earthy-red dunes which roll right into the Atlantic ocean, the Namib Desert is thought to be between 50-80 millions years old, making it the oldest desert in the world. It’s also one of the world's most inhospitable places—an unpredictable, arid and remote region that on the surface has no appeal whatsoever. With temperatures fluctuating from blistering hot to dangerously cold and sand for as far as the eye can see, it extends from the country of Angola, through Namibia and down to South Africa. That’s over 31 thousand square miles of desert.
But don't be fooled, there’s more to these sandy plains than meets the eye. The Namib is home to the Skeleton Coast. And despite this desert’s penchant for death, The Skeleton Coast is teeming with rare wildlife.
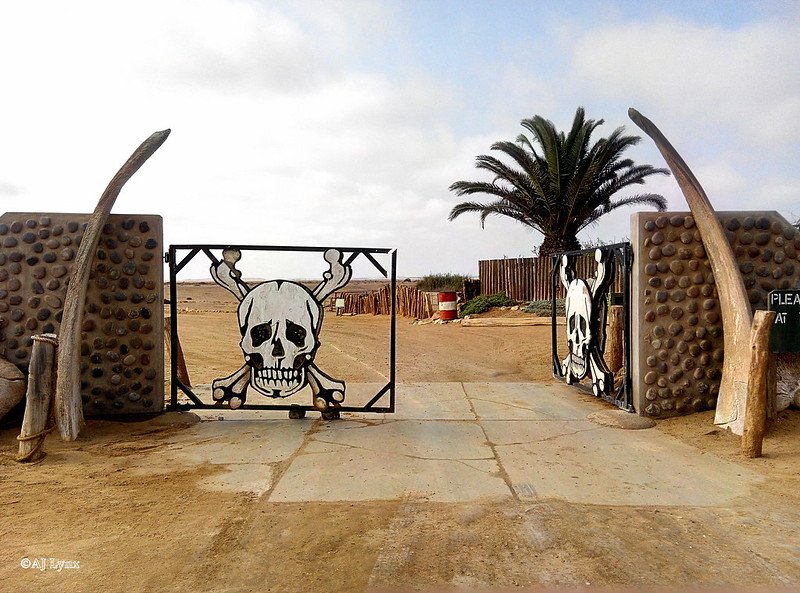
What is the Skeleton Coast
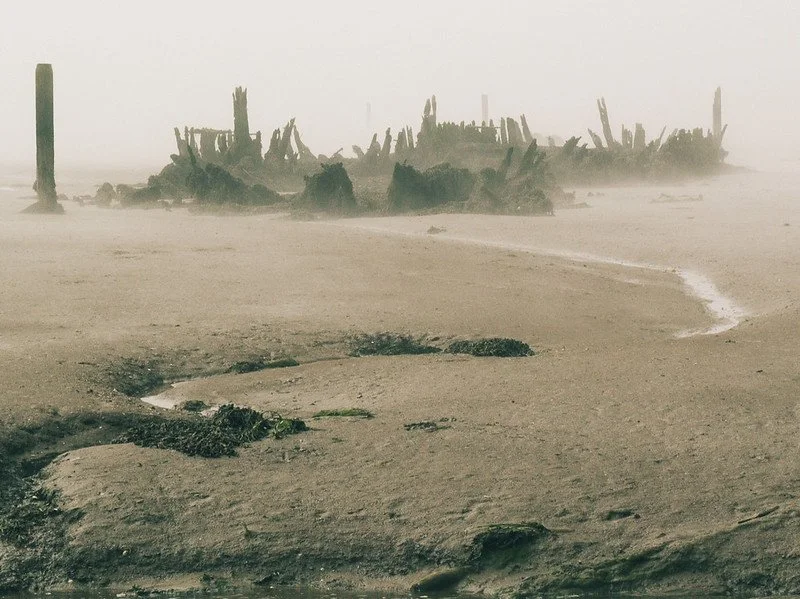
The Skeleton Coast is on the northern shores of this ancient and unexpected desert and earned its macabre name from the whale and seal bones that once littered the shore from the whaling industry. The Ovahimba who have since settled in the far north-eastern parts of Namibia once used the whale bones for building their shelters. In modern times, the Skeleton Coast hides its infamous graveyard buried beneath the sand, and with the exception of a rare adventure seeker looking for a wave to surf, the odds of seeking a human along this part of the coast are slim.
A shipwreck in the fog on the Skeleton Coast. Lee | CC BY 2.0
The Unique Climate of the Namib Desert
The bones scattered across Namibia’s Skeleton Coast aren’t from ocean mammals alone. Over the centuries, ships have ended up stranded on its shores for various reasons, but the main culprit is caused by the unique geography of the region. Hot, dry air from the interior of the continent and desert blows west combining with the cold wet air from Antarctica via a northward flowing ocean current called the Benguela Current. The hot dry winds act as a cap or roof not only prevents the cold wet air from escaping, but also from forming rain clouds. Instead, there is an eerie fog, and a lot of it.
In fact, for 180 days of the year there is fog on the Skeleton Coast so dense, it’s caused thousands upon thousands of ships to run aground throughout history; the oldest of which is from the 1500’s. The ocean's intense surf would have prevented anyone from getting back into the water, and with a wrecked ship, this meant that sailors stranded on this isolated coast were left with only one choice: to make their way through the Namib Desert. With a dryness rivaling South America’s Atacama Desert (the driest place on Earth), and sand dunes reaching nearly 1000 ft high, this option was nearly as dangerous as swimming out to sea and surely has added human bones to its burial collection.
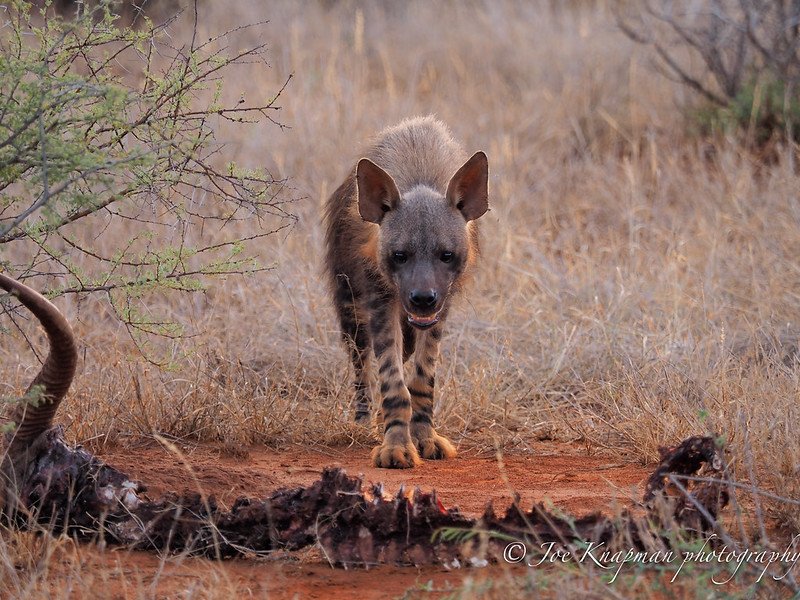
A brown hyena stands over a carcass in the Namib Desert. Joe Knapman | CC BY 2.0
Wildlife on the Skeleton Coast
Incredibly diverse, the Skeleton Coast has more near-endemic species than any other desert in the world. Elephants, black rhinos, desert lions, jackals, giraffes, seals, oryx, kudus and zebras and just some of the desert adapted species inhabiting this wilderness. One such animal is the brown hyaena. They’re usually on the move after darkness has fallen, which adds to their elusiveness. The name strandwolf was coined on Namibia’s Skeleton Coast where they scavenge for dead seals along the shoreline. If you are fortunate enough to spot one, make sure you take a really good look, because sightings of these inscrutable carnivores is never guaranteed. A truly endemic avian, the Dune Lark, inhabits thinly vegetated dunes along the Skeleton Coast and larger Namibian dune system associated with Bushman grasses and Nara melons.
A blooming welwitschias. Ragnhild&Neil Crawford |CC BY 2.0
A spiny looking nara bush in the Namib Desert. Palmora| CC BY 2.0
Nara Melons are just one of the many plants incredibly adapted to the rainless area and depend solely on the warning fog from the Atlantic Ocean. The nara bush is of great importance not only to the people of the region, but it is ecologically key to maintaining the unique desert habitat. More plants include welwitschias—which is a dwarf tree with only two leaves that can live for several thousand years—several lithops succulent plants known as living stones, lichen, pencil bush and the vividly colored succulents of rainbow colored agate mountains dotting the shore.
The Lion’s Roar, a desert phenomenon
The phenomena of the Skeleton Coast doesn’t stop at bones, fog and compelling flora and fauna. Travelers, nomads and lost sailors once believed in the presence of desert spirits—singing songs through the mist. When the dunes form a bowl with the right acoustic properties, even a small flow of disturbed sand causes a terrific noise that resembles rolling thunder or even a low-flying airplane. The phenomenon is known locally on the Skeleton Coast as ‘the lion’s roar’.
Ugab River Gate, Agnieszka Rysio | CC BY 2.0
The Skeleton Coast National Park
Luckily, this wildly unique, albeit creepy shoreline, along with its diverse inhabitants is protected. In 1971, Namibia established a well-maintained national park to protect the curious treasures, bones and wildlife which makes the Skeleton Coast so incredible. The park is divided into a northern and southern section; the southern section is open to travelers with four wheel drive vehicles who are welcomed to go as far north as the Ugab River Gate. There, they will be greeted by a sign with a skull and crossbones warning you to go no further. The northern section is off limits, its loose, enveloping sands will literally swallow you up and can therefore only be accessed by airplane with a certified guide. It also happens to be the most attractive region of the park with lunar-esque vistas as far as the eye can see. The park attracts all types of travelers, both local and international fishers, photographers, ecologists and folks just looking for a unique adventure to one of the world's most understated treasures.
Raeann Mason
Raeann is the Content and Community Manager at CATALYST, an avid traveler, digital storyteller and guide writer. She studied Mass Communication & Media at the Walter Cronkite School of Journalism where she found her passion for a/effective journalism and cultural exchange. An advocate of international solidarity and people's liberation, Raeann works to reshape the culture of travel and hospitality to be ethically sound and sustainable.
ART REVIEW: Photographer Tony Gum Takes On Post-Colonialism in South Africa
In her newest exhibit titled “Milked In Africa”, South African photographer Tony Gum captures a blend of rich tradition and modern commercialism.
Read MoreSouth Africa’s Town of Penguins
The small port town Simon’s Town is full of amazing marine life, most notably the African Penguin colony that is just outside the town center.
Jackass Penguins Simon’s Town SA. Donnie Ray. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Located on the southwestern coast of South Africa, Simon’s Town is a small village surrounded by both the ocean and the mountains. Being so close to Cape Town, Simon’s Town is a beautiful, small port city.
Simon’s Town is on a part of the Cape Peninsula known as False Bay. This area is a Hope Spot, an important and protected area for the ocean’s health. It is a valuable area for wildlife, with various species of birds and marine life coming to live off the area. Large marine creatures such as dolphins, whales, seals and sharks can be found near the town, some close enough to see while kayaking and others closer to Seal Island, 8 nautical miles away from the harbor.
However, much smaller than these other sea creatures is Simon’s Town’s famous attarction –the penguin colony. Penguins are found on every continent in the Southern Hemisphere, all the way from the Galápagos Islands at the equator to Antarctica. Here in this small town in South Africa, one colony of African penguins known as the Boulders Colony regularly comes ashore. Because of the colony, the town is also named Penguin Town. Breeding season for these birds is between February to August, so it is more common to see penguins during those months, but the birds will also come to land while they are molting. People can watch them from afar, and even swim alongside them, as long as they don’t get too close or chase them because the penguins will bite.
Simon’s Town (9). Joe Pyrek. CC BY-SA 2.0
African penguins–also known as black-footed penguins, Cape penguins, and jackass penguins (the last one because of their unique braying-like sounds)–are an endangered species of penguins, with only around 140,000 penguins in the world. They are small birds, only growing between 24-27 inches and weighing around 8-9 pounds. In addition to the black backs and white fronts, they have a black, parabolic band across their chests, though chicks and juvenile members are brown and gray. The population of this species started declining in the 1980s due to commercial fishing and oil pollution. Though penguins do eat more than just fish, it is the largest part of their diet and commercial fishing has been taking all the species that the penguins eat. Luckily, commercial fishing has been banned in False Bay, so African penguins’ food supply belongs to them and the other sea creatures again. The oil pollution is another serious issue for the birds because the oil will destroy their waterproof feathers, making it hard for them to swim.
There are 27 breeding sites for African penguins, and each of them is a protected habitat, including Simon’s Town, though the town did have to erect fences and boardwalks to prevent the penguins from wandering too far inland and into people’s gardens and backyards. The entire area is a sanctuary for penguins, and keeping them from invading residents’ properties can help people respect the animals, as well as helping the number of penguins to increase.
Katherine Lim
Katherine Lim is an undergraduate student at Vassar College studying English literature and Italian. She loves both reading and writing, and she hopes to pursue both in the future. With a passion for travel and nature, she wants to experience more of the world and everything it has to offer.
Pride and Punishment: The Struggles of the LGBTQ+ Community of Africa
In 32 African countries, homosexuality is deemed unlawful—punishable by imprisonment and in some cases, death. The LGBTQ+ community is fighting prejudice in a battle to be their truest selves.
Ugandan citizens at a pride parade. Chrisjohnbeckett. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Out of the 54 countries that make up the African continent, 32 of them outlaw homosexuality. Historically a continent that traveling members of the queer community steer clear of, Africa has a deep and intricate history with politics surrounding sexuality. However, Africans who identify with the LGBTQ+ community fight fiercely to change legislation, stigma and prejudice in their respective countries, challenging this lineage of controversy. Those who are brave enough to protest for their rights to love whomever they desire organize in-person parades and protests, while those under threat of harm—or even death—find ways to demonstrate their pride in, generating virtual communities and workshops that allow for the LGBTQ+ community to connect across the globe without leaving the safety of their homes.
Map of African countries with anti-gay laws. Amnesty International. CC BY-ND
To understand the hardships facing the LGBTQ+ community of Africa today, it is important to know the causal factors that led to such a homophobic climate. Anti-queer sentiments were introduced to the continent during Western colonization; previous to imperialism affects on the continent, African tribes in many regions practiced homosexuality freely. Val Kalende writes in The Guardian that “there is ethnographic evidence of same-sex relationships in pre-colonial Africa.” This cultural history also demonstrates the lack of importance placed on strict gender roles.
Additionally, the evidence also shows the practice of choice-based pronoun usage; women in positions of power would occasionally label themselves with male pronouns. Post-colonization laws that targeted the cultural muting of African traditions and practices formed the foundations for homophobia by outlawing same-sex relationships and visibly impacted African sentiments around the LGBTQ+ community for the foreseeable future.
Now, on the foundations of decades of hatred inspired by colonizers and imperialists, queer citizens of countries throughout Africa struggle under harsh legislation to simply be their truest selves. In most of the 32 countries that outlaw same-sex relationships, legislation punishes queer people by prison time and fines. Financial punishments vary in size and currency depending on the country. Prison sentences also range widely, varying anywhere between one year (as demonstrated in Ethiopia’s legislation) and lifetime imprisonment (such is the law in Kenya).
There are four countries in Africa that make same sex relationships punishable by death: Mauritania, Somalia, Nigeria and South Sudan. In Nigeria, a country ranked by Forbes as #1 in “The 20 Most Dangerous Places for LGBTQ+ Travelers,” members of the LGBTQ+ community who are found out be participating in homosexual relationships face death by stoning.
LGBTQ+ activists hanging signs. Distelfliege. CC BY 2.0.
Despite the gravity of the punishments for being queer, brave members of the LGBTQ+ community continue to demonstrate their pride. Unwilling to be silenced, queer people all around Africa organize pride parades, protests and online conferences to discuss ways they can fight the systemic homophobia they face in legislation. Further, the same people work hard to destigmatize same-sex relationships, challenging the post-colonial homophobia that has overpowered the original nature of African culture.
Groups like PRIDE OF AFRICA (POA) organize yearly events to celebrate pride, inviting and encouraging queer Africans to “live their most authentic selves.” POA also founded the Johannesburg Pride Parade in 2019, which has recently gone online due to the COVID-19 pandemic, but continues to invite members of the LGBTQ+ community to speak and rally. POA also holds online conferences, so those who wish to stay at home and stay anonymous can do so to limit the threat of prejudicial punishments.
For activists in imminent danger should their sexuality be outed, their protesting and pride demonstrations are more closely guarded. For those who need to seek exile in other countries or continents after being unexpectedly outed, journalism, photography and participation in parades like UK Black Pride (which focuses on Pride in the Black community and is based in London) are their only options to avoid death while still being able to demonstrate their pride.
To Get Involved
There are a handful of organizations centered on the eradication of hate crimes, stigmatization, improper health care and prejudicial legislation that accept donations to support their missions. Organizations like OUT that support the destigmatization of queer lifestyles and SHE (Social, Health and Empowerment Collective) specifically serve the African queer community. To find a collective list of legitimate organizations including OUT, SHE, and other foundations actively assisting the LGBTQ+ community of Africa, click here.
POA and UK Black Pride serve the same purposes: to allow for queer Africans to have a safe place to demonstrate their pride. POA takes place mostly online and in South Africa, and UK Black Pride is held in London.
To learn more about POA events, mission statements, and goals, click here.
To learn more about the UK Black Pride Parade and their mission statements, click here.
Ava Mamary
Ava is an undergraduate student at the University of Illinois, double majoring in English and Communications. At school, she Web Writes about music for a student-run radio station. She is also an avid backpacker, which is where her passion for travel and the outdoors comes from. She is very passionate about social justice issues, specifically those involving women’s rights, and is excited to write content about social action across the globe.
6 Things to Know About Kilimanjaro From a Past Climber
Tanzania is home to the tallest mountain in Africa, Mount Kilimanjaro. However, here are six things everyone should know before deciding if they are ready to brave the mountain.
Mount Kilimanjaro. Gary Craig. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Mount Kilimanjaro was created by three volcanic cones called Kibo, Shira, and Mawenzi about 2.5 million years ago. Standing at 19,341 feet, it is home to almost every ecological system: cultivation, forest, heather-moorland, alpine desert, and arctic summit zones. Climbers pass through each of these ecosystems in stages based on elevation. What many may not realize is that Kilimanjaro is dormant, not dead. This means the dormant Kibo cone could erupt again.
I made the climb in January. I will be extremely honest; it was quite miserable at times. It is simply impossible to put into words what hiking a mountain like that will do to you. From the daily struggles of altitude sickness and the feeling of breathing almost nonexistent air, to being the most exhausted you have ever been in your life, dehydrated, starving but unable to keep food down, to having to use the “bathroom” behind a rock right on the side of the trail. I even saw someone lose their life from cardiac arrest. Though it is, thankfully, not a common occurrence, it was rough.
With that said, the struggles make the reward that much sweeter. When I reminisce on my experience, I remember the hard times, but the beautiful moments I was fortunate enough to be a part of are more prominent. The dance and guitar sessions the group would have on our breaks, the feeling of being in a place completely isolated from the world, climbing higher than the plane that got me there, finding a new strength in myself that otherwise would have remained unknown. Kilimanjaro is a monster mountain, but it was the best experience of my life.
1. “Pole, Pole” are words to live by
“Pole, pole” translates to “slowly,” and I cannot stress enough how important this simple phrase is. It doesn’t matter what your physical abilities are, if you do not take your time, you will be hurting. Taking at least five days (depending on your route), this hike is no joke. It’s important to put your pride aside and accept that you might not be the fastest person to get up the mountain, and that’s completely OK! This was something I quickly learned. On the first day, I tried keeping up with the front of my group and very quickly learned I simply wouldn’t make it all six days if I kept that up. No matter what your pace, a guide will always stay by your side, carry things for you if you are struggling, and motivate you to keep going. Guides want you to succeed just as much as you want to, so definitely listen to their advice. They’re lifesavers—literally!
2. You will create amazing connections with your guides and porters
Photo taken by John Willard, my guide on my Kilimanjaro hike.
Your team on Kili will be absolutely amazing, no doubt about it. They will do whatever they can to help you summit, practically carry you if need be. They are extremely selfless and charismatic people, and they make the experience so much more enjoyable. Porters are the men and women who dedicate themselves to carrying all of your gear up the mountain, setting up camp, cooking meals, and creating a vibrant hike experience. Guides spend time with you on your hike—helping you stay on the trail, keeping an eye on your health, and really just guiding you to the summit. On my trip, the team loved to dance and sing and always invited us to join them on breaks and when at camp. They welcomed us to become immersed in the culture and understand the historical importance of Mount Kilimanjaro. The guides and porters truly enhanced the experience, so much that you simply won’t want to leave them. You will want to have WhatsApp downloaded on your phone so you can put in your favorite porters’ and guides’ numbers; when you get home, having those connections will keep a piece of Kili in your heart forever.
3. You will probably get sick
I hate to be the bearer of bad news, but if you decide to climb Kili, you will most likely find yourself experiencing at least some altitude sickness symptoms. It’s inevitable when going up 19,000 feet. Headache, nausea, and exhaustion are some of the more common symptoms. They will not end your hike early, but they will make life a little more miserable on the mountain. You just have to push through! Your guides will keep track of your vitals every day and will encourage you to eat and drink as much as your body will allow—food and water will be your best friend up there. You may hear people say that getting to high elevations eliminates your appetite, and this is very true. I found it hard to stomach even soup broth on my hike. It is best to pack some of your favorite snacks to help get past your lack of appetite. Many people, including myself, take altitude sickness pills to help combat symptoms. They are worth taking as long as they don’t cause negative effects on your body. They helped lessen the severity of my symptoms.
4. It is like being in a movie
Aerial View of Mount Kilimanjaro.Takashi Muramatsu. CC BY-ND 2.0.
Kilimanjaro is absolutely breathtaking. I remember feeling like I was living in a Star Wars scene for the majority of the hike. The sunsets and sunrises are unlike anything you will ever see again. Barranco Camp, where you will find yourself after hiking from Shira to Lava Tower to Barranco, was the highlight of my entire hike. Beautiful waterfalls, camping on a cliff in the clouds, being surrounded by the massive Barranco Wall (which you will be climbing up the next morning)—it is a beautiful and untouched part of the world. It makes the everyday battle worth it. When you’re feeling like giving up, just stop and turn around. The view you see will give you the courage to keep going.
5. You may see some horrific things
Barranco Wall on Mount Kilimanjaro. Haleigh Kierman
This is not a guarantee, but it is best to know what can happen. During my hike, I witnessed a man pass away right on the trail from cardiac arrest. I never thought I would see something like this, so it is important you know that really anything is possible before deciding if the hike is right for you. It is much more common to see people get physically sick or use the “bathroom” in clear sight, which are things we can typically move on with. With that said, there is always the possibility you can see something more severe. Do not fear though, Kilimanjaro is remarkably safe given its size. Around 30,000 hikers attempt each year with only a 0.03% death rate. If you know and trust your individual abilities and health, there is little to be concerned about.
6. You will discover an unimaginable amount of self-pride when you finish
Sunrise on Summit Day. Haleigh Kierman
Summit day: it’s killer. You begin the final trek to the summit around 11:30 p.m. and get to the top around 8 a.m., depending on your pace. At this point, you will be sleep-deprived, feeling as though you are suffocating with every step you take because the air is so thin. But somehow, you will find that strength in you to keep going. And when you finally make it to the top, all you will feel is euphoria. You may even shed a tear or two. Kili will push you to your limit and then past that. You really will discover a new part of yourself you didn’t know was there. If you set your mind to conquering Kilimanjaro, you can do it. It will be one of the hardest things you will ever do, but the reward is a feeling of accomplishment that will change your life forever.
Haleigh Kierman
Haleigh is a student at The University of Massachusetts, Amherst. A double Journalism and Communications major with a minor in Anthropology, she is initially from Guam, but lived in a small, rural town outside of Boston most of her life. Travel and social action journalism are her two passions and she is appreciative to live in a time where writers voices are more important than ever.
VIDEO: Mama Rwanda
Located at the converging point between the African Great Lakes region and East Africa, the Republic of Rwanda is an environmentally, economically and culturally diverse country rebuilding its identity in the wake of the 1994 Rwandan genocide, in which approximately 800,000 Tutsis were killed by Hutu extremists. The country takes pride in its regional fauna, which includes elephants, gorillas, hippos, giraffes and zebras. Travelers interested in viewing Rwandan wildlife can observe it in three national parks: Volcanoes National Park, Nyungwe Forest National Park and Akagera National Park. “Mama Rwanda” also shows Kigali, the capital of Rwanda and the heart of its economic and cultural life. The city boasts a vibrant marketplace and architecture that combines traditional and modern styles. Outside the city, Rwanda’s expansive coffee growing fields are tended by over 450,000 planters. Basket weaving has been an important aspect of Rwandan culture for centuries and is now being used by women impacted by the Rwandan genocide to pursue greater economic independence as producers within an international market. Hutu and Tutsi women have come together to weave baskets, a practice that is now a symbol of national reconciliation. These businesses sell their wares to both small stores and large department stores like Macy’s. The profits of weaving companies are often used to support Rwandan families in need of food and medicine.
Aerial view of Ambalandingana, a village in the Amoron’i Mania region of Madagascar. Bernard Gagnon. CC BY-SA 3.0.
8 Only-in-Madagascar Experiences
You may know about lemurs and baobabs, but here are more amazing and unique cultural and wildlife experiences that the island nation of Madagascar has to offer.
Sand Mining Threatens Coastline as Sierra Leone Rebuilds
Within a few miles of Sierra Leone’s capital, sand mining is having a devastating effect. As beaches slowly disappear, so do the country’s hopes of post-war revival.
Freetown Beach in Sierra Leone, Erik Cleves Kristensen, CC BY 2.0
Twenty years after Sierra Leone's 11-year civil war, the economic promises of sand mining prove to be costly. The war, which took thousands of lives and led nearly half the country's population into poverty, destroyed most of the country. What followed was a construction boom made possible by an essential ingredient of modern civilization: sand. However, as Sierra Leone’s 300 miles of glorious beaches slowly disappear, so does the revival of tourism and the protection of 55% of the population who live along the country’s coast from the dangers of rising sea levels due to climate change.
As part of a post-civil war move to help communities benefit from local resources, Sierra Leone’s central government gave regulation of sand mining to local councils. Under the 2004 Local Government Act, local committees operate the trucks and strictly hire local people to mine the sand. After a long day of mining, the sand is dried and sold to developers to pave and extend roads as new homes, hotels and restaurants go up across the country.
Government officials defend sand mining as an essential source of jobs and a necessary component in rebuilding Sierra Leone. Kasho Cole, chairman of the Western Area Rural District Council, told the Los Angeles Times that his council is “sensitive to environmental concerns, having banned sand mining on certain beaches because of the devastation it has already caused.”
Cole also acknowledged that assessments had not been carried out anywhere in the district to determine sand mining’s environmental impact. Due to large-scale illegal sand mining operations, Cole could not provide a definite amount of sand extracted from the beaches.
Sand theft, the unauthorized and illegal form of sand mining, has led to a worldwide non-renewable resource depletion issue, causing the permanent loss of sand and significant habitat destruction. Sand mining has already made a significant environmental impact in North Stradbroke Island and Kurnell in Australia; the Indian states of Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Goa; and the Red River in Yunnan, China.
In the United States, the sand mining market generates slightly over $1 billion per year. The industry continues to grow annually by nearly 10% because of its use in hydrocarbon extraction. Globally, sand mining is a $70 billion industry, with sand selling for up to $90 per cubic yard.
In Sierra Leone, sand mining operations are regulated on John Obey Beach, a village 20 miles south of the Western Area (Freetown Peninsula.) According to the Environmental Protection Agency, sand mining should be banned on all beaches apart from John Obey. However, when the police leave the beaches at 5 p.m., the mining continues after dark.
Efforts to address the issue are hampered by conflicts of interest from those involved: miners who need the work, construction companies who need the supply and investors who are getting rich taxing the sand. Last year, a press statement from the local police force confirmed “certain service personnel appear to be aiding and abetting this illegal act.”
As dump trucks continue to haul sand away and tides push further inland, John Obey Beach is slowly disappearing—taking trees, businesses, homes and dry land with it as far down the coast as Bureh, a surf town two miles south. While the activity contributes to Sierra Leone's coastal erosion, which is proceeding at up to 6 meters a year, the removal of sand also changes wave patterns that move sand along the coast, altering the quality of surf that Bureh, a renowned surf spot in Africa, is known for.
Prior to the war, Sierra Leone’s beaches were packed with adventurous travelers from around the world. Kolleh Bangura, the director of Sierra Leone’s Environmental Protection Agency, told The New Humanitarian that “sand-mining is a calamity for the tourism industry… Anywhere in the world, sand is the resource of tourism, but now our beaches are being degraded.”
Lakka, a coastal town located 10 miles from Freetown, was once known for its large beaches and seaside resorts, offering a glimpse of the future if actions are not taken. Sand mining on Lakka Beach is illegal now, but the ban came too late—leaving a thin wedge of sand lined by crumbling buildings, many of which have been left abandoned.
Even the miners themselves recognize sand mining is not sustainable; however, with a youth unemployment rate of 70%, the pressure falls on the government to provide alternative jobs. “In time, they need to ban it, as we want to bring tourism here,” Abu Bakarr, a sand miner, told The New Humanitarian. “But we need sand-mining to sustain our lives…The government needs to give us jobs. If there are no jobs, the youths will mine the sand.”
Papanie Bai-Sessay, the biodiversity officer at Conservation Society of Sierra Leone, told the Los Angeles Times that “the sand has been a buffer… we are destroying our first line of defense. If we don’t stop, it will be a disaster for millions.”
Claire Redden is a freelance journalist from Chicago, where she received her Bachelor’s of Communications from the University of Illinois. While living and studying in Paris, Claire wrote for the magazine, Toute La Culture. As a freelancer she contributes to travel guides for the up and coming brand, Thalby. She plans to take her skills to London, where she’ll pursue her Master’s of Arts and Lifestyle Journalism at the University of Arts, London College of Communication.
VIDEO: Growing Up in a Megaslum in Kenya
Joseph Djemba grew up in Kibera, Kenya, the largest urban slum in Africa. Djemba found himself there when his mother became unable to support her eleven children after the death of her husband. Djemba describes his childhood sleeping outside and begging for food, detailing the psychological impacts of living in poverty. He also notes the large gap between the rich and the poor in Kenya and discusses how impoverished people help each other survive. Djemba is the main character in “Megaslumming,” a book by Adam Parsons. In his work, Parsons explores how the settlement of Kibera came into existence and documents what life is like for those who live in slums.
Get Involved:
Touch Kibera Foundation is a non-profit organization devoted to uplifting children who live in Kibera, Kenya through sports programs, sexual health programs, education support and mentorship opportunities. Donations are accepted online, and more information can be found here.
Polycom Development Project is a foundation which seeks to provide educational and athletic opportunities to girls and women in Kibera. The organization is also devoted to promoting sanitation and public health. Donations are accepted online, and more information can be found here.
St. Vincent de Paul Community Development Organization aims to provide support to orphaned and other vulnerable children in Kibera. The organization supports families and seeks to intervene on behalf of children at an early stage in their development. Donations are accepted online, and more information can be found here.
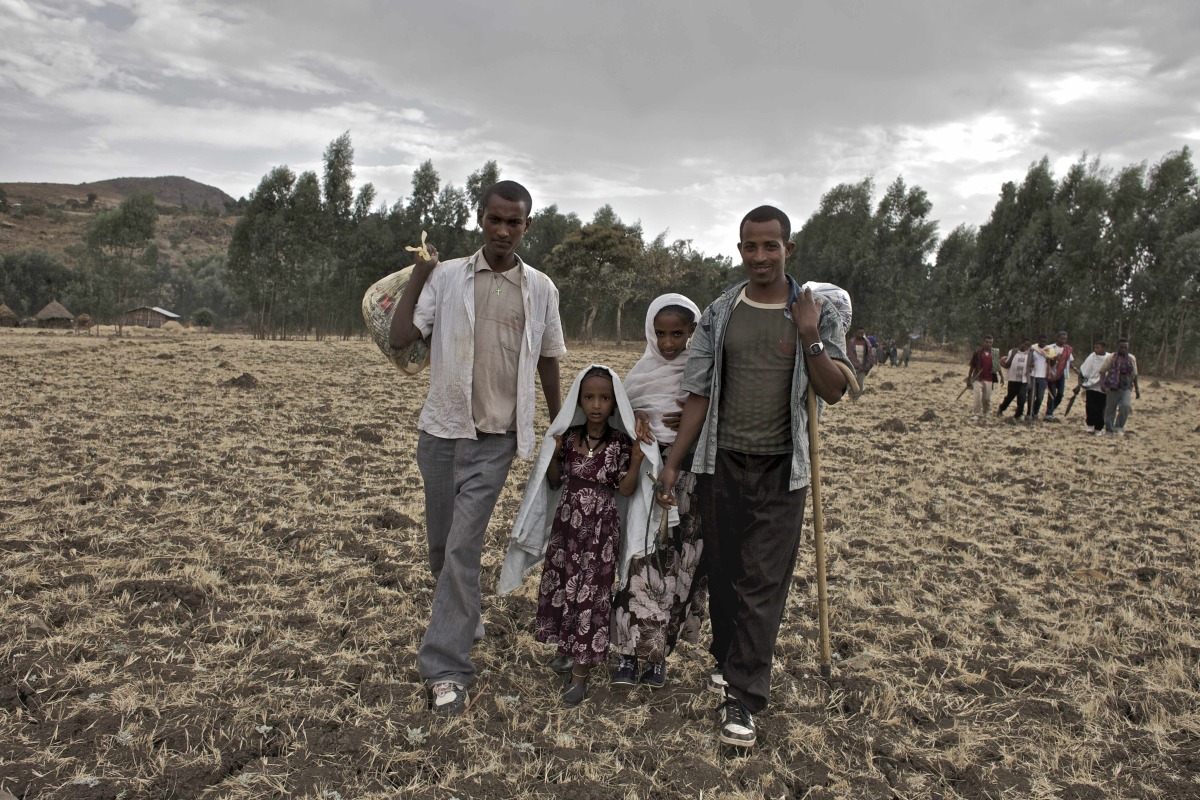
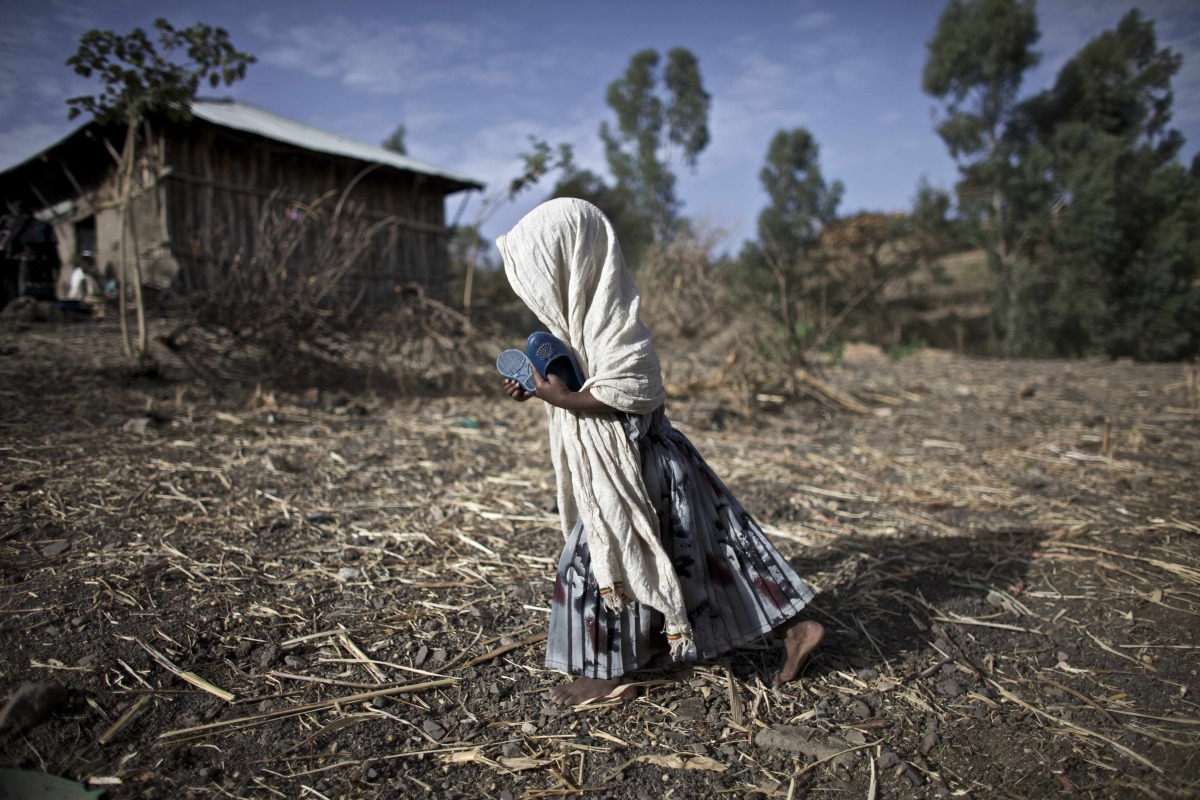















PHOTO ESSAY: Child Marriage in Ethiopia
While it may seem shocking, in Ethiopia girls are married off at ages as young as 5 years old, and 48% of rural women are married before age 15. Photographer Guy Calaf documents these young child brides and their marriages in this photo essay.
Read More